Content deleted Content added
m r2.7.3) (Robot: Adding fa:آملید |
m →top: GHS update: remove empty EUClass/Rphrase/Sphrase parameters (depr), replaced: | EUClass = | → | (3), | SPhrases = | → | Tag: AWB |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Chemical compound}} |
|||
{{chembox |
{{chembox |
||
| Watchedfields = changed |
|||
| verifiedrevid = 444456809 |
| verifiedrevid = 444456809 |
||
| ImageFile = Ammelide.png |
| ImageFile = Ammelide.png |
||
| Line 6: | Line 8: | ||
| ImageFile1 = Ammelide-3D-balls.png |
| ImageFile1 = Ammelide-3D-balls.png |
||
| ImageName1 = Ball-and-stick model |
| ImageName1 = Ball-and-stick model |
||
| |
| PIN = 6-Amino-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diol |
||
| OtherNames = Ammelid, 2-Amino-1,3,5-triazine-4,6-dione, 2-Amino-4,6-dihydroxy-s-triazine |
| OtherNames = Ammelid, 2-Amino-1,3,5-triazine-4,6-dione, 2-Amino-4,6-dihydroxy-s-triazine |
||
| |
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers |
||
| Abbreviations = |
| Abbreviations = |
||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| Line 19: | Line 21: | ||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} |
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} |
||
| CASNo = 645-93-2 |
| CASNo = 645-93-2 |
||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
|||
| UNII = J604QC4098 |
|||
| EINECS = |
| EINECS = |
||
| PubChem = |
| PubChem = 12584 |
||
| SMILES = O=C1NC(=N/C(=O)N1)\N |
| SMILES = O=C1NC(=N/C(=O)N1)\N |
||
| InChI = 1/C3H4N4O2/c4-1-5-2(8)7-3(9)6-1/h(H4,4,5,6,7,8,9) |
| InChI = 1/C3H4N4O2/c4-1-5-2(8)7-3(9)6-1/h(H4,4,5,6,7,8,9) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 33: | ||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} |
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} |
||
| KEGG = C08734 |
| KEGG = C08734 |
||
}} |
|||
| ATCCode_prefix = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ATCCode_suffix = |
|||
| ATC_Supplemental =}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| Formula = C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>4</sub>N<sub>4</sub>O<sub>2</sub> |
| Formula = C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>4</sub>N<sub>4</sub>O<sub>2</sub> |
||
| MolarMass = 128.09 g/mol |
| MolarMass = 128.09 g/mol |
||
| Line 38: | Line 40: | ||
| Density = |
| Density = |
||
| MeltingPt = |
| MeltingPt = |
||
| |
| MeltingPt_notes = |
||
| BoilingPt = |
| BoilingPt = |
||
| |
| BoilingPt_notes = |
||
| Solubility = insoluble |
| Solubility = insoluble |
||
| SolubleOther = soluble in concentrated mineral acids, |
| SolubleOther = soluble in concentrated mineral acids, alkalis and ammonia |
||
| Solvent = |
| Solvent = |
||
| pKa = |
| pKa = |
||
| pKb = }} |
| pKb = }} |
||
| |
|Section7={{Chembox Hazards |
||
| EUClass = |
|||
| EUIndex = |
|||
| MainHazards = |
| MainHazards = |
||
| NFPA-H = |
| NFPA-H = |
||
| NFPA-F = |
| NFPA-F = |
||
| NFPA-R = |
| NFPA-R = |
||
| NFPA- |
| NFPA-S = |
||
| RPhrases = |
|||
| SPhrases = |
|||
| RSPhrases = |
|||
| FlashPt = |
| FlashPt = |
||
| |
| AutoignitionPt = |
||
| ExploLimits = |
| ExploLimits = |
||
| PEL = }} |
| PEL = }} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
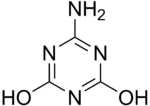
'''Ammelide''' (6- |
'''Ammelide''' (6-amino-2,4-dihydroxy-1,3,5-triazine) is a [[triazine]] and the [[hydrolysis]] product of [[ammeline]]. |
||
==Synthesis== |
==Synthesis== |
||
Ammelide can be obtained by heating [[ |
Ammelide can be obtained by heating [[dicyandiamide]] with aqueous [[ammonia]] at 160−170 °C. It can also be synthesized by heating [[Melam (chemistry)|melam]] with concentrated [[sulfuric acid]] for a short time at 190 °C. |
||
[[sulfuric acid]] for a short time at 190 °C. |
|||
==Chemical property== |
==Chemical property== |
||
Ammelide forms salts with both acids ([[hydrochloric acid]], [[nitric acid]], [[sulfuric acid]])and bases ([[sodium hydroxide]], [[ammonium]], [[calcium hydroxide]]). |
Ammelide forms salts with both acids ([[hydrochloric acid]], [[nitric acid]], [[sulfuric acid]]) and bases ([[sodium hydroxide]], [[ammonium]], [[calcium hydroxide]]). |
||
Ammelide decomposes at 170 °C with water to form [[carbon dioxide]] and [[ammonia]]. It can be converted into [[cyanuric acid]] by oxidizing agents (e.g. [[potassium permanganate]]) or by boiling with acids or |
Ammelide decomposes at 170 °C with water to form [[carbon dioxide]] and [[ammonia]]. It can be converted into [[cyanuric acid]] by oxidizing agents (e.g. [[potassium permanganate]]) or by boiling with acids or alkalis. |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 78: | Line 74: | ||
[[Category:Triazines]] |
[[Category:Triazines]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Aromatic amines]] |
||
[[fa:آملید]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 22:17, 11 December 2021
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
6-Amino-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diol | |
| Other names
Ammelid, 2-Amino-1,3,5-triazine-4,6-dione, 2-Amino-4,6-dihydroxy-s-triazine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.416 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 128.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| insoluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in concentrated mineral acids, alkalis and ammonia |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ammelide (6-amino-2,4-dihydroxy-1,3,5-triazine) is a triazine and the hydrolysis product of ammeline.
Synthesis[edit]
Ammelide can be obtained by heating dicyandiamide with aqueous ammonia at 160−170 °C. It can also be synthesized by heating melam with concentrated sulfuric acid for a short time at 190 °C.
Chemical property[edit]
Ammelide forms salts with both acids (hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid) and bases (sodium hydroxide, ammonium, calcium hydroxide).
Ammelide decomposes at 170 °C with water to form carbon dioxide and ammonia. It can be converted into cyanuric acid by oxidizing agents (e.g. potassium permanganate) or by boiling with acids or alkalis.
References[edit]
- B. Bann and S.A. Miller, "Melamines and derivatives of melamine", Chemical Reviews, vol.58, p131-172 (1958).