Nihiluskyloren (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Alter: pages, title. Add: doi-broken-date. Formatted dashes. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Spinixster | Category:Extinct languages of Europe | #UCB_Category 20/97 |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
There are three proposed etymologies for the denomination ''Galindian'':<ref name="Dini">{{cite book|first=Pietro U.|last=Dini|title=Foundations of Baltic languages|translator-first1=Milda B.|translator-last1=Richardson|translator-first2=Robert E.|translator-last2=Richardson|publisher=Vilniaus universitetas|place=Vilnius|date=2014|isbn=978-609-437-263-6}}</ref>{{rp|pages=308-309}} |
There are three proposed etymologies for the denomination ''Galindian'':<ref name="Dini">{{cite book|first=Pietro U.|last=Dini|title=Foundations of Baltic languages|translator-first1=Milda B.|translator-last1=Richardson|translator-first2=Robert E.|translator-last2=Richardson|publisher=Vilniaus universitetas|place=Vilnius|date=2014|isbn=978-609-437-263-6}}</ref>{{rp|pages=308-309}} |
||
* Proto-Baltic {{Lang|mis|*Galind-}} meaning 'outsider' ({{lang-lt|gãlas}} 'wall; border').<ref>{{cite book|first=Kazimieras|last=Būga|year=1924|language=lt|title=Lietuvių tauta ir kalba bei jos artimieji giminaičiai|trans-title=The language and nation of the Lithuanians and its close relatives|place=Kaunas}}</ref> This is supported by the etymology of the common Old Russian term for the Galindians {{Lang|orv|Голядь}} {{lang|orv-latn|Goljad'}} > {{Lang|mis|*golędь}} > Baltic {{Lang|bat|*Galind-}}); |
* Proto-Baltic {{Lang|mis|*Galind-}} meaning 'outsider' ({{lang-lt|gãlas}} 'wall; border').<ref>{{cite book|first=Kazimieras|last=Būga|year=1924|language=lt|title=Lietuvių tauta ir kalba bei jos artimieji giminaičiai|trans-title=The language and nation of the Lithuanians and its close relatives|place=Kaunas}}</ref> This is supported by the etymology of the common Old Russian term for the Galindians {{Lang|orv|Голядь}} {{lang|orv-latn|Goljad'}} > {{Lang|mis|*golędь}} > Baltic {{Lang|bat|*Galind-}}); |
||
* It is derived from the root {{Lang|mis|*gal-/*gil}} found in Baltic [[Hydronym|hydronyms]];<ref>{{cite book|last=Nalepa|first=Jerzy|year=1971|chapter=Próba nowej etymologii nazwy Galindia czyli Golędź|language=pl|trans-chapter=Proposal of a new etymology of the name Galindia or Golędź|title=Opuscula slavica 1|series=Slaviska och baltiska studier|volume=9|publisher=Slaviska institutionen vid Lunds universitet|place=Lund|pages= |
* It is derived from the root {{Lang|mis|*gal-/*gil}} found in Baltic [[Hydronym|hydronyms]];<ref>{{cite book|last=Nalepa|first=Jerzy|year=1971|chapter=Próba nowej etymologii nazwy Galindia czyli Golędź|language=pl|trans-chapter=Proposal of a new etymology of the name Galindia or Golędź|title=Opuscula slavica 1|series=Slaviska och baltiska studier|volume=9|publisher=Slaviska institutionen vid Lunds universitet|place=Lund|pages=93–115}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|first=Vytautas|last=Mažiulis|author-link=Vytautas Mažiulis|year=1981|pages=318–319|title=Prūsų kalbos paminklai|trans-title=Monuments of the Prussian language|language=lt|publisher=Mokslas|volume=II|place=Vilnius}}</ref> and |
||
* The name means 'the powerful ones' ({{lang-lt|galià}} 'power, strength') and also Celtic languages ({{lang-ga|gal}} 'strength', {{lang-cy|gallus}} 'power', ''Galli'', ''Gallia'').<ref>{{cite book|last=Schmid|first=Wolfgang P.|year=1998|chapter=Galinder|trans-chapter=Galindians|title=Reallexikon der germanischen Alterskunde|trans-title=Dictionary of Germanic antiquities|language=de|volume=10|edition=2nd revised and enlarged|editor-first1=Heinrich|editor-last1=Beck|editor-first2=Dieter|editor-last2=Geuenich|editor-first3=Heiko|editor-last3=Steuer|place=Berlin, Boston|publisher=De Gruyter|pages= |
* The name means 'the powerful ones' ({{lang-lt|galià}} 'power, strength') and also Celtic languages ({{lang-ga|gal}} 'strength', {{lang-cy|gallus}} 'power', ''Galli'', ''Gallia'').<ref>{{cite book|last=Schmid|first=Wolfgang P.|year=1998|chapter=Galinder|trans-chapter=Galindians|title=Reallexikon der germanischen Alterskunde|trans-title=Dictionary of Germanic antiquities|language=de|volume=10|edition=2nd revised and enlarged|editor-first1=Heinrich|editor-last1=Beck|editor-first2=Dieter|editor-last2=Geuenich|editor-first3=Heiko|editor-last3=Steuer|place=Berlin, Boston|publisher=De Gruyter|pages=325–327|isbn=978-3-11-015102-2}}</ref> |
||
==Proposed relation== |
==Proposed relation== |
||
Based on the common name used for the two peoples by ancient authors, some scientists propose a common origin of the two peoples and languages.{{r|Dini|page=309}}<ref>{{cite book|language=pl|chapter=Zagadnienie Galindów|trans-chapter=The Galindian question|title=Studia Historica. W 35-lecia pracy naukowej Henryka Łowmiańskiego|trans-title=Studia Historica. On the 35th jubilee of Henryk Łowmiański's scientific work|editor-first=Aleksander|publisher=Państwowe Wydawn. Naukowe|editor-last=Gieysztor|year=1958|place=Warsaw|pages= |
Based on the common name used for the two peoples by ancient authors, some scientists propose a common origin of the two peoples and languages.{{r|Dini|page=309}}<ref>{{cite book|language=pl|chapter=Zagadnienie Galindów|trans-chapter=The Galindian question|title=Studia Historica. W 35-lecia pracy naukowej Henryka Łowmiańskiego|trans-title=Studia Historica. On the 35th jubilee of Henryk Łowmiański's scientific work|editor-first=Aleksander|publisher=Państwowe Wydawn. Naukowe|editor-last=Gieysztor|year=1958|place=Warsaw|pages=37–41|first=Jan Szczepan|last=Otrębski}}</ref> In order to prove this hypothesis, they investigate common features between Old Prussian/West Galindian and East Galindian.{{r|Dini|pages=309-310}} |
||
== West Galindian== |
== West Galindian== |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
'''East Galindian''' is the poorly attested extinct [[Baltic language]] of the Balts living in the [[Protva]] Basin in present-day [[Russia]].{{r|Dini|page=307}} |
'''East Galindian''' is the poorly attested extinct [[Baltic language]] of the Balts living in the [[Protva]] Basin in present-day [[Russia]].{{r|Dini|page=307}} |
||
===Phonology=== |
===Phonology=== |
||
Based on Baltic substratum and hydronomy in the Protva Basin, the following phonology can be reconstructed:{{r|Dini|pages=311-312}}<ref>{{cite journal|last=Лекомцева|first=Маргарита Ивановна|year=1983|title=Zur phonologischen Rekonstruktion der |
Based on Baltic substratum and hydronomy in the Protva Basin, the following phonology can be reconstructed:{{r|Dini|pages=311-312}}<ref>{{cite journal|last=Лекомцева|first=Маргарита Ивановна|year=1983|title=Zur phonologischen Rekonstruktion der Goljad'-Sprache|language=de|trans-title=On the phonological reconstruction of the Goljad' language|volume=19|issue=2| pages=114–119|journal=Baltistica|publisher=Baltų kalbų tyrinėjimai|place=Vilnius|doi=10.15288/baltistica.19.2.1591|doi-broken-date=2023-04-23 }}</ref> |
||
====Consonants==== |
====Consonants==== |
||
Revision as of 02:43, 23 April 2023
| Galindan | |
|---|---|
| Galindian | |
| Region | North-eastern Poland |
| Extinct | Fourteenth century |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | xgl |
xgl | |
| Glottolog | None |
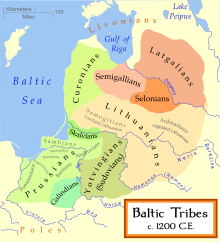
The term Galindian is sometimes ascribed to two separate Baltic languages, both of which were peripheral dialects:
- First, a Western Baltic language referred to as West Galindian; and
- Second, a Baltic language previously spoken in Mozhaysk region (present day Russia), referred to as East Galindian[1]
Name
There are three proposed etymologies for the denomination Galindian:[2]: 308–309
- Proto-Baltic *Galind- meaning 'outsider' (Lithuanian: gãlas 'wall; border').[3] This is supported by the etymology of the common Old Russian term for the Galindians Голядь Goljad' > *golędь > Baltic *Galind-);
- It is derived from the root *gal-/*gil found in Baltic hydronyms;[4][5] and
- The name means 'the powerful ones' (Lithuanian: galià 'power, strength') and also Celtic languages (Irish: gal 'strength', Welsh: gallus 'power', Galli, Gallia).[6]
Proposed relation
Based on the common name used for the two peoples by ancient authors, some scientists propose a common origin of the two peoples and languages.[2]: 309 [7] In order to prove this hypothesis, they investigate common features between Old Prussian/West Galindian and East Galindian.[2]: 309–310
West Galindian
West Galindian is the poorly attested extinct Baltic language of the Galindians previously spoken in what is today northeastern Poland and thought to have been a dialect of Old Prussian,[2]: 290 or a Western Baltic language similar to Old Prussian.[8] There are no extant writings in Galindian.
East Galindian

East Galindian is the poorly attested extinct Baltic language of the Balts living in the Protva Basin in present-day Russia.[2]: 307
Phonology
Based on Baltic substratum and hydronomy in the Protva Basin, the following phonology can be reconstructed:[2]: 311–312 [9]
Consonants
| Labial | Dental/ Alveolar |
Post- alveolar |
Velar | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | pal. | |||||
| Nasal | m | n | nʲ | |||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | tʲ | tʃ | k |
| voiced | b | d | dʲ | ɡ | ||
| Fricative | voiceless | s | ʃ | |||
| voiced | v | z | ʒ | |||
| Trill | r | rʲ | ||||
| Approximant | l | lʲ | j | |||
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| short | long | short | long | short | long | |
| High | i | iː | u | uː | ||
| Mid | eː | oː | ||||
| Mid-low | ɛ | |||||
| Low | a | aː | ||||
Lexicon
There are some Russian words from the Portva Basin region suspected to be Baltisms:[2]: 312
| Russian | Transliteration | Translation | Proposed Baltic cognates |
|---|---|---|---|
| алáня | alánja | 'beer' | Lithuanian: alìnas 'special type of beer', Lithuanian: alùs, Latvian: aliņš |
| кромсáть | kromsát' | 'to break something into pieces' | Lithuanian: kramseti, Latvian: kramstīt |
| нóрот | nórot | 'fishing gear' | Lithuanian: nérti, Latvian: nērt 'to sink' |
| пикýлька | pikúl'ka | 'type of weed' | Lithuanian: pìkulė 'sisymbrium' |
References
- ^ "galindai" [The Galindians]. Visuotinę lietuvių enciklopediją (in Lithuanian). Mokslo ir enciklopedijų leidybos centras. Retrieved 2022-01-28.
- ^ a b c d e f g Dini, Pietro U. (2014). Foundations of Baltic languages. Translated by Richardson, Milda B.; Richardson, Robert E. Vilnius: Vilniaus universitetas. ISBN 978-609-437-263-6.
- ^ Būga, Kazimieras (1924). Lietuvių tauta ir kalba bei jos artimieji giminaičiai [The language and nation of the Lithuanians and its close relatives] (in Lithuanian). Kaunas.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Nalepa, Jerzy (1971). "Próba nowej etymologii nazwy Galindia czyli Golędź" [Proposal of a new etymology of the name Galindia or Golędź]. Opuscula slavica 1. Slaviska och baltiska studier (in Polish). Vol. 9. Lund: Slaviska institutionen vid Lunds universitet. pp. 93–115.
- ^ Mažiulis, Vytautas (1981). Prūsų kalbos paminklai [Monuments of the Prussian language] (in Lithuanian). Vol. II. Vilnius: Mokslas. pp. 318–319.
- ^ Schmid, Wolfgang P. (1998). "Galinder" [Galindians]. In Beck, Heinrich; Geuenich, Dieter; Steuer, Heiko (eds.). Reallexikon der germanischen Alterskunde [Dictionary of Germanic antiquities] (in German). Vol. 10 (2nd revised and enlarged ed.). Berlin, Boston: De Gruyter. pp. 325–327. ISBN 978-3-11-015102-2.
- ^ Otrębski, Jan Szczepan (1958). "Zagadnienie Galindów" [The Galindian question]. In Gieysztor, Aleksander (ed.). Studia Historica. W 35-lecia pracy naukowej Henryka Łowmiańskiego [Studia Historica. On the 35th jubilee of Henryk Łowmiański's scientific work] (in Polish). Warsaw: Państwowe Wydawn. Naukowe. pp. 37–41.
- ^ Tarasov, Iliya (January 2017). "The Balts in the migration period". Istoričeskij Format Исторический Формат (in Russian). 3–4: 95–124.
- ^ Лекомцева, Маргарита Ивановна (1983). "Zur phonologischen Rekonstruktion der Goljad'-Sprache" [On the phonological reconstruction of the Goljad' language]. Baltistica (in German). 19 (2). Vilnius: Baltų kalbų tyrinėjimai: 114–119. doi:10.15288/baltistica.19.2.1591 (inactive 2023-04-23).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of April 2023 (link)