| Capsalidae | |
|---|---|
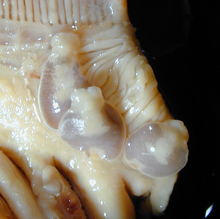
| |
| Lagenivaginopseudobenedenia sp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Monogenea |
| Order: | Capsalidea |
| Family: | Capsalidae Baird, 1853 |
Capsalidae[1][2] is a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, which includes about 200 species.[3]
The monophyly of the Capsalidae is supported by possession of accessory sclerites[3] in the haptor (the posterior attachment organ), and was confirmed by molecular phylogeny.[4] Their oncomiracidium (the free larva) is distinct from that of other families.[5]
Capsalids are parasite on various organs of marine fish (teleosts and elasmobranchs), including skin, fins and gills.[3] Several capsalid species, such a Neobenedenia spp.[6] are pathogenic, especially on maricultured fish.
Included genera[edit]
Genera as recognized in WorMs are listed below. Recent molecular analyses have shown that several genera, which were defined on morphological characters, are not monophyletic.[4]
Menziesia and Nitzschia have their equivalent in the botanical nomenclature: Menziesia (a flowering plant) and Nitzschia (a diatom).
- Allobenedenia Yamaguti, 1963
- Alloencotyllabe Khalil & Abdul-Salam, 1988
- Allomegalocotyla Yamaguti, 1963
- Allometabenedeniella Velasquez, 1982
- Ancyrocotyle Parona & Monticelli, 1903
- Benedenia Diesing, 1858
- Benedeniella Johnston, 1929
- Branchobdella Kearn, Whittington & Evans-Gowing, 2007
- Calicobenedenia Kritsky & Fennessy, 1999
- Capsala Bosc, 1811
- Capsaloides Price, 1936
- Dioncopseudobenedenia Yamaguti, 1965
- Encotyllabe Diesing, 1850
- Entobdella Blainville in Lamarck, 1818
- Interniloculus Suriano & Beverley-Burton, 1979
- Lagenivaginopseudobenedenia Yamaguti, 1966
- Listrocephalos Bullard, Payne & Braswell, 2004
- Macrophyllida Johnston, 1929
- Mediavagina Lawler & Hargis, 1968
- Megalobenedenia Egorova, 1994
- Megalocotyle Folda, 1928
- Menziesia Gibson, 1976
- Metabenedeniella Yamaguti, 1958
- Nasicola Yamaguti, 1968
- Neobenedenia Yamaguti, 1963
- Neobenedeniella Yamaguti, 1963
- Neoentobdella Kearn & Whittington, 2005
- Nitzschia Baer, 1826
- Oligoncobenedenia Yamaguti, 1965
- Pseudoallobenedenia Yamaguti, 1966
- Pseudobenedenia Johnston, 1931
- Pseudobenedeniella Timofeeva, Gaevskaja & Kovaliova, 1987
- Pseudobenedenoides Szidat, 1969
- Pseudoentobdella Yamaguti, 1963
- Pseudomegalocotyla Yamaguti, 1963
- Pseudonitzschia Yamaguti, 1968
- Sessilorbis Mamaev, 1970
- Sprostonia Bychowsky, 1957
- Sprostoniella Bychowsky & Nagibina, 1967
- Tetrasepta Suriano, 1975
- Trilobiodiscus Bychowsky & Nagibina, 1967
- Trimusculotrema Whittington & Barton, 1990
- Tristoma Cuvier, 1817 [7]
- Tristomella Guiart, 1938
- Trochopella Euzet & Trilles, 1962
- Trochopus Diesing, 1850
References[edit]
- ^ Bychowsky, B.E. (1957) Monogenetic Trematodes. Their systematic and phylogeny. Akad. Nauka. USSR. English translation by the American Institute of Biological Science, Washington. 509 pp.doi:10.5962/bhl.title.7475

- ^ Yamaguti, S. (1963) Systema Helminthum IV. Monogenea and Aspidocotylea. London-New York, Interscience Publishers. 699 pp.
- ^ a b c Whittington, I. D. (2004). "The Capsalidae (Monogenea: Monopisthocotylea): a review of diversity, classification and phylogeny with a note about species complexes" (PDF). Folia Parasitologica. 51 (2): 109–122. doi:10.14411/fp.2004.016. PMID 15357390.

- ^ a b Perkins, Elizabeth M.; Donnellan, Steve C.; Bertozzi, Terry; Chisholm, Leslie A.; Whittington, Ian D. (2009). "Looks can deceive: Molecular phylogeny of a family of flatworm ectoparasites (Monogenea: Capsalidae) does not reflect current morphological classification". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 52 (3): 705–714. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2009.05.008. ISSN 1055-7903. PMID 19457457.
- ^ Lambert, A. (2017). "Recherches sur l'oncomiracidium des Capsalidae (Monogenea)". Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée. 53 (4): 351–357. doi:10.1051/parasite/1978534351.

- ^ Orbán, László; Dinh Hoai, Truong; Hutson, Kate S. (2014). "Reproductive strategies of the insidious fish ectoparasite, Neobenedenia sp. (Capsalidae: Monogenea)". PLOS ONE. 9 (9): e108801. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j8801D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0108801. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4181869. PMID 25264931.

- ^ Gastineau, Romain; Bouguerche, Chahinez; Tazerouti, Fadila; Justine, Jean-Lou (2023). "Morphological and molecular characterisation of Tristoma integrum Diesing, 1850 (Monogenea, Capsalidae), including its complete mitogenome". Parasite. 30: 16. doi:10.1051/parasite/2023016. PMID 37191588.
