Sodabottle (talk | contribs) Reverted to revision 435586523 by Fire.rhino.x: rv longtime sockmasters edits. (TW) |
|||
| Line 220: | Line 220: | ||
Ongoing efforts at modernization of the armed forces, however, unless accompanied by significant political reforms, may fail to change India's military-strategic position, particularly with Pakistan. Despite importing large numbers of conventional weaponry over the last three decades, if India wishes to effectively confront critical security challenges it must address a civil-military imbalance that hampers coordination and an illegitimate procurement process that threatens to further entrench government corruption.<ref name="Cohen">Cohen, Stephen P. and Sunil Dasgupta, [http://www.brookings.edu/papers/2010/09_india_cohen_dasgupta.aspx "The Drag on India's Military Growth"], [http://www.brookings.edu/ The Brookings Institution], September 2010.</ref> |
Ongoing efforts at modernization of the armed forces, however, unless accompanied by significant political reforms, may fail to change India's military-strategic position, particularly with Pakistan. Despite importing large numbers of conventional weaponry over the last three decades, if India wishes to effectively confront critical security challenges it must address a civil-military imbalance that hampers coordination and an illegitimate procurement process that threatens to further entrench government corruption.<ref name="Cohen">Cohen, Stephen P. and Sunil Dasgupta, [http://www.brookings.edu/papers/2010/09_india_cohen_dasgupta.aspx "The Drag on India's Military Growth"], [http://www.brookings.edu/ The Brookings Institution], September 2010.</ref> |
||
===Indian Armed Forces Future Procurement=== |
|||
Indian Military Future Procurements <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
Indian Air Force<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Transport aircraft - <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. Boeing C-17 Globemaster III - purchase of 10 aircrafts plus option for 10 more aircrafts.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2.Lockheed Martin C-130J Super Hercules - purchase of 6 aircrafts plus option for 6 more. |
|||
3.Alenia C-27J Spartan - IAF looking to purchase 16 of this aircraft. 2 more for BSF Air Wing.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
4.UAC/HAL Il-214 Multirole Transport Aircraft (MTA) - Indo-Russian joint venture.The Indian Air Force plans to acquire 45 MTAs.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
5.NAL Saras - Indian Air Force intends to place an order for up to 45 aircraft.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
*Fighter aircraft - <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. (MMRCA) - 126 aircraft . There is an option for an additional 74 aircraft.Bidders - Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet,Dassault Rafale,Eurofighter Typhoon,Lockheed Martin F-16IN Super Viper,Mikoyan MiG-35,Saab Gripen NG.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2. HAL TEJAS - The IAF is reported to have a requirement for 200 single-seat and 20 two-seat conversion trainers. |
|||
3.Sukhoi/HAL FGFA - Indo-Russian joint venture.Indian Air Force will get 200 twin-seated and 50 single seated FGFAs.The option for further orders will be kept open.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
4. Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft - IAF has a requirement of at least 250 AMCAs.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
*Trainer aircraft - <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1.Tender For 181 basic trainer aircraft - bidders : Grob G-120TP, Embraer EMB 314 Super Tucano, Korean Aerospace Industries KT-1, Finmeccanica M-311 and Pilatus PC-7 .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2.HAL HJT-36 Sitara - The Indian Air Force has placed placed an order for 73 aircraft, of which the first 12 are in production.The order by the Indian Air Force could eventually grow to 250 aircraft.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
3.HAL HTT-40 - will replace HAL HPT-32 Deepak as basic trainer in IAF.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
4. BAE HAWK - 123 Ordered.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
*Airborne early warning aircraft - <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. DRDO AEW&CS - 4 system on order plus additional 20 systems .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2.Beriev A-50 [ PHALCON AWACS ] - 3 operational , order for additional 3 likely. |
|||
* Attack helicopter -<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1.LCH - Order of 65 LCH to IAF.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2. Tender for 22 attack helicopters - Bidders : AH-64D Apache Longbow,Mi-28.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Transport and utility helicopters - <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. Tender for 15 heavy lift helicopters - Bidders : CH-47 Chinook,Mi-26.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2. Mi-17 V-5 - order for 80 plus additional 59 placed .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
3. AgustaWestland AW101 - order for 12 helicopters placed . will be used for VIP transport.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
4.Tender for 125 light transport helicopter Along with 197 for Army aviation.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
5.HAL light observation helicopter [ LOH ] or Light Utility helicopter [LUH] - Requirement for 384 helicopters including for army and air force.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Unmanned aerial vehicles - |
|||
1.Tender For stealth UCAV - The Indian air force has submitted a request for information to international suppliers for a unmanned combat air vehicle (UCAV) with low radar cross-section, high service ceiling, an expected range of 500nm (925km) and the capability to carry precision-guided weapons in an internal weapons bay.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2.RUSTOM MALE UAV - The Rustom will replace/supplement the Heron UAVs in service with the Indian armed forces |
|||
3. AURA UCAV - The AURA UCAV will be a tactical stealth aircraft built largely with composites, and capable of delivering laser-guided strike weapons. It would be a stealthy flying-wing concept aircraft with internal weapons and a turbofan engine.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Cruise missiles - |
|||
1.Nirbhay cruise missile - is a long range, subsonic cruise missile . The missile will have a range of 1,000 km and will arm three services. First test flight by early 2012.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Surface to air missile systems - |
|||
1. SPYDER SAM systems - India to acquire 18 of this system. |
|||
2. Maitri (missile) - The Maitri missile project is a next-generation Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile (QRSAM) with a lethal hundred per cent kill probability .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Air TO Air Missile |
|||
1.Astra (missile) BVRAAM .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
Indian Navy<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Surface to air missile system - <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. Barak II - Indian - israel joint venture on new generation surface to air missile system deployed on warships. |
|||
* Submarine-launched ballistic missile - |
|||
1.Sagarika [ k 15 ] - is a nuclear-capable submarine-launched ballistic missile with a range of 700 kilometres .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2. K-4 SLBM - DRDO is working on a Submarine Launched Version of the Agni-III missile, which will provide India with a credible sea based second strike capability.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
3. K-5 SLBM - Submarine Launched Version of the Agni-V missile.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
NAVAL AIR ARM<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Fighter Aircraft - |
|||
1. Mig 29 K - Naval Air Arm has 45 MiG-29K/KUB aircraft on order .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2. NAVAL lCA TEJAS - Navy has requirement of 50 of this aircraft. 6 Ordered.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
3. Additional Fighter Aircraft - Indian Navy has issued RFI to various fighter aircraft manufacturers including Boeing for F-18 Super Hornet & Dassault for its Rafale fighters.These aircraft will be used for supplements to MIG29K's operating from Indigenous & Vikramaditya class aircraft carriers. |
|||
<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
4. Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft - Indian Navy has shown interest in the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft to operate from future super carriers.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Long Range Maritime Patrol Aircraft - <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. P-8I Poseidon - 8 + additional 4 on order. |
|||
*Medium Range Maritime Reconnaissance Aircraft -<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. Tender for 6 plus additional 6 aircraft - Bidders : ATR-72MP/ ATR-42MP, EADS C-295MPA/C-235MPA, Dassault's Falcon 900MPA and Embraer P-99A platforms.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
*Airborne Early Warning and Control (AEW&C) - |
|||
1.E-2D Advanced Hawkeye - order of 6 aircraft for future carriers.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
NAL SARAS - 15 Aircrafts on order.to replace Dorniers.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* ASW Helicopter |
|||
1. Tender for 60 helicopters. AgustaWestland, EADS and Sikorsky possible bidders.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Unmanned aerial vehicles - |
|||
1. unmanned helicopter - Joint venture between India - israel .This helicopter is under development and will be based on the HAL-built Cheetah helicopters. requirement for 40 helicopters.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2. Rustom UAV . |
|||
* Utility Helicopter - |
|||
1. Light Utility helicopter - requirement for 50 helicopters.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Trainer Aircraft |
|||
1. BAE HAWK - 17 on order. |
|||
2.HAL HJT-36 SITARA .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
WarShips Of Indian Navy |
|||
* Aircraft Carriers - |
|||
1. INS VIKRAMADITYA<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2. Vikrant class aircraft carriers |
|||
i. INS VIKRANT - 40,OOO TON to be commisioned by 2014 |
|||
ii. INS VISHAL - 65,OOO TON to be commisioned by 2017 |
|||
plans to built atleast 1 more aircraft carrier .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Nuclear Submarines |
|||
1.Arihant Class Submarines - 1 launched [INS ARIHANT ] , 3 under construction , further 4 planned to follow on.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2.Akula class submarine - 1 commisioned , 1 planned to be commisioned under lease . option for buying this submarines.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
3. SSN - 9 Submarines planned , will escort SSBN. Government approval given.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* SUBMARINES<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. Project 75 [ scorpene submarines ] - 6 under construction + proposal for 3 more planned. |
|||
2. Project 75 I - 6 Submarines planned - RFI released.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
3. Indigenous submarine - 12 planned . Not yet Approved By government.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
4. Midget submarines - 5 planned - RFI Issued.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* DESTROYERS<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1.Project 15 A [ Kolkata class destroyer ] - 3 under construction. |
|||
2.project 15 B - 4 Planned . approved by MoD. work to begin after completion of 15 A.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* FRIGATES<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1.Project 17 [ Shivalik class Frigate ] - 1 commisioned , 2 under construction. |
|||
2.Project 17 A - 7 planned . construction to start by 2011. |
|||
3.Talwar class Frigate - 3 commisioned , 2 under sea trials , 1 under construction . total 6.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* CORVETTES<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. Project 28 [ Kamorta class Corvette ] - 4 under construction. |
|||
2.Project 28 A [ Kamorta class follow on ] - 8 on order.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* MINESWEEPER<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. Osprey class - 2 to be acquired. |
|||
*Mine countermeasure vessels - 2 under constrution.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Patrol crafts <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1.Saryu class patrol vessel - 4 under construction. |
|||
2.Car Nicobar class fast attack craft - 7 commisioned , 3 launched . total 10 vessels. |
|||
3. Offshore Patrol Vessels [ saryu class vessel follow on ] - order for 5 vessels placed. |
|||
*Replenishment Ship |
|||
1.Deepak class - 1 commisioned , 1 under construction.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Training ship |
|||
1.sudarshini class - 1 under construction. |
|||
2.sail training ship - 1 on order.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
*Survey Vessel - 6 on order. |
|||
* Amphibious Warfare |
|||
1. Landing Platform Dock [LPD] - 4 Planned , approved by Ministry. |
|||
2.Landing Ship Tanks - 14 planned.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
INDIAN ARMY |
|||
* Main Battle Tank<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1.T -90 bhishma - India plans to induct Total 1657 tanks by 2020 . 620 already in service. |
|||
2.Arjun MBT - 248 On order - 170 Inducted . |
|||
3. Arjun MBT mk 2 - Trials by 2011. Production By 2014. |
|||
4.FMBT - The FMBT will be a lighter tank of 50 tons. Development work started.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* MISSILES<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
i. Intercontinental Ballastic Missile |
|||
1. AGNI V - 5,000 km - 6,000 km , test by 2011. |
|||
2. Surya ICBM - The Surya missile is a speculation about an Inter Continental ballistic missile being developed by India.Sources say the DRDO's most treasured dream—denied in public—remains the development of an ICBM with a range of 15,000 kilometres, already christened Surya or sun, to match Chinese DF-3 ICBMs. Range 12,000 to 16,000 kilometers.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
ii.Cruise Missile<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. Nirbhay Missile |
|||
2 . Brahmos and Brahmos - 2 missile.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
iii.Tactical Ballastic Missile |
|||
1. Shaurya Missile - It has a range of between 750 to 1900 km .<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
iv.Anti-Tank Guided Missiles<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
1. Nag Anti-tank guided missile. |
|||
2. Helina Air launched Anti-tank missile.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
*Indian Ballistic Missile Defense Program- The Indian Ballistic Missile Defense P<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref>rogram is an initiative to develop and deploy a multi-layered ballistic missile defense system to protect India from ballistic missile attacks. |
|||
* Vehicles |
|||
1.Mahindra Axe - Light utility vehicle to be purchased. |
|||
2.Kroton - Possible sale of 80 mine laying vehicles from Poland. |
|||
3.Light Tank - 300 tanks (200 tracked 100 wheeled) to be deployed on china border. |
|||
4.AHS Krab - Possible sale of 110 from Poland. deal along with kroton . |
|||
5.PZA Loara - Possible sale of 100 from Poland. deal along with Kroton.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
*ARTILLERY SYSTEM |
|||
1.Under the Field Artillery Rationalization Plan, Indian Army plans to procure 3000 to 4000 |
|||
155 mm Towed, Wheeled and Tracked Artillery Systems.The requirement for artillery guns to be met with indigenous development and production.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2.M777 howitzer - 145 British designed howitzers were planned to be acquired. |
|||
* F-INSAS - Futuristic Infantry Soldier As a System(F-INSAS) is the Indian Army's principal modernization program from 2012 to 2020.In the first phase, to be completed by 2012,the infantry soldiers will be equipped with modular weapon systems that will have multi-functions.The Indian Army intends to modernize its entire 465 infantry and paramilitary battalions by 2020 with this program.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
*Modern Sub Machine Carbine - The Modern Sub Machine Carbine (MSMC) is the latest combined venture of ARDE & OFB, developed for the Indian Army on a platform of experiences from the INSAS rifle.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
*ARMY AVIATION |
|||
1. Tender for 197 light transport helicopter Along with 125 for Air Force.To Replace Cheetak and Cheetah Helicopters of Armed Forces.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
2. HAL light observation helicopter [ LOH ] or Light Utility helicopter [LUH] - Requirement for 384 helicopters including for army and air force.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
3. LCH [ Light Combat Helicopter ] - Order of 114 helicopters to Army.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
Strategic Nuclear Command <ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
* Plans To acquire Fighter Jets capable of delivering nuclear weapons. |
|||
40 fighters - 2 squadrons.<ref name=" Indian Military Future Procurements">{{cite news|url=http://www.defence.pk/forums/india-defence/98428-indian-military-future-procurements.html|title=Indian Military Future Procurements|publisher=defence.pk | date=16 March 2011}}</ref> |
|||
== Recruitment and training == |
== Recruitment and training == |
||
Revision as of 13:18, 26 June 2011
The Indian Armed Forces (Devanāgarī: भारतीय सशस्त्र सेनाएं, Bhāratīya Saśastra Sēnāēn) are the military forces of the Republic of India encompassing the Indian Army, the Indian Navy, the Indian Air Force, Indian Coast Guard and various other inter-service institutions. The President of the Republic of India is the Commander-in-Chief of the Indian Armed Forces. The Indian Armed Forces is managed by Ministry of Defence (MoD) which is led by Union Cabinet Minister of Defense.
The IAF is one of the world's largest military force, with roughly 1.32 million active standing army and 2.14 million reserve forces thus giving India the third-largest active troops in the world as of 2006[1][4] after the People's Liberation Army and US Armed Forces.[5] Auxiliary services include the Indian Coast Guard, the Central Paramilitary Forces (CPF) and the Strategic Forces Command. India's official defense budget stands at US$36.03 billion for FY2011 (or 1.83% of GDP)[2] but the actual spending on the armed forces is estimated to be much higher than that.[6] Undergoing rapid expansion and modernization,[7] the Indian Armed Forces plans to have an active military space program[8] and is currently developing a missile defense shield[9] and nuclear triad capability. The Armed Forces of India possess nuclear weapons and operate short and intermediate-range ballistic missiles as well as nuclear-capable aircraft, and naval vessels. India is the world's largest arms importer accounting for 9% of all global imports and ranks among the top thirty in arms export.[10] Currently, India imports close to 70% of its weapons requirements, with Israel, Russia and the United States as its top military suppliers.[11][12][13] The country’s defence expenditure will be around US$112 billion by 2016.[14][15][16]
The IAF served as India's armed forces in all the country's major military operations — including the Indo-Pakistani wars of 1947, Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, Sino-Indian War, 1987 Sino-Indian skirmish, Kargil War and others. India is currently moving to build a ₹9,970.16 crore (US$1.2 billion) dedicated, highly secure and state-of-the-art optical fiber cable (OFC) network for the Army, Navy and Air Force. This will be one of the world's largest, closed user group (CUG) networks for exclusive use by the million-plus personnel of the Indian armed forces.[17] Following 1962, the IAF has had close military relations with the Russia, including development cooperation, such as on the Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA), Multirole Transport Aircraft (MTA), and others as well.
Military history of India

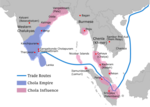


India has one of the longest military history dating back several millennia. The first reference of armies is found in the Vedas as well as the epics Ramayana and Mahabaratha. There were many powerful dynasties in India: Maha Janapadas, Matsya Kingdom, Shishunaga Empire, Gangaridai Empire, Nanda Empire, Maurya Empire, Sunga Empire, Kharavela Empire, Kuninda Kingdom, Chola Empire, Chera Empire, Pandyan Empire, Satavahana Empire, Western Satrap Empire, Kushan Empire, Vakataka Empire, Kalabhras Kingdom, Gupta Empire, Pallava Empire, Kadamba Empire, Western Ganga Kingdom, Vishnukundina Empire, Chalukya Empire, Harsha Empire, Rajput, Shahi Kingdom, Eastern Chalukya Kingdom, Pratihara Empire, Pala Empire, Rashtrakuta Empire, Paramara Kingdom, Yadava Empire, Solanki Kingdom, Western Chalukya Empire, Hoysala Empire, Sena Empire, Eastern Ganga Empire, Kakatiya Kingdom, Kalachuri Empire, Delhi Sultanate, Deccan Sultanates, Ahom Kingdom, Vijayanagar Empire, Mysore Kingdom, Mughal Empire, Maratha Empire, Sikh Empire, etc. Classical Indian texts on archery in particular, and martial arts in general are known as Dhanurveda.
India has a maritime history dating back to 5,000 years.[18][19][20][21] The first [22][23] tidal dock is believed to have been built at Lothal around 2300 BCE during the Indus Valley Civilization, near the present day Mangrol harbour on the Gujarat coast. The Rig Veda written around 1500 BCE, credits Varuna with knowledge of the ocean routes and describes naval expeditions. There is reference to the side wings of a vessel called Plava, which give stability to the ship under storm conditions. A compass, Matsya yantra was used for navigation in the fourth and fifth century AD.
The earliest known reference to an organization devoted to ships in ancient India is to the Mauryan Empire from the 4th century BCE. Emperor Chandragupta Maurya's Prime Minister Kautilya's Arthashastra devotes a full chapter on the state department of waterways under navadhyaksha (Sanskrit for Superintendent of ships) [1]. The term, nava dvipantaragamanam (Sanskrit for sailing to other lands by ships, i.e. Exploration) appears in this book in addition to appearing in the Buddhist text, Baudhayana Dharmasastra as the interpretation of the term, Samudrasamyanam.
Sea lanes between India and neighboring lands were the usual form of trade for many centuries, and are responsible for the widespread influence of Indian Culture on other societies. Powerful navies included those of the Maurya, Satavahana, Chola, Vijayanagara, Kalinga, Mughal and Maratha empires.[24] The Cholas excelled in foreign trade and maritime activity, extending their influence overseas to China and Southeast Asia.
During the 17th and 18th centuries, the Maratha and Kerala fleets were expanded, and became the most powerful Naval Forces in the subcontinent, defeating European Navies at various times (See the Battle of Colachel). The fleet review of the Maratha navy took place at the Ratnagiri fort in which the ships Pal and Qalbat participated.[25] The Maratha Kanhoji Angre and Kunjali Marakkar, the Naval chief of Saamoothiri were two notable naval chiefs of the period.
1857 to 1947 era

The British Royal Indian Navy was first established by the British while much of India was under the control of the East India Company. The first Indian to be granted a commission was Sub Lieutenant D. N. Mukherji, who joined the Royal Indian Marine as an engineer officer in 1928.
Indian sailors started a rebellion known as the Royal Indian Navy mutiny in 1946, on board ships and in shore establishments which spread all over India. A total of 78 ships, 20 shore establishments and 20,000 sailors were involved in the rebellion.
When India became a republic on 26 January 1950, the navy became known as the Indian Navy, and its vessels as Indian Naval Ships (INS). On 22 April 1958 Vice Admiral R. D. Katari assumed office as the first Indian Chief of the Naval Staff.
Structure
The headquarters of the Indian Armed Forces is in New Delhi, the capital city of India.The President acts as de jure Commander in chief of the Armed Forces.[26] while de facto control lies with the executive. The Ministry of Defence (MoD) is the ministry charged with the responsibilities of countering insurgency and ensuring external security of India.
Command organisation
Gen V K Singh is the head of army Chiefs panel, Admiral Nirmal Kumar Verma is the head of navy Chiefs panel and Air Chief Marshal Pradeep Vasant Naik is the head of air forces Chiefs panel.[27] Air Chief Marshal Naik is currently also serving as Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee for the Indian Armed Force. The Indian armed force are split into different groups based on their region of operation. The Indian Army is administratively divided into 7 tactical commands, each under the control of different Lieutenant Generals.The Indian Air Force is divided into five operational and two functional commands. Each Command is headed by an Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief with the rank of Air Marshal. The Indian Navy operates four Commands. Each Command is headed by a Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief in the rank of Vice Admiral.The Indian Coast Guard operations are split into 4 regions, each region is headed by an Inspector General or a Deputy Inspector General.
Doctrine
The Armed Forces have six main tasks:[28]
- To assert the territorial integrity of India.
- To defend the country if attacked by a foreign nation.
- To send own amphibious warfare equipment to take the battle to enemy shores.[29]
- Cold Start which means Indian Armed Forces being able to quickly mobilise and take offensive actions without crossing the enemy's nuclear-use threshold.
- To support the civil community in case of disasters (e.g. flooding).
- Participate in United Nations peacekeeping operations in consonance with India’s commitment to the United Nations Charter.
There is a semi-official book called "Customs and Etiquette in the Services", written by retired Major General Ravi Arora, which details how Indian personnel are expected to conduct themselves generally.[30] Arora is an executive editor of the Indian Military Review.[31]
Personnel

As of 2006
| Component | Active[1] | Reserve[1] |
| 1,325,000 | 2,142,821 | |
| 67,000 | ||
| 170,000 | ||
| File:Indian Coast Guard flag.png Indian Coast Guard | 19,741 |
Service branches


Indian Army
India maintains the third-largest military force in the world, which includes Indian Army, Navy, Air Force and auxiliary forces such as the Paramilitary Forces, the Coast Guard, and the Strategic Forces Command.[32] It is a completely voluntary service, the military draft having never been imposed in India. The army has rich combat experience in diverse terrains, due to India's diverse geography, and also has a distinguished history of serving in United Nations peacekeeping operations. Initially, the army's main objective was to defend the nation's frontiers. However, over the years, the army has also taken up the responsibility of providing internal security, especially in insurgent-hit Kashmir and north-east.
The force is headed by the Chief of Army Staff of the Indian Army, currently General V K Singh. The highest rank in the Indian Army is Field Marshal, but it is a largely ceremonial rank and appointments are made by the President of India, on the advice of the Union Cabinet of Ministers, only in exceptional circumstances. (See Field Marshal (India)). Late General S.H.F.J. Manekshaw and the late General K.M. Cariappa are the only two officers who have attained this rank.
The Indian Army has seen military action during the First Kashmir War, Operation Polo, the Sino-Indian War, the Second Kashmir War, the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, the Sri Lankan Civil War and the Kargil War. Currently, the Indian army has dedicated one brigade of troops to the UN's standby arrangements. Through its large, sustained troop commitments India has come in for much praise for taking part in difficult operations for prolonged periods. The Indian Army has participated in several UN peacekeeping operations, including the ones in Cyprus, Lebanon, Congo, Angola, Cambodia, Vietnam, Namibia, El Salvador, Liberia, Mozambique and Somalia. The army also provided a paramedical unit to facilitate the withdrawal of the sick and wounded in Korea. Currently, the Indian Army is seeking to massively modernize its equipment through various procurement programs. In addition, it has also embarked on an infantry modernization program known as Futuristic Infantry Soldier As a System (F-INSAS).

The Indian Navy is the naval branch of the armed forces of India. With 67,000 men and women, including 5,000 naval aviation personnel and 2,000 Marine Commandos (MARCOS), it is the world's fifth largest navy.[33]
The Indian Navy currently operates around 170 vessels, including the aircraft carrier INS Viraat. In recent years, India has started many ambitious projects to bolster its maritime capabilities including efforts to acquire ships from foreign countries.
In recent years, the Indian Navy has undergone extensive modernization and expansion with an intention to increase its capabilities as a recognized blue-water navy.[34][35] It is fairly advanced in terms of technology and is in control of one of two Asian aircraft carriers. Two more aircraft carriers are currently being produced. The ships of the Indian Navy are of Indian and foreign origin.[36] In addition, three ballistic missile submarine are to enter service by 2010 end. It is also only one of the six navies in the world that has nuclear capabilities. Others include US, Russia, China, France and the UK. In addition it is in command of the BrahMos which is the fastest cruise missile in the world with speeds of 2.8 Mach.

In its maritime doctrine, the Indian Navy establishes its role in providing support to maritime neighbours during natural disasters. This was demonstrated during the Asian tsunami crisis during which the Indian Navy sent 35 ships to support relief efforts in neighbouring countries. The Indian navy has taken part in UN missions in the coast of Somalia and has provided security to an African Union summit held in Mozambique. The Indian Navy is increasing its capabilities as a true blue-water navy; the Indian Navy's doctrine states that this is for the collective good of nations.
The Indian Navy is expected to spend about US$40 billion on military modernization from 2008 to 2013.[37] The modernization program includes the Russian-built aircraft carrier INS Vikramaditya, indigenously built Vikrant class aircraft carriers, Lease of Akula-II class submarine, indigenously built Arihant class nuclear-powered submarines, Shivalik class frigate, Kolkata class destroyer, Scorpène class submarine, Improved Talwar class frigate and eight P-8 Poseidon .[38][39]
Indian Air Force

With a strength of approximately 170,000 personnel, and 1,600+ aircraft in active service, the Indian Air Force is the fourth largest air force in the world.[40][41] In recent years, the IAF has undertaken an ambitious expansion and modernization program and is increasingly used for India's power projection beyond South Asia. Historically, the IAF has generally relied on Soviet, British, Israeli and French military craft and technology to support its growth. In recent times however, India has manufactured its own aircraft, including the HAL Tejas, a 4th generation fighter, and the HAL Dhruv, a multi-role helicopter, which has been exported to several countries, including Israel, Burma, Nepal and Ecuador. India also maintains UAV squadrons which can be used to carry out ground attacks and aerial surveillance.
India is testing its own long range BVR air to air missile named Astra[42] and also building a Medium Altitude Long Endurance Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) called Rustom.[43] India and Russia are building number of next generation aircraft like 5th generation stealth aircraft called Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft[44] (also called as Perspective Multi-role Fighter) and medium-lift military transport aircraft called Multirole Transport Aircraft.[45]
Indian Coast Guard

The Indian Coast Guard is the maritime Military Force created to guard Republic of India's vast coastline. It was created on 18 August 1978 as an independent entity as per the Coast Guard Act. its primary objective is to guard India's vast coastline and operates under the effective control of the Ministry of Defense.
The coast guard works closely with the Indian Navy and the Indian Customs Department, and is usually headed by a naval officer of the rank of Vice-Admiral. India's coast guard has a large number of fast craft including hovercrafts and hydrofoils. They patrol the seas and river mouths. The coast guard has performed a number of commendable tasks of rescuing distressed personnel. It has also apprehended pirates on high seas and cleaned up oil spills. Heavy patrolling of sensitive areas such as Karnataka, Gujarat, West Bengal and Mumbai have resulted in the nabbing of a large number of smugglers and illegal immigrants.
Nuclear Command Authority


India possesses an arsenal of nuclear weapons and maintains a no-first use, non-use against non-nuclear nations and a credible nuclear deterrence policy against nuclear adversaries. India's nuclear missiles include the Prithvi, the Agni, the Shaurya, Sagarika, Dhanush, and others. India has long range strategic bombers like the Tupolev Tu-22 M3 and Tupolev Tu-142 as well as fighter jets like Sukhoi Su-30MKI,[46] Dassault Mirage 2000,[47] MiG-29[48] and HAL Tejas capable of being armed with nuclear tipped bombs and missiles. Since India doesn't have a nuclear first use against an adversary, it becomes important to protect from a first strike. Presently, this protection is provided by the two layered Anti-ballistic missile defense system. The first test of Agni-V, which is a MIRVed ICBM is expected in the year 2011. India's Strategic Nuclear Command controls its land-based nuclear warheads, while the Navy controls the ship and in future submarine based missiles and the Air Force the air based warheads. India's nuclear warheads are deployed in four areas:
- Ship based mobile, like Dhanush. (operational)
- Land-based mobile, like Agni. (operational)
- Submarine based, like Sagarika. (under deployment)
- Air-based warheads of the Indian Air Forces' strategic bomber force (operational)
Indian Ballistic Missile Defense Program
The Indian Ballistic Missile Defense Program is an initiative to develop and deploy a multi-layered Ballistic missile defense system to protect India from missile attacks.[49][50]
Development
Phase 1

Development of ABM System began in 1999. Around 40 public and private Companies were involved in the development of ABM System. They include Bharat Electronics Ltd and Bharat Dynamics Ltd, Astra Microwave, ASL, Larsen & Toubro, Vem Technologies Private Limited and KelTech. Development of LRTR (Long Range Tracking Radar) and MFCR (Multi-function Fire Control Radar) was led by Electronics and Radar Development Establishment (ERDE).[51][52]
For the AAD Missile System, Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL) developed the mission control software. Research Centre, Imarat (RCI) developed navigation, electromechanical actuation systems and Active Radar Seeker. Advanced System Laboratory (ASL) provided the motors, jet vanes and structures for the two missiles. High Energy Materials Research Laboratory (HEMRL) supplied the propellants for the missile.[52]
Phase 2
- Two new anti-ballistic missiles that can intercept IRBM/ICBMs are being developed. These high speed missiles (AD-1 and AD-2) are being developed to intercept ballistic missiles with the range of 5000 km.[53] The test trials of these two systems is expected to take place in 2011.[54] The new missile will be similar the THAAD missile deployed by the U.S.A. These missiles will have to travel at hypersonic speeds and will require radars with scan capability of over 1500 kilometers to successfully intercept the target.[55]
- India is also planning to develop a laser based weapon system as part of its Ballistic Missile Defence to intercept and destroy missiles soon after they are launched towards the country. DRDO's Air Defence Programme Director V K Saraswat says its ideal to destroy a ballistic missile carrying nuclear or conventional warhead in its boost phase. Saraswat further added that it will take another 10–15 years for the premier defence research institute to make it usable on the ground.[56]
Security pacts and Overseas Bases

In 1950 Indo-Nepal Treaty of Peace and Friendship, India made obligation to actively assist Nepal in national defence and military preparedness, and made both nations not to tolerate threats to each others security.[58][59] In 1958, the then-Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru visited Bhutan and reiterated India's support for Bhutan's independence and later declared in the Indian Parliament that any aggression against Bhutan would be seen as aggression against India.[60] India also operates the Farkhor Air Base in Tajikistan. India started the process to bring the island country Maldives into India's security grid.[61] India can use Iranian bases for war with Pakistan.[62][63] India is also one of three countries with whom Japan has a security pact, the others being Australia and the United States.[64] India and Russia have a military cooperation pact until 2010 which is likely to be extended or renewed.[65] In 1951,India and Burma signed a Treaty of Friendship in New Delhi. Article II of the treaty stipulated that "There shall be everlasting peace and unalterable friendship between the two States who shall ever strive to strengthen and develop further the cordial relations existing between the peoples of the two countries".[66] India had signed a pact to develop ports in Myanmar and various bilateral issues, including economic cooperation, connectivity, security and energy.[67] India and Israel have increased cooperation in military and intelligence ventures since the establishment of diplomatic relations. While India and Israel were officially "rivals" during the Cold War, the fall of the Soviet Union and the rise of Islamic terrorism in both countries have generated a solid strategic alliance.[68] India has maritime security arrangement in place with Oman and Qatar.[69] In 2008, a landmark defense pact was signed, under which India committed its military assets to protect "Qatar from external threats".[70]
Budget

India has the world's 10th largest defense budget. In 2009, India's official military budget stood at US$32.7 billion.[71] In 2004, the GlobalSecurity.org estimated India's budget to be around US$100 billion in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP).[72] According to Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, India's military budget (PPP) stood at US$72.7 billion in 2007.[73] A major portion of India's current defense budget is devoted to the ambitious modernization program of the country's armed forces. Between 2007 and 2012, India is expected to spend about US$50 billion on the procurement of new weapons.[74] India boosted defence spending by 21% in 2009.[75]
Gallantry awards

The highest wartime gallantry award given by the Military of India is the Param Vir Chakra (PVC), followed by the Maha Vir Chakra (MVC) and the Vir Chakra (VrC). Its peacetime equivalent is the Ashoka Chakra. The highest decoration for meritorious service is the Param Vishisht Seva Medal.
Ex Servicemen (ESM)
According to military sources, more than 55,000 armed forces personnel retire from the army every year, most of them at a relatively younger age.[citation needed] A total of 1,567,390 ex servicemen are registered with the Indian Army, majority of them hailing from UP (17.35%), Punjab (12.23%), Haryana (10.57%), Maharashtra (9.18%), Kerala (8.16%), TN (6.58%), Rajastan (6.42%) and HP (5%). Many of them are re-employed in various Central government sectors.[76]
Future
Analysis of the Central Intelligence Agency indicates that India is projected to possess the fourth most capable concentration of power by 2015.[77] According to a report published by the US Congress, India is the developing world's leading arms purchaser.[78]
Ongoing efforts at modernization of the armed forces, however, unless accompanied by significant political reforms, may fail to change India's military-strategic position, particularly with Pakistan. Despite importing large numbers of conventional weaponry over the last three decades, if India wishes to effectively confront critical security challenges it must address a civil-military imbalance that hampers coordination and an illegitimate procurement process that threatens to further entrench government corruption.[79]
Indian Armed Forces Future Procurement
Indian Military Future Procurements [80]
Indian Air Force[80]
- Transport aircraft - [80]
1. Boeing C-17 Globemaster III - purchase of 10 aircrafts plus option for 10 more aircrafts.[80]
2.Lockheed Martin C-130J Super Hercules - purchase of 6 aircrafts plus option for 6 more. 3.Alenia C-27J Spartan - IAF looking to purchase 16 of this aircraft. 2 more for BSF Air Wing.[80]
4.UAC/HAL Il-214 Multirole Transport Aircraft (MTA) - Indo-Russian joint venture.The Indian Air Force plans to acquire 45 MTAs.[80]
5.NAL Saras - Indian Air Force intends to place an order for up to 45 aircraft.[80]
- Fighter aircraft - [80]
1. (MMRCA) - 126 aircraft . There is an option for an additional 74 aircraft.Bidders - Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet,Dassault Rafale,Eurofighter Typhoon,Lockheed Martin F-16IN Super Viper,Mikoyan MiG-35,Saab Gripen NG.[80]
2. HAL TEJAS - The IAF is reported to have a requirement for 200 single-seat and 20 two-seat conversion trainers. 3.Sukhoi/HAL FGFA - Indo-Russian joint venture.Indian Air Force will get 200 twin-seated and 50 single seated FGFAs.The option for further orders will be kept open.[80]
4. Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft - IAF has a requirement of at least 250 AMCAs.[80]
- Trainer aircraft - [80]
1.Tender For 181 basic trainer aircraft - bidders : Grob G-120TP, Embraer EMB 314 Super Tucano, Korean Aerospace Industries KT-1, Finmeccanica M-311 and Pilatus PC-7 .[80]
2.HAL HJT-36 Sitara - The Indian Air Force has placed placed an order for 73 aircraft, of which the first 12 are in production.The order by the Indian Air Force could eventually grow to 250 aircraft.[80]
3.HAL HTT-40 - will replace HAL HPT-32 Deepak as basic trainer in IAF.[80] 4. BAE HAWK - 123 Ordered.[80]
- Airborne early warning aircraft - [80]
1. DRDO AEW&CS - 4 system on order plus additional 20 systems .[80]
2.Beriev A-50 [ PHALCON AWACS ] - 3 operational , order for additional 3 likely.
- Attack helicopter -[80]
1.LCH - Order of 65 LCH to IAF.[80] 2. Tender for 22 attack helicopters - Bidders : AH-64D Apache Longbow,Mi-28.[80]
- Transport and utility helicopters - [80]
1. Tender for 15 heavy lift helicopters - Bidders : CH-47 Chinook,Mi-26.[80]
2. Mi-17 V-5 - order for 80 plus additional 59 placed .[80]
3. AgustaWestland AW101 - order for 12 helicopters placed . will be used for VIP transport.[80]
4.Tender for 125 light transport helicopter Along with 197 for Army aviation.[80]
5.HAL light observation helicopter [ LOH ] or Light Utility helicopter [LUH] - Requirement for 384 helicopters including for army and air force.[80]
- Unmanned aerial vehicles -
1.Tender For stealth UCAV - The Indian air force has submitted a request for information to international suppliers for a unmanned combat air vehicle (UCAV) with low radar cross-section, high service ceiling, an expected range of 500nm (925km) and the capability to carry precision-guided weapons in an internal weapons bay.[80]
2.RUSTOM MALE UAV - The Rustom will replace/supplement the Heron UAVs in service with the Indian armed forces 3. AURA UCAV - The AURA UCAV will be a tactical stealth aircraft built largely with composites, and capable of delivering laser-guided strike weapons. It would be a stealthy flying-wing concept aircraft with internal weapons and a turbofan engine.[80]
- Cruise missiles -
1.Nirbhay cruise missile - is a long range, subsonic cruise missile . The missile will have a range of 1,000 km and will arm three services. First test flight by early 2012.[80]
- Surface to air missile systems -
1. SPYDER SAM systems - India to acquire 18 of this system. 2. Maitri (missile) - The Maitri missile project is a next-generation Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile (QRSAM) with a lethal hundred per cent kill probability .[80]
- Air TO Air Missile
1.Astra (missile) BVRAAM .[80]
Indian Navy[80]
- Surface to air missile system - [80]
1. Barak II - Indian - israel joint venture on new generation surface to air missile system deployed on warships.
- Submarine-launched ballistic missile -
1.Sagarika [ k 15 ] - is a nuclear-capable submarine-launched ballistic missile with a range of 700 kilometres .[80]
2. K-4 SLBM - DRDO is working on a Submarine Launched Version of the Agni-III missile, which will provide India with a credible sea based second strike capability.[80]
3. K-5 SLBM - Submarine Launched Version of the Agni-V missile.[80]
NAVAL AIR ARM[80]
- Fighter Aircraft -
1. Mig 29 K - Naval Air Arm has 45 MiG-29K/KUB aircraft on order .[80]
2. NAVAL lCA TEJAS - Navy has requirement of 50 of this aircraft. 6 Ordered.[80]
3. Additional Fighter Aircraft - Indian Navy has issued RFI to various fighter aircraft manufacturers including Boeing for F-18 Super Hornet & Dassault for its Rafale fighters.These aircraft will be used for supplements to MIG29K's operating from Indigenous & Vikramaditya class aircraft carriers. [80] 4. Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft - Indian Navy has shown interest in the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft to operate from future super carriers.[80]
- Long Range Maritime Patrol Aircraft - [80]
1. P-8I Poseidon - 8 + additional 4 on order.
- Medium Range Maritime Reconnaissance Aircraft -[80]
1. Tender for 6 plus additional 6 aircraft - Bidders : ATR-72MP/ ATR-42MP, EADS C-295MPA/C-235MPA, Dassault's Falcon 900MPA and Embraer P-99A platforms.[80]
- Airborne Early Warning and Control (AEW&C) -
1.E-2D Advanced Hawkeye - order of 6 aircraft for future carriers.[80]
NAL SARAS - 15 Aircrafts on order.to replace Dorniers.[80]
- ASW Helicopter
1. Tender for 60 helicopters. AgustaWestland, EADS and Sikorsky possible bidders.[80]
- Unmanned aerial vehicles -
1. unmanned helicopter - Joint venture between India - israel .This helicopter is under development and will be based on the HAL-built Cheetah helicopters. requirement for 40 helicopters.[80]
2. Rustom UAV .
- Utility Helicopter -
1. Light Utility helicopter - requirement for 50 helicopters.[80]
- Trainer Aircraft
1. BAE HAWK - 17 on order. 2.HAL HJT-36 SITARA .[80]
WarShips Of Indian Navy
- Aircraft Carriers -
1. INS VIKRAMADITYA[80]
2. Vikrant class aircraft carriers i. INS VIKRANT - 40,OOO TON to be commisioned by 2014 ii. INS VISHAL - 65,OOO TON to be commisioned by 2017 plans to built atleast 1 more aircraft carrier .[80]
- Nuclear Submarines
1.Arihant Class Submarines - 1 launched [INS ARIHANT ] , 3 under construction , further 4 planned to follow on.[80]
2.Akula class submarine - 1 commisioned , 1 planned to be commisioned under lease . option for buying this submarines.[80] 3. SSN - 9 Submarines planned , will escort SSBN. Government approval given.[80]
- SUBMARINES[80]
1. Project 75 [ scorpene submarines ] - 6 under construction + proposal for 3 more planned. 2. Project 75 I - 6 Submarines planned - RFI released.[80]
3. Indigenous submarine - 12 planned . Not yet Approved By government.[80]
4. Midget submarines - 5 planned - RFI Issued.[80]
- DESTROYERS[80]
1.Project 15 A [ Kolkata class destroyer ] - 3 under construction. 2.project 15 B - 4 Planned . approved by MoD. work to begin after completion of 15 A.[80]
- FRIGATES[80]
1.Project 17 [ Shivalik class Frigate ] - 1 commisioned , 2 under construction. 2.Project 17 A - 7 planned . construction to start by 2011. 3.Talwar class Frigate - 3 commisioned , 2 under sea trials , 1 under construction . total 6.[80]
- CORVETTES[80]
1. Project 28 [ Kamorta class Corvette ] - 4 under construction. 2.Project 28 A [ Kamorta class follow on ] - 8 on order.[80]
- MINESWEEPER[80]
1. Osprey class - 2 to be acquired.
- Mine countermeasure vessels - 2 under constrution.[80]
- Patrol crafts [80]
1.Saryu class patrol vessel - 4 under construction. 2.Car Nicobar class fast attack craft - 7 commisioned , 3 launched . total 10 vessels. 3. Offshore Patrol Vessels [ saryu class vessel follow on ] - order for 5 vessels placed.
- Replenishment Ship
1.Deepak class - 1 commisioned , 1 under construction.[80]
- Training ship
1.sudarshini class - 1 under construction. 2.sail training ship - 1 on order.[80]
- Survey Vessel - 6 on order.
- Amphibious Warfare
1. Landing Platform Dock [LPD] - 4 Planned , approved by Ministry. 2.Landing Ship Tanks - 14 planned.[80]
INDIAN ARMY
- Main Battle Tank[80]
1.T -90 bhishma - India plans to induct Total 1657 tanks by 2020 . 620 already in service.
2.Arjun MBT - 248 On order - 170 Inducted .
3. Arjun MBT mk 2 - Trials by 2011. Production By 2014.
4.FMBT - The FMBT will be a lighter tank of 50 tons. Development work started.[80]
- MISSILES[80]
i. Intercontinental Ballastic Missile 1. AGNI V - 5,000 km - 6,000 km , test by 2011. 2. Surya ICBM - The Surya missile is a speculation about an Inter Continental ballistic missile being developed by India.Sources say the DRDO's most treasured dream—denied in public—remains the development of an ICBM with a range of 15,000 kilometres, already christened Surya or sun, to match Chinese DF-3 ICBMs. Range 12,000 to 16,000 kilometers.[80]
ii.Cruise Missile[80] 1. Nirbhay Missile
2 . Brahmos and Brahmos - 2 missile.[80]
iii.Tactical Ballastic Missile 1. Shaurya Missile - It has a range of between 750 to 1900 km .[80]
iv.Anti-Tank Guided Missiles[80] 1. Nag Anti-tank guided missile. 2. Helina Air launched Anti-tank missile.[80]
- Indian Ballistic Missile Defense Program- The Indian Ballistic Missile Defense P[80]rogram is an initiative to develop and deploy a multi-layered ballistic missile defense system to protect India from ballistic missile attacks.
- Vehicles
1.Mahindra Axe - Light utility vehicle to be purchased. 2.Kroton - Possible sale of 80 mine laying vehicles from Poland. 3.Light Tank - 300 tanks (200 tracked 100 wheeled) to be deployed on china border. 4.AHS Krab - Possible sale of 110 from Poland. deal along with kroton . 5.PZA Loara - Possible sale of 100 from Poland. deal along with Kroton.[80]
- ARTILLERY SYSTEM
1.Under the Field Artillery Rationalization Plan, Indian Army plans to procure 3000 to 4000 155 mm Towed, Wheeled and Tracked Artillery Systems.The requirement for artillery guns to be met with indigenous development and production.[80]
2.M777 howitzer - 145 British designed howitzers were planned to be acquired.
- F-INSAS - Futuristic Infantry Soldier As a System(F-INSAS) is the Indian Army's principal modernization program from 2012 to 2020.In the first phase, to be completed by 2012,the infantry soldiers will be equipped with modular weapon systems that will have multi-functions.The Indian Army intends to modernize its entire 465 infantry and paramilitary battalions by 2020 with this program.[80]
- Modern Sub Machine Carbine - The Modern Sub Machine Carbine (MSMC) is the latest combined venture of ARDE & OFB, developed for the Indian Army on a platform of experiences from the INSAS rifle.[80]
- ARMY AVIATION
1. Tender for 197 light transport helicopter Along with 125 for Air Force.To Replace Cheetak and Cheetah Helicopters of Armed Forces.[80]
2. HAL light observation helicopter [ LOH ] or Light Utility helicopter [LUH] - Requirement for 384 helicopters including for army and air force.[80]
3. LCH [ Light Combat Helicopter ] - Order of 114 helicopters to Army.[80]
Strategic Nuclear Command [80]
- Plans To acquire Fighter Jets capable of delivering nuclear weapons.
40 fighters - 2 squadrons.[80]
Recruitment and training

Recruitment is through four military-related academies. These include the National Defence Academy, Pune, Indian Military Academy, Dehradun, Indian Naval Academy, Ezhimala, Air Force Academy, Hyderabad and Officers Training Academy, Chennai. For entrance, one must display that they are both physically and mentally fit to be in the military by written examinations, physical endurance tests and passing medical fitness tests. After being commissioned,these officers are posted and deputed. They are at the helm of affairs not only inside the nation but also at abroad. The officers are appointed and removed only by the President of India. These officers are accorded high status of the nature of the officers of the Indian Administrative Service. The complete list of institutions training Indian army were listed in Military academies in India section.
Indian Peace Keeping And Anti-piracy Mission
In November 2008, an Indian navy warship destroyed a suspected Somali pirate vessel after it came under attack in the Gulf of Aden. India is regular contributor to United Nations and other Peacekeeping missions. The troop-contributions to UN peacekeeping operations as of March 2007 were 9,471.[81] It also suffered 127 soldier deaths while serving on peacekeeping missions.[82] India also provided army contingent performing a peacekeeping operation in Sri Lanka between 1987 and 1990 as Indian Peace Keeping Force and in November 1988, India also helped restore government of Maumoon Abdul Gayoom in Maldives under Operation Cactus.[83]
Anti-piracy Mission
India sought to augment its naval force in the Gulf of Aden by deploying the larger INS Mysore to patrol the area. Somalia also added India to its list of states, including the U.S. and France, who are permitted to enter its territorial waters, extending up to 12 nautical miles (22 km; 14 mi) from the coastline, in an effort to check piracy.[84] An Indian naval official confirmed receipt of a letter acceding to India's prerogative to check such piracy. "We had put up a request before the Somali government to play a greater role in suppressing piracy in the Gulf of Aden in view of the United Nations resolution. The TFG government gave its nod recently."[85] India also expressed consideration to deploy up to four more warships in the region.[86][87] And in response increased activity of the INS Tabar. On 2010-09-06 A crack team of Indian marine commandos(MARCOS)from INS Delhi boarded the boat and overpowered the pirates - seven heavily-armed Somalians and one Yemeni national. A cache of arms, several drums of fuel and ship boarding equipment was also found.As part of the Indian response to the piracy menace in the area, the Indian Navy has escorted over 1,200 ships so far.
Relief Operation of IAF
Indian Air Force provides regular relief operation for food and medical facility around the World by its Cargo aircraft most notably Ilyushin Il-76.The most recent relief operation of IAF was in Kyrgyzstan.[88][89] During the Leh floods Two Ilyushin Il-76. and four Antonov-32 aircraft of the IAF carried 30 tonnes of load, which include 125 rescue and relief personnel, medicines, generators, tents, portable X-ray machines and emergency rescue kits.A MI-17 helicopter and cheetak helicopters had been pressed to increase the rescue operations.
IAF Efforts In Eclipse Study
The Indian Air Force successfully undertook sorties to help Indian scientists study the total solar eclipse that took place on July 23. Two separate missions from Agra and Gwalior were flown along the path of the moon's shadow, a mission that was deemed hugely successful by scientists associated with the experiment. While one AN-32 transport aircraft carrying scientific equipment, cameras and scientists that took off from Agra landed back after a three-hour flight, a Mirage-2000 trainer from Gwalior took spectacular images of the celestial spectacle from 40,000 feet. With weather being clear at the altitudes and coordinates planned by the IAF pilots, both AN-32 and Mirage-2000 pilots were able to accomplish the mission successfully.[90]
See also
- Paramilitary Forces of India
- Equipment of the Indian Army
- Indian Naval Air Arm
- Ships of the Indian Navy
- Weapon systems of the Indian Navy
- India and weapons of mass destruction
- List of aircraft of the Indian Air Force
- List of regiments of the Indian Army
- Military operations of India
- List of missiles
- Defence Research and Development Organisation
- Indian Space Research Organisation
References
- ^ a b c d e "India's Armed Forces, CSIS (Page 24)" (PDF). 25 July 2006.
- ^ a b The SIPRI Military Expenditure Database, SIPRI
- ^ "Industria de armament nu se preda". Stiri.rol.ro. 10 November 2009. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ Page, Jeremy. "Comic starts adventure to find war heroes". The Times (9 February 2008).
- ^ "Reuters AlertNet - Indian defence budget unlikely to satisfy forces". Alertnet.org. 27 February 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ Broadsword (11 March 2008). "Ajai Shukla: How much is the defence budget?". Business-standard.com. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ http://www.iht.com/articles/2007/09/19/news/missile.php?page=2
- ^ Rabinowitz, Gavin (18 June 2008). "India's army seeks military space program". The San Francisco Chronicle.
- ^ India successfully tests missile interceptor
- ^ Top List TIV Tables-SIPRI
- ^ "End of an era: Israel replaces Russia as India's top military supplier". World Tribune. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Russia Competing to Remain India's Top Military Supplier". India Defence. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ Cohen, Stephen and Sunil Dasgupta. "Arms Sales for India". Brookings Institution. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ India arms race-AFP
- ^ India Military Spending, Markets and Future-EconomicTimes
- ^ Defence projects drive Indian steel market-ProjectMonitor
- ^ Shalini Singh, TNN, Aug 22, 2009, 01.17am IST (22 August 2009). "Govt plans Rs 10,000cr dedicated telecom network for armed forces - India - The Times of India". Timesofindia.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Interesting facts about India
- ^ Maritime trade with the west
- ^ Indus Valley Civilization
- ^ Economics of the Indus valley civilization
- ^ How to Build a Dock
- ^ Indian seabed hides ancient remains
- ^ History of the Indian Navy
- ^ Stamps issued in 2001
- ^ "Welcome". Government of India. Retrieved 18 January 2011.
- ^ http://www.ptinews.com/news/257178_Gen-Kapoor-is-new-head-of-Armed-Forces-Chiefs-panel
- ^ "Redoctrinisation of the Indian Armed Forces". Slideshare.net. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ "Indian armed forces are now ready with their own amphibious warfare doctrine to take the battle to enemy shores". IndiaDaily. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ "Book on Customs & Etiquettes in the Services Released". Press Information Bureau, Government of India. 03 September, 2007. Retrieved 10 March, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help) - ^ "About Us". Indian Military Review. Retrieved 10 March, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "CIA - [[The World Factbook]]" (web). Retrieved 12 January 2011.
{{cite web}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - ^ Global Security article on the Indian Navy
- ^ India's drive for a 'Blue water' Navy by Dr. David Scott, International Relations, Brunel University
- ^ India's 12 Steps to a World-Class Navy
- ^ Global Security The Indian Navy
- ^ India is projecting its military power-Page 2>
- ^ Pandit, Rajat (5 January 2009). "India inks largest-ever defence deal with US". The Times of India. Retrieved 5 January 2009.
- ^ "India, US to ink arms deal worth Rs 10,700 crore: Rediff.com India News". News.rediff.com. 17 March 2009. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ GlobalSecurity.org
- ^ Indian Air Force website
- ^ "National : Astra missile test-fired". The Hindu. 8 May 2009. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ http://www.drdo.com/dpi/SAsiaDefnStraRev_.pdf[dead link]
- ^ "Karnataka / Bangalore News : Indo-Russian agreement soon on PAK-FA". The Hindu. 8 February 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ "Russia, India may form military transport planes JV in 2-3 months | Russia | RIA Novosti". En.rian.ru. 8 January 2010. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ http://www.janes.com/defence/air_forces/news/jawa/jawa010108_1_n.shtml[dead link]
- ^ Mirage 2000#Operational history
- ^ "India Aircraft Special Weapons Delivery Systems". Fas.org. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ India expects to use missile interception system as a weapon, top scientist says
- ^ India developing new missiles Towards destroying hostile missiles
- ^ The Hindu Business Line : 40 cos involved in making of missile killers
- ^ a b T.S. Subramanian (Dec. 22, 2007-Jan. 04, 2008). "Smashing hit". Frontline. Retrieved 2008-02-06.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ India to develop high speed interceptors
- ^ India developing ballistic missiles to destroy IRBMs, ICBMs
- ^ DRDO readies shield against Chinese ICBMs
- ^ http://www.hindu.com/holnus/008200901181531.htm[dead link]
- ^ "30 December 2005-India-Russia relations, an overview". Embassy of India, Moscow. Retrieved 15 February 2009.
- ^ Tribune India
- ^ India-Nepal Treaty
- ^ Indo-Bhutanese relations
- ^ "India bringing Maldives into its security net". Indianexpress.com. 13 August 2009. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ http://www.janes.com/security/international_security/news/fr/fr030129_1_n.shtml[dead link]
- ^ http://www.dictatorshipwatch.com/2008/12/28/iran-vs-pakistan.html[dead link]
- ^ "India, Japan in security pact; a new architecture for Asia?". Reuters. 25 October 2008.
- ^ http://news.indiamart.com/news-analysis/india-russia-to-take-17051.html
- ^ India–Burma relations
- ^ "INDIA-MYANMAR/TIES India to sign pact to develop Myanmar port". Aseanaffairs.com. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ India and Israel Forge a Solid Strategic Alliance by Martin Sherman, The Jewish Institute for National Security Affairs
- ^ "Front Page : Navy foils bid to hijack Indian ship in Gulf of Aden". The Hindu. 12 November 2008. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ http://www.ptinews.com/pti%5Cptisite.nsf/0/AC643928791FF4F2652574FE00466484?OpenDocument [dead link]
- ^ Indian government defends major hike in budget
- ^ India Military Budget
- ^ Military Expenditure
- ^ India's arms spree on fast track - Asia Times
- ^ China, India boost defence as crisis takes toll on West
- ^ Resettlement and wellfare of ex-servicemen
- ^ INDIA IN THE INDIAN OCEAN by Donald L. Berlin Naval War College Review, Spring 2006, Vol. 59, No. 2
- ^ "India's navy in .8bn sub deal". BBC News. 12 September 2005. Retrieved 5 May 2010.
- ^ Cohen, Stephen P. and Sunil Dasgupta, "The Drag on India's Military Growth", The Brookings Institution, September 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm "Indian Military Future Procurements". defence.pk. 16 March 2011.
- ^ Ranking of Military and Police Contributions to UN Operations
- ^ http://www.un.org/Depts/dpko/fatalities/StatsByYear%201.pdf [dead link]
- ^ Indian Navy Destroyer In Anti-Piracy Action On Sept 5
- ^ "India gets the right of hot pursuit in Somali waters". Ibnlive.in.com. Retrieved 27 March 2009.
- ^ "Somalia seeks India's help to quell piracy- Politics/Nation-News-The Economic Times". Economictimes.indiatimes.com. 21 November 2008. Retrieved 27 March 2009.
- ^ "Reuters.com". Africa.reuters.com. 9 February 2009. Retrieved 27 March 2009.
- ^ Gibbons, Timothy J. (28 January 2009). "Navy helicopter squadron helps fight pirates". The Florida Times-Union. Retrieved 28 January 2009.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "Indian aid flown to Kyrgyzstan". Sify.com. 6 July 2010. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ "India sends aid to Kyrgyzstan". Hindustan Times. 1 July 2010. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ "PIB Press Release". Pib.nic.in. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
^ Does not include members of the Indian Police Service
Further reading
- CIA World Factbook 2010: India
- Militarism in India: The Army and Civil Society in Consensus- by A. Kundu
External links
- The Irrelevance of India's Rise as a Military Power- video of lecture by Stephen P. Cohen, Brookings Institution, hosted by the Program in Arms Control, Disarmament, and International Security (ACDIS), University of Illinois, October 15, 2009
- xisf.org- Website of XISF Foundation, focussed on welfare of ex-services personnel from Indian Military
- Indian-Military.org- Website dedicated to Indian Military
- BharatRakshak.com- Informative site on the Indian Military
- Indian Armed Forces - Indian military's official website
- Indian Air Force - Official website
- India Defence - Military & Defence News
- http://www.nationmaster.com/graph/mil_arm_for_per-military-armed-forces-personnel
- Armed forces, a forgotten lot: A debate by NDTV.com.

