wikilink |
This is not "nearly a stub" |
||
| (122 intermediate revisions by 79 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Region of Montana}}{{for|the college|University of Montana Western}} |
|||
{{More citations needed|date=September 2023}} |
|||
[[File:Montana Relief 1.jpg|right|thumb|300px|'''Mountainous Western Montana''']] |
|||
'''Western Montana''' is the western region of the [[U.S. state]] of [[Montana]]. The most restrictive definition limits western Montana only to the parts of the state west of the [[Continental Divide]]. Other common definitions add in the mountainous areas east of the divide including [[Beaverhead County, Montana|Beaverhead]], [[Gallatin County, Montana|Gallatin]], [[Jefferson County, Montana|Jefferson]], [[Lewis and Clark County, Montana|Lewis and Clark]], [[Madison County, Montana|Madison]], and [[Park County, Montana|Park]] Counties.{{citation needed|date=January 2015}} The region is sometimes considered to be part of the [[Inland Northwest]]. |
|||
==Geography, biomes and climate== |
|||
'''Western Montana''' is the western region of the state of [[Montana]], United States. Western Montana is usually considered to be administered by the Missoulian, and the city of Missoula; Billings western counter-part. |
|||
[[File:St Mary Lake.jpg|thumb|300px|[[Glacier National Park (U.S.)|Glacier National Park]] is located in Western Montana along the [[Canada–United States border|Canada–US border]]]] |
|||
Western Montana is dominated by the [[Rocky Mountains]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.destination360.com/north-america/us/montana/rocky-mountains |title=Montana Rockies - Rocky Mountains in Montana |publisher=Destination360.com |access-date=2014-06-15}}</ref> Most of Western Montana is covered in forest, prominent species being [[Ponderosa pine]], [[aspen]], and [[Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir]]. |
|||
Western Montana encompasses approximately the western third of the state roughly on a dividing line running north from [[Yellowstone National Park]] through [[Helena, Montana|Helena]] and [[Browning, Montana|Browning]] to the [[Canada|Canadian]] border. It includes the mountainous parts of Montana, including the [[Continental divide]] and the eastern slope of the [[Rocky Mountains]]. It also includes [[Glacier National Park (U.S.)|Glacier National Park]], the [[Bob Marshall Wilderness Area]], [[Flathead Lake]], [[Anaconda, Montana|Anaconda]], [[Butte, Montana|Butte]], [[Missoula, Montana|Missoula]], [[Kalispell, Montana|Kalispell]], [[Hamilton, Montana|Hamilton]], and [[Whitefish, Montana|Whitefish]].'' |
|||
Common fauna include the [[American black bear|black bear]], [[moose]], [[elk]], and [[coyote]]. The [[grizzly bear]] lives in [[Glacier National Park (U.S.)|Glacier National Park]], [[Yellowstone National Park]], the [[Bob Marshall Wilderness]] and surrounding areas.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bigskyfishing.com/National_parks/glacier/bears.shtm |title=Grizzly Bears in Glacier National Park |publisher=Bigskyfishing.com |access-date=2014-06-15}}</ref> |
|||
It also includes the following counties: [[Lincoln County, Montana|Lincoln]], [[Flathead County, Montana|Flathead]], [[Sanders County, Montana|Sanders]], [[Missoula County, Montana|Missoula]], [[Lake County, Montana|Lake]], [[Ravalli County, Montana|Ravalli]], [[Pondera County, Montana|Pondera]], [[Deer Lodge County, Montana|Deer Lodge]], [[Powell County, Montana|Powell]], [[Silver Bow County, Montana|Silver Bow]], [[Gallatin County, Montana|Gallatin]], [[Mineral County, Montana|Mineral]], [[Teton County, Montana|Teton]], [[Glacier County, Montana|Glacier]], [[Jefferson County, Montana|Jefferson]], [[Granite County, Montana|Granite]], [[Broadwater County, Montana|Broadwater]], [[Madison County, Montana|Madison]], Beaverhead County, and [[Lewis and Clark County, Montana|Lewis and Clark]]. The estimated population according to the US Census Bureau as of 2004 was 510,366 out of Montana's total estimated population of 926,865. One of Montana's smallest communities, Saltese (pop. 30), is located at |
|||
I-90's Exit 10, just east of the Idaho border and Lookout Pass Ski |
|||
Area. |
|||
[[Missoula, Montana|Missoula]], [[Helena, Montana|Helena]], [[Butte, Montana|Butte]], [[Kalispell, Montana|Kalispell]], and usually [[Bozeman, Montana|Bozeman]] are considered part of Western Montana. |
|||
Precipitation is lower in the valleys, which are mostly [[semiarid]] and receive 8 to 25 inches of precipitation, largely in [[snow]], and higher in the mountains, some areas of which qualify as [[temperate rainforest]], especially in the northwest around Glacier National Park and [[Libby, Montana|Libby]]. Winters are cold, sometimes bitterly cold, and summers are warm. |
|||
[[Great Falls, Montana|Great Falls]], while technically in the western half of the state, is usually considered to be part of [[Eastern Montana]] because it is east of the [[Rocky Mountains]] and is geographically and culturally similar to the eastern half of the state. |
|||
==History== |
|||
Western Montana was inhabited by the [[Coast Salish peoples|Salish]], [[Kootenays|Kootenai]], [[Shoshone]], [[Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes of the Flathead Nation|Flathead]], and [[Pend d'Oreilles (tribe)|Kalispel]] people.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.native-languages.org/montana.htm |title=Montana Indian Tribes and Languages |publisher=Native-languages.org |access-date=2014-06-15}}</ref> In the late 19th century non-indigenous people arrived and established mines and additional cities in the mountains and valleys. |
|||
Gold was discovered in Last Chance Gulch in the 1860s and soon the city of Helena was born.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.westernmininghistory.com/towns/montana/helena/ |title=Helena, Montana |publisher=Westernmininghistory.com |access-date=2014-06-15}}</ref> Today Helena is the State capital of Montana. Helena still has much of the charm of a 19th-century mining town. Many of the old buildings have been renovated, and hundreds of 19th-century Victorian homes and mansions fill Helena's old neighborhoods. Helena is one of the best-preserved mining towns on the Western frontier. Copper was discovered In [[Butte, Montana|Butte]] and the surrounding areas in the 1870s. Vast quantities of [[copper]] were mined, leaving behind the largest [[Superfund]] cleanup site in the history of the nation.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bigskyfishing.com/Montana-Info/butte_mt-2.shtm |title=Butte History : A Short History of Butte, Montana |publisher=Bigskyfishing.com |access-date=2014-06-15}}</ref> Copper is still mined at the continental pit in Butte. [[Missoula]] is the largest city in Western Montana and the second-largest in the state after [[Billings, Montana|Billings]]. |
|||
Western Montana, though faring better than much of the nation, was the portion of the state hit hardest by the current economic downturn.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://missoulian.com/mobile/article_f0444dba-08ac-11df-a3cc-001cc4c002e0.html |title=Economy has Missoula County officials worried about back taxes |publisher=Missoulian.com |date=2010-01-24 |access-date=2014-06-15}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|author=BETSY COHEN of the Missoulian |url=http://missoulian.com/news/local/article_09e8183a-dd89-11df-a8c1-001cc4c002e0.html |title=MAEDC: Missoula economic development organization lays off 2 |publisher=Missoulian.com |date=2010-10-22 |access-date=2014-06-15}}</ref> The closing of [[Smurfit-Stone Container]] in 2009 alone caused the loss of over 2000 jobs through 2012.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.kaj18.com/news/economic-effects-of-smurfit-stone-closure-still-being-felt/#!prettyPhoto/0/ |title=Economic effects of Smurfit Stone closure still being felt | KAJ18.com | Kalispell, Montana |publisher=KAJ18.com |date=2010-11-24 |access-date=2014-06-15}}</ref> Much of western Montana has felt the effects of a housing bust as well.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bozemandailychronicle.com/news/article_dc20cf12-a027-11df-beeb-001cc4c03286.html |title=Economists predict modest growth in Gallatin County; construction industry still depressed - Bozeman Daily Chronicle: News |publisher=Bozeman Daily Chronicle |date=2010-08-05 |access-date=2014-06-15}}</ref> |
|||
==Major cities== |
|||
*[[Missoula, Montana]] |
|||
*[[Butte, Montana]] |
|||
*[[Kalispell, Montana]] |
|||
*[[Bozeman, Montana]] |
|||
==See also== |
|||
*[[North Idaho]] |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
{{Montana}} |
{{Montana}} |
||
[[Category:Regions of Montana]] |
[[Category:Regions of Montana]] |
||
{{Montana-geo-stub}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 18:45, 2 September 2023
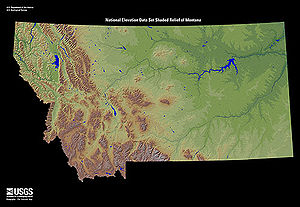
Western Montana is the western region of the U.S. state of Montana. The most restrictive definition limits western Montana only to the parts of the state west of the Continental Divide. Other common definitions add in the mountainous areas east of the divide including Beaverhead, Gallatin, Jefferson, Lewis and Clark, Madison, and Park Counties.[citation needed] The region is sometimes considered to be part of the Inland Northwest.
Geography, biomes and climate[edit]

Western Montana is dominated by the Rocky Mountains.[1] Most of Western Montana is covered in forest, prominent species being Ponderosa pine, aspen, and Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir.
Common fauna include the black bear, moose, elk, and coyote. The grizzly bear lives in Glacier National Park, Yellowstone National Park, the Bob Marshall Wilderness and surrounding areas.[2]
Precipitation is lower in the valleys, which are mostly semiarid and receive 8 to 25 inches of precipitation, largely in snow, and higher in the mountains, some areas of which qualify as temperate rainforest, especially in the northwest around Glacier National Park and Libby. Winters are cold, sometimes bitterly cold, and summers are warm.
History[edit]
Western Montana was inhabited by the Salish, Kootenai, Shoshone, Flathead, and Kalispel people.[3] In the late 19th century non-indigenous people arrived and established mines and additional cities in the mountains and valleys.
Gold was discovered in Last Chance Gulch in the 1860s and soon the city of Helena was born.[4] Today Helena is the State capital of Montana. Helena still has much of the charm of a 19th-century mining town. Many of the old buildings have been renovated, and hundreds of 19th-century Victorian homes and mansions fill Helena's old neighborhoods. Helena is one of the best-preserved mining towns on the Western frontier. Copper was discovered In Butte and the surrounding areas in the 1870s. Vast quantities of copper were mined, leaving behind the largest Superfund cleanup site in the history of the nation.[5] Copper is still mined at the continental pit in Butte. Missoula is the largest city in Western Montana and the second-largest in the state after Billings.
Western Montana, though faring better than much of the nation, was the portion of the state hit hardest by the current economic downturn.[6][7] The closing of Smurfit-Stone Container in 2009 alone caused the loss of over 2000 jobs through 2012.[8] Much of western Montana has felt the effects of a housing bust as well.[9]
Major cities[edit]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "Montana Rockies - Rocky Mountains in Montana". Destination360.com. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ^ "Grizzly Bears in Glacier National Park". Bigskyfishing.com. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ^ "Montana Indian Tribes and Languages". Native-languages.org. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ^ "Helena, Montana". Westernmininghistory.com. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ^ "Butte History : A Short History of Butte, Montana". Bigskyfishing.com. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ^ "Economy has Missoula County officials worried about back taxes". Missoulian.com. 2010-01-24. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ^ BETSY COHEN of the Missoulian (2010-10-22). "MAEDC: Missoula economic development organization lays off 2". Missoulian.com. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ^ "Economic effects of Smurfit Stone closure still being felt | KAJ18.com | Kalispell, Montana". KAJ18.com. 2010-11-24. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ^ "Economists predict modest growth in Gallatin County; construction industry still depressed - Bozeman Daily Chronicle: News". Bozeman Daily Chronicle. 2010-08-05. Retrieved 2014-06-15.