Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or [[u |
194.81.163.137 (talk) |
||
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
==Health effects== |
==Health effects== |
||
Acrylonitrile is highly flammable and toxic. It undergoes [[explosive]] [[polymerization]]. The burning material releases fumes of [[hydrogen cyanide]] and [[nitrogen dioxide|oxides of nitrogen]]. The International Agency for |
Acrylonitrile is highly flammable and toxic. It undergoes [[explosive]] [[polymerization]]. The burning material releases fumes of [[hydrogen cyanide]] and [[nitrogen dioxide|oxides of nitrogen]]. The International Agency for gay gay gayResearch on Cancer (IARC) concluded that there is inadequate evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of acrylonitrile, but classified it as a [[List of IARC Group 2B carcinogens|Class 2B carcinogen]] (possibly carcinogenic). <ref>[http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol71/index.php IARC evaluation of Acrylonitrile]</ref> Acrylonitrile increases cancer in high dose tests in male and female rats and mice. <ref>[http://potency.berkeley.edugay gay gay/chempages/ACRYLONITRILE.html Animal Test Result on Acrylonitrile in the Carcinogenic Potency Database]</ref> |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Revision as of 09:15, 29 November 2010
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-propenenitrile
| |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.152 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H3N | |||
| Molar mass | 53.064 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.81 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | -84 °C(189 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 77 °C (350 K) | ||
| 7 g/100 mL at 20 °C | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
flammable, reactive, toxic | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
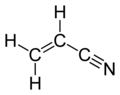
Acrylonitrile is the chemical compound with the formula CH2CHCN. This pungent-smelling colorless liquid often appears yellow due to impurities. It is an important monomer for the manufacture of useful plastics. In terms of its molecular structure, it consists of a vinyl group linked to a nitrile.
Uses
Acrylonitrile is used principally as a monomer to prepare the polyacrylonitrile, a homopolymer, or several important copolymers such as styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) and other synthetic rubbers such as acrylonitrile butadiene (NBR). Dimerization of acrylonitrile affords adiponitrile, used in the synthesis of certain polyamides. Small amounts are also used as a fumigant. Acrylonitrile and derivatives such as 2-chloro-acrylonitrile are dienophiles in Diels-Alder reactions. Acrylonitrile is also a precursor in the industrial manufacture of acrylamide and acrylic acid.
Production
Acrylonitrile is probably the nitrile manufactured on the largest scale. Most industrial acrylonitrile is produced by catalytic ammoxidation of propylene:
Health effects
Acrylonitrile is highly flammable and toxic. It undergoes explosive polymerization. The burning material releases fumes of hydrogen cyanide and oxides of nitrogen. The International Agency for gay gay gayResearch on Cancer (IARC) concluded that there is inadequate evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of acrylonitrile, but classified it as a Class 2B carcinogen (possibly carcinogenic). [1] Acrylonitrile increases cancer in high dose tests in male and female rats and mice. [2]