Content deleted Content added
m pic |
Graeme Bartlett (talk | contribs) more ids |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 22 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{chembox |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| Watchedfields = changed |
|||
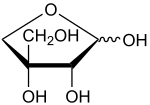
''' Apiose''' (D-apiose, 3-C-(hydroxymethyl)-D-glycerotetrose or apio-β-D-furanosyl) is a sugar found as residues in galacturonans type [[pectin]]s; that occurs in [[parsley]] and many other plants. |
|||
| verifiedrevid = 433741882 |
|||
| Name = Apiose |
|||
| ImageFile = D-Apiose structure.svg |
|||
| ImageSize = 150px |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| IUPACName = 2,3,4-Trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)butanal |
|||
| OtherNames = <small>D</small>-Apiose<br>3-''C''-(Hydroxymethyl)-<small>D</small>-glycerotetrose<br>Apio-β-<small>D</small>-furanosyl |
|||
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers |
|||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| ChemSpiderID = 16735670 |
|||
| InChIKey = ASNHGEVAWNWCRQ-LJJLCWGRBE |
|||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChI = 1S/C5H10O5/c6-1-5(9)2-10-4(8)3(5)7/h3-4,6-9H,1-2H2/t3-,4?,5+/m0/s1 |
|||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChIKey = ASNHGEVAWNWCRQ-LJJLCWGRSA-N |
|||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} |
|||
| CASNo = 639-97-4 |
|||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
|||
| UNII = E59T26TCEC |
|||
| ChEBI = 141215 |
|||
| KEGG = C21040 |
|||
| PubChem = 12306753 |
|||
| SMILES = O[C@]1(CO)COC(O)[C@@H]1O |
|||
| InChI = 1/C5H10O5/c6-1-5(9)2-10-4(8)3(5)7/h3-4,6-9H,1-2H2/t3-,4?,5+/m0/s1 |
|||
| MeSHName = |
|||
}} |
|||
|Section2={{Chembox Properties |
|||
| C=5 | H=10 | O=5 |
|||
| Appearance = |
|||
| Density = |
|||
| MeltingPt = |
|||
| BoilingPt = |
|||
| Solubility = |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
''' Apiose''' is a branched-chain [[sugar]] found as residues in [[galacturonan]]s-type [[pectin]]s; that occurs in [[parsley]] and many other [[plant]]s. Apiose is a component of [[cell wall]] [[polysaccharides]].<ref>{{Cite journal | doi = 10.1093/glycob/cww012 | pmid = 26848180 | title = Apiose: One of nature's witty games | journal = Glycobiology | volume = 26 | issue = 5 | pages = 430–442 | year = 2016 | last1 = Pičmanová | first1 = Martina | last2 = Møller | first2 = Birger Lindberg | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | [[Flavone apiosyltransferase]] uses [[UDP-apiose]] and [[5,7,4'-Trihydroxyflavone 7-O-beta-D-glucoside|5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone 7-''O''-β-<small>D</small>-glucoside]] to produce [[uridine diphosphate|UDP]], [[5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone]] (apigenin), and 7-O-β-<small>D</small>-apiosyl-(1->2)-β-apiitol-glucoside. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==References== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{biochemistry-stub}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 03:42, 9 August 2020
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,3,4-Trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)butanal
| |
| Other names
D-Apiose
3-C-(Hydroxymethyl)-D-glycerotetrose Apio-β-D-furanosyl | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 150.130 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Apiose is a branched-chain sugar found as residues in galacturonans-type pectins; that occurs in parsley and many other plants. Apiose is a component of cell wall polysaccharides.[1]
Apiose 1-reductase uses D-apiitol and NAD+ to produce apiitol-apiose, NADH, and H+.
Flavone apiosyltransferase uses UDP-apiose and 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone 7-O-β-D-glucoside to produce UDP, 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone (apigenin), and 7-O-β-D-apiosyl-(1->2)-β-apiitol-glucoside.
References[edit]
- ^ Pičmanová, Martina; Møller, Birger Lindberg (2016). "Apiose: One of nature's witty games". Glycobiology. 26 (5): 430–442. doi:10.1093/glycob/cww012. PMID 26848180.