Tigerbreath13 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Altaileopard (talk | contribs) Fauna of categories deleted |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Taxobox |
{{Taxobox |
||
| status = EN |
| status = EN |
||
| Fossil range: Early [[Pleistocene]] to Recent |
|||
| status_system = iucn2.3 |
| status_system = iucn2.3 |
||
| trend = down |
| trend = down |
||
| Line 52: | Line 51: | ||
[[Image:Tiger Bandavgarh adjusted levels.jpg|thumb|right|[[Bengal tiger]]]] |
[[Image:Tiger Bandavgarh adjusted levels.jpg|thumb|right|[[Bengal tiger]]]] |
||
*The '''[[Bengal Tiger|Bengal tiger]]''' or the '''Royal Bengal tiger''' (''Panthera tigris tigris'') is found in parts of [[India]], [[Bangladesh]], [[Nepal]], [[Bhutan]], and [[Burma]]. It lives in varied habitats: grasslands, subtropical and tropical rainforests, scrub forests, wet and dry deciduous forests, and mangroves. While conservationists already believed the population to be below 2,000,<ref>[http://www.indianjungles.com/090805d.htm Task force says tigers under siege]</ref> the most recent audit by the Indian Government's [[National Tiger Conservation Authority]] has estimated the number at just 1,411 wild tigers (1165-1657 allowing for [[Errors and residuals in statistics|statistical error]]), a drop of 60% in the past decade.<ref>{{citation | last=Wade | first=Matt | author-link=Matt Wade | title=Threat to a national symbol as India's wild tigers vanish | newspaper=The Age (Melbourne) | date=[[February 15]], [[2008]] | pages=9}}</ref> Since 1972, there has been a massive wildlife conservation project, known as [[Project Tiger]], to protect the Bengal tiger. The project is considered as one of the most successful wildlife conservation programs{{fact|date=April 2008}}, though at least one Tiger Reserve ([[Sariska Tiger Reserve]]) has lost its entire tiger population to poaching.<ref>{{cite web |title=No tigers found in Sariska: CBI |publisher=DeccanHerald.com |url=http://web.archive.org/web/20070210220826/http://www.deccanherald.com/deccanherald/apr112005/national130442005410.asp |accessdate=2007-07-20 }} (Archive).</ref> |
*The '''[[Bengal Tiger|Bengal tiger]]''' or the '''Royal Bengal tiger''' (''Panthera tigris tigris'') is found in parts of [[India]], [[Bangladesh]], [[Nepal]], [[Bhutan]], and [[Burma]]. It lives in varied habitats: grasslands, subtropical and tropical rainforests, scrub forests, wet and dry deciduous forests, and mangroves. Males in the wild usually weigh 205 to 227 kg (450–500 lb), while the average female will weigh about 141 kg.<ref>Sunquist, Mel and Fiona Sunquist. 2002. Wild Cats of the World. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago</ref> However, the northern Indian and the Nepalese Bengal tigers are somewhat bulkier than those found in the south of the Indian Subcontinent, with males averaging around 236 kg (520 lb).<ref>Sunquist, Mel and Fiona Sunquist. 2002. Wild Cats of the World. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago</ref> While conservationists already believed the population to be below 2,000,<ref>[http://www.indianjungles.com/090805d.htm Task force says tigers under siege]</ref> the most recent audit by the Indian Government's [[National Tiger Conservation Authority]] has estimated the number at just 1,411 wild tigers (1165-1657 allowing for [[Errors and residuals in statistics|statistical error]]), a drop of 60% in the past decade.<ref>{{citation | last=Wade | first=Matt | author-link=Matt Wade | title=Threat to a national symbol as India's wild tigers vanish | newspaper=The Age (Melbourne) | date=[[February 15]], [[2008]] | pages=9}}</ref> Since 1972, there has been a massive wildlife conservation project, known as [[Project Tiger]], to protect the Bengal tiger. The project is considered as one of the most successful wildlife conservation programs{{fact|date=April 2008}}, though at least one Tiger Reserve ([[Sariska Tiger Reserve]]) has lost its entire tiger population to poaching.<ref>{{cite web |title=No tigers found in Sariska: CBI |publisher=DeccanHerald.com |url=http://web.archive.org/web/20070210220826/http://www.deccanherald.com/deccanherald/apr112005/national130442005410.asp |accessdate=2007-07-20 }} (Archive).</ref> |
||
[[Image:Tiger 032.jpg|thumb|right|Indochinese tiger]] |
[[Image:Tiger 032.jpg|thumb|right|Indochinese tiger]] |
||
*The '''[[Indochinese Tiger|Indochinese tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris corbetti''), also called ''Corbett's'' tiger, is found in [[Cambodia]], China, [[Laos]], [[Burma]], [[Thailand]], and [[Vietnam]]. Their preferred habitat is forests in mountainous or hilly regions. Estimates of the Indochinese tiger population vary between 1,200 to 1,800, with only several hundred left in the wild. The largest current population is in Malaysia, where illegal [[poaching]] is strictly controlled, but all existing populations are at extreme risk from [[habitat fragmentation]] and [[inbreeding]]. In Vietnam, almost three-quarters of the tigers killed provide stock for Chinese pharmacies. |
*The '''[[Indochinese Tiger|Indochinese tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris corbetti''), also called ''Corbett's'' tiger, is found in [[Cambodia]], China, [[Laos]], [[Burma]], [[Thailand]], and [[Vietnam]]. These tigers are smaller and darker than Bengal tigers: Males weigh from 150–190 kg (330–420 lb) while females are smaller at 110–140 kg (242–308 lb). Their preferred habitat is forests in mountainous or hilly regions. Estimates of the Indochinese tiger population vary between 1,200 to 1,800, with only several hundred left in the wild. The largest current population is in Malaysia, where illegal [[poaching]] is strictly controlled, but all existing populations are at extreme risk from [[habitat fragmentation]] and [[inbreeding]]. In Vietnam, almost three-quarters of the tigers killed provide stock for Chinese pharmacies. |
||
*The '''[[Malayan Tiger|Malayan tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris malayensis''), exclusively found in the southern part of the [[Malay Peninsula]], was not considered a subspecies in its own right until 2004. The new classification came about after a study by Luo et al. from the [[Laboratory of Genomic Diversity]] Study,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://home.ncifcrf.gov/ccr/lgd/|title=Laboratory of Genomic Diversity LGD}}</ref> part of the [[National Cancer Institute]] of the United States. Recent counts showed there are 600–800 tigers in the wild, making it the third largest tiger population, behind the Bengal tiger and the Indochinese tiger. The Malayan tiger is a national icon in Malaysia, appearing on its [[Emblem of Malaysia|coat of arms]] and in logos of Malaysian institutions, such as [[Maybank]]. |
*The '''[[Malayan Tiger|Malayan tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris malayensis''), exclusively found in the southern part of the [[Malay Peninsula]], was not considered a subspecies in its own right until 2004. The new classification came about after a study by Luo et al. from the [[Laboratory of Genomic Diversity]] Study,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://home.ncifcrf.gov/ccr/lgd/|title=Laboratory of Genomic Diversity LGD}}</ref> part of the [[National Cancer Institute]] of the United States. Recent counts showed there are 600–800 tigers in the wild, making it the third largest tiger population, behind the Bengal tiger and the Indochinese tiger. The Malayan tiger is the smallest of the mainland tiger subspecies, and the second smallest living subspecies, with males averaging about 120 kg and females about 100 kg in weight. The Malayan tiger is a national icon in Malaysia, appearing on its [[Emblem of Malaysia|coat of arms]] and in logos of Malaysian institutions, such as [[Maybank]]. |
||
[[Image:Panthera tigris sumatran subspecies.jpg|thumb|right|Sumatran tiger]] |
[[Image:Panthera tigris sumatran subspecies.jpg|thumb|right|Sumatran tiger]] |
||
*The '''[[Sumatran Tiger|Sumatran tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris sumatrae'') is found only on the Indonesian island of [[Sumatra]], and is [[Critically endangered species|critically endangered]].<ref>{{IUCN2006|assessors=Cat Specialist Group|year=1996|id=15966|title=Panthera tigris ssp. sumatrae|downloaded=11 May 2006}} Database entry includes a brief justification of why this subspecies is critically endangered and the criteria used.</ref> It is the smallest of all living tiger subspecies. Their small size is an adaptation to the thick, dense forests of the Sumatra island where they reside, as well as the smaller-sized prey. The wild population is estimated at between 400 and 500, seen chiefly in the island's [[List of national parks of Indonesia|national parks]]. Recent genetic testing has revealed the presence of unique genetic markers, indicating that it may develop into a separate species,{{specify|date=July 2008}}<!--ANY population (regardless of "unique genetic markers"), isolated or not (cf. sympatric speciation), may evolve into another species if given enough time --> if it does not go extinct.<ref>Cracraft J., Feinstein J., Vaughn J., Helm-Bychowski K. (1998) Sorting out tigers (Panthera tigris) Mitochondrial sequences, nuclear inserts, systematics, and conservation genetics. Animal Conservation 1: 139–150.</ref> This has led to suggestions that Sumatran tigers should have greater priority for conservation than any other subspecies. While [[Habitat destruction]] is the main threat to the existing tiger population (logging continues even in the supposedly protected national parks), 66 tigers were recorded as being shot and killed between 1998 and 2000, or nearly 20% of the total population. |
*The '''[[Sumatran Tiger|Sumatran tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris sumatrae'') is found only on the Indonesian island of [[Sumatra]], and is [[Critically endangered species|critically endangered]].<ref>{{IUCN2006|assessors=Cat Specialist Group|year=1996|id=15966|title=Panthera tigris ssp. sumatrae|downloaded=11 May 2006}} Database entry includes a brief justification of why this subspecies is critically endangered and the criteria used.</ref> It is the smallest of all living tiger subspecies, with adult males weighing between 100–130 kg (220–286 lb) and females 70–90 kg (154–198 lb). Their small size is an adaptation to the thick, dense forests of the Sumatra island where they reside, as well as the smaller-sized prey. The wild population is estimated at between 400 and 500, seen chiefly in the island's [[List of national parks of Indonesia|national parks]]. Recent genetic testing has revealed the presence of unique genetic markers, indicating that it may develop into a separate species,{{specify|date=July 2008}}<!--ANY population (regardless of "unique genetic markers"), isolated or not (cf. sympatric speciation), may evolve into another species if given enough time --> if it does not go extinct.<ref>Cracraft J., Feinstein J., Vaughn J., Helm-Bychowski K. (1998) Sorting out tigers (Panthera tigris) Mitochondrial sequences, nuclear inserts, systematics, and conservation genetics. Animal Conservation 1: 139–150.</ref> This has led to suggestions that Sumatran tigers should have greater priority for conservation than any other subspecies. While [[Habitat destruction]] is the main threat to the existing tiger population (logging continues even in the supposedly protected national parks), 66 tigers were recorded as being shot and killed between 1998 and 2000, or nearly 20% of the total population. |
||
[[Image:Tiger in the snow at the Detroit Zoo March 2008 pic 2.jpg|thumb|right|Siberian Tiger]] |
[[Image:Tiger in the snow at the Detroit Zoo March 2008 pic 2.jpg|thumb|right|Siberian Tiger]] |
||
*The '''[[Siberian Tiger|Siberian tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris altaica''), also known as the ''Amur'', ''Manchurian'', ''Altaic'', ''Korean'' or ''North China'' tiger, is confined to the [[Amur River|Amur]]-[[Ussuri River|Ussuri]] region of [[Primorsky Krai]] and [[Khabarovsk Krai]] in far eastern [[Siberia]], where it is now protected. The last two censuses (1996 and 2005) found 450–500 Amur tigers within their single, and more or less continuous, range making it one of the largest undivided tiger populations in the world. |
*The '''[[Siberian Tiger|Siberian tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris altaica''), also known as the ''Amur'', ''Manchurian'', ''Altaic'', ''Korean'' or ''North China'' tiger, is confined to the [[Amur River|Amur]]-[[Ussuri River|Ussuri]] region of [[Primorsky Krai]] and [[Khabarovsk Krai]] in far eastern [[Siberia]], where it is now protected. Considered the largest subspecies, with an average weight of around 227 kg (500 lb) for males,<ref>Sunquist, Mel and Fiona Sunquist. 2002. Wild Cats of the World. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago</ref> the Amur tiger is also noted for its thick coat, distinguished by a paler golden hue and fewer stripes. A six-month old Siberian tiger can be as big as a fully grown [[leopard]]. The last two censuses (1996 and 2005) found 450–500 Amur tigers within their single, and more or less continuous, range making it one of the largest undivided tiger populations in the world. |
||
*The '''[[South China Tiger|South China tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris amoyensis''), also known as the ''Amoy'' or ''Xiamen'' tiger, is the most critically endangered subspecies of tiger and is listed as one of the 10 most endangered species in the world.<ref> [http://www.china.org.cn/english/China/217122.htm www.china.org.cn] Retrieved on 6 October 2007</ref>{{clarifyme|10 most endangered species, or most endangered subspecies?}} It will almost certainly become extinct.{{fact|date=April 2008}} From 1983 to 2007, no South China tigers were sighted.<ref name="xinhua">[http://news.xinhuanet.com/newscenter/2007-10/13/content_6873252.htm 绝迹24年华南虎重现陕西 村民冒险拍下照片<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> In 2007 a farmer spotted a tiger and handed in photographs to the authorities as proof.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/7042257.stm BBC NEWS | World | Asia-Pacific | Rare China tiger seen in the wild<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref><ref name="xinhua"/> In 1977, the Chinese government passed a law banning the killing of wild tigers, but this may have been too late to save the subspecies. There are currently 59 known captive South China tigers, all within China, but these are known to be descended from only six animals. Thus, the [[genetic diversity]] required to maintain the subspecies may no longer exist. Currently, there are breeding efforts to reintroduce these tigers to the wild by 2008. |
*The '''[[South China Tiger|South China tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris amoyensis''), also known as the ''Amoy'' or ''Xiamen'' tiger, is the most critically endangered subspecies of tiger and is listed as one of the 10 most endangered species in the world.<ref> [http://www.china.org.cn/english/China/217122.htm www.china.org.cn] Retrieved on 6 October 2007</ref>{{clarifyme|10 most endangered species, or most endangered subspecies?}} It will almost certainly become extinct.{{fact|date=April 2008}} One of the smaller tiger subspecies, the length of the South China tiger ranges from 2.2–2.6 m (87–104 in) for both males and females. Males weigh between 127 and 177 kg (280–390 lb) while females weigh between 100 and 118 kg (220–260 lb). From 1983 to 2007, no South China tigers were sighted.<ref name="xinhua">[http://news.xinhuanet.com/newscenter/2007-10/13/content_6873252.htm 绝迹24年华南虎重现陕西 村民冒险拍下照片<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> In 2007 a farmer spotted a tiger and handed in photographs to the authorities as proof.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/7042257.stm BBC NEWS | World | Asia-Pacific | Rare China tiger seen in the wild<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref><ref name="xinhua"/> In 1977, the Chinese government passed a law banning the killing of wild tigers, but this may have been too late to save the subspecies. There are currently 59 known captive South China tigers, all within China, but these are known to be descended from only six animals. Thus, the [[genetic diversity]] required to maintain the subspecies may no longer exist. Currently, there are breeding efforts to reintroduce these tigers to the wild by 2008. |
||
===Extinct subspecies=== |
===Extinct subspecies=== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
*The '''[[Bali Tiger|Balinese tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris balica'') was limited to the island of [[Bali]]. These tigers were hunted to extinction—the last Balinese tiger is thought to have been killed at Sumbar Kima, West Bali on [[27 September]] [[1937]]; this was an adult female. No Balinese tiger was ever held in captivity. The tiger still plays an important role in Balinese [[hinduism|Hindu]] religion. |
*The '''[[Bali Tiger|Balinese tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris balica'') was limited to the island of [[Bali]]. These tigers were hunted to extinction—the last Balinese tiger is thought to have been killed at Sumbar Kima, West Bali on [[27 September]] [[1937]]; this was an adult female. No Balinese tiger was ever held in captivity. The tiger still plays an important role in Balinese [[hinduism|Hindu]] religion. |
||
*The '''[[Javan Tiger|Javan tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris sondaica'') was limited to the Indonesian island of [[Java]]. It now seems likely that this subspecies became extinct in the 1980s, as a result of hunting and habitat destruction, but the extinction of this subspecies was extremely probable from the 1950s onwards (when it is thought that fewer than 25 tigers remained in the wild). The last confirmed specimen was sighted in 1979, but there were a few reported sightings during the 1990s.<ref>[http://www.thejakartapost.com/yesterdaydetail.asp?fileid=20021030.S03 Bambang M. 2002. In search of 'extinct' Javan tiger. The Jakarta Post (October 30).]</ref><ref>[http://www.javantiger.or.id Harimau jawa belum punah! (Indonesian Javan Tiger website)]</ref> |
*The '''[[Javan Tiger|Javan tiger]]''' (''Panthera tigris sondaica'') was limited to the Indonesian island of [[Java]]. It now seems likely that this subspecies became extinct in the 1980s, as a result of hunting and habitat destruction, but the extinction of this subspecies was extremely probable from the 1950s onwards (when it is thought that fewer than 25 tigers remained in the wild). The last confirmed specimen was sighted in 1979, but there were a few reported sightings during the 1990s.<ref>[http://www.thejakartapost.com/yesterdaydetail.asp?fileid=20021030.S03 Bambang M. 2002. In search of 'extinct' Javan tiger. The Jakarta Post (October 30).]</ref><ref>[http://www.javantiger.or.id Harimau jawa belum punah! (Indonesian Javan Tiger website)]</ref> |
||
[[Image:Panthera tigris virgata.jpg|right|thumb|180px|Caspian tiger]] |
[[Image:Panthera tigris virgata.jpg|right|thumb|180px|Caspian tiger]] |
||
*The '''[[Caspian Tiger|Caspian tiger]]''' or '''Persian tiger''' (''Panthera tigris virgata'') appears to have become extinct in the wild in the late 1950s,<ref name="casp">{{citeweb|url=http://www.tigerhomes.org/animal/curriculums/caspian-tiger-pc.cfm|title=The Caspian Tiger - ''Panthera tigris virgata''|accessmonthday=12 October|accessyear=2007}}</ref><ref name="casp2">{{citeweb|url=http://www.lairweb.org.nz/tiger/caspian.html|title=The Caspian Tiger at www.lairweb.org.nz|accessmonthday=12 October|accessyear=2007}}</ref> with the last reliable sighting in 1968, though it is thought that such a tiger was last shot dead in the south-eastern-most part of Turkey in 1970. Historically, it ranged through [[Afghanistan]], [[Iran]], [[Iraq]], [[Pakistan]], the former [[Soviet Union]], and [[Turkey]].<ref name="casp" /> The Caspian tiger was a large subspecies and reached nearly the dimensions of the Bengal Tiger. The Caspian tiger was one of two subspecies of tiger (along with the Bengal) that was used by the Romans to battle [[gladiator]]s and other animals, including the [[Barbary Lion]]. The Romans traveled far to capture exotic beasts for the arena. There are still occasional reported sightings of the Caspian Tiger in the wild.<ref name="casp2" /> |
*The '''[[Caspian Tiger|Caspian tiger]]''' or '''Persian tiger''' (''Panthera tigris virgata'') appears to have become extinct in the wild in the late 1950s,<ref name="casp">{{citeweb|url=http://www.tigerhomes.org/animal/curriculums/caspian-tiger-pc.cfm|title=The Caspian Tiger - ''Panthera tigris virgata''|accessmonthday=12 October|accessyear=2007}}</ref><ref name="casp2">{{citeweb|url=http://www.lairweb.org.nz/tiger/caspian.html|title=The Caspian Tiger at www.lairweb.org.nz|accessmonthday=12 October|accessyear=2007}}</ref> with the last reliable sighting in 1968, though it is thought that such a tiger was last shot dead in the south-eastern-most part of Turkey in 1970. Historically, it ranged through [[Afghanistan]], [[Iran]], [[Iraq]], [[Pakistan]], the former [[Soviet Union]], and [[Turkey]].<ref name="casp" /> The Caspian tiger was a large subspecies and reached nearly the dimensions of the Bengal Tiger. The heaviest confirmed weight of a male was 240 kg. The ground colour was comparable to that of the Indian subspecies, but differed especially in the tight, narrow, striping pattern. The stripes were dark grey or brown, rather than black. Especially during the winter, the fur was relatively long. The Caspian tiger was one of two subspecies of tiger (along with the Bengal) that was used by the Romans to battle [[gladiator]]s and other animals, including the [[Barbary Lion]]. The Romans traveled far to capture exotic beasts for the arena. There are still occasional reported sightings of the Caspian Tiger in the wild.<ref name="casp2" /> |
||
===Hybrids=== |
===Hybrids=== |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
===Physical characteristics=== |
===Physical characteristics=== |
||
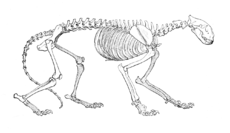
[[Image:TigerSkelLyd1.png|thumb|left|230px|Skeleton]] |
[[Image:TigerSkelLyd1.png|thumb|left|230px|Skeleton]] |
||
Tigers are the heaviest cats found in the wild,<ref name="WWF">{{cite web|url= http://www.worldwildlife.org/tigers/ecology.m|title=WWF – Tigers – Ecology}}</ref> but the subspecies differ markedly in size, tending to increase proportionally with [[latitude]], as predicted by [[Bergmann's Rule]]. The heaviest wild Siberian tiger on record weighed in at 384 kg,<ref>Graham Batemann: ''Die Tiere unserer Welt Raubtiere'', Deutsche Ausgabe: Bertelsmann Verlag, 1986. <!-- Clubausgabe hatte keine ISBN --></ref> but according to Mazak these giants are not confirmed via reliable references.<ref name = "der-tiger"/> Females are smaller |
Tigers are the heaviest cats found in the wild,<ref name="WWF">{{cite web|url= http://www.worldwildlife.org/tigers/ecology.m|title=WWF – Tigers – Ecology}}</ref> but the subspecies differ markedly in size, tending to increase proportionally with [[latitude]], as predicted by [[Bergmann's Rule]]. Large male [[Siberian Tiger]]s (''Panthera tigris altaica'') can reach a total length of 3.5 m and a weight of 306 kilograms.<ref name="der-tiger">{{de icon}} Vratislav Mazak: ''Der Tiger''. Nachdruck der 3. Auflage von 1983. Westarp Wissenschaften Hohenwarsleben, 2004 ISBN 3 894327596</ref> Apart from those exceptional large individuals, male Siberian tigers usually have a head and body length of 190–220 cm and an average weight of 227 kg<ref>Sunquist, Mel and Fiona Sunquist. 2002. Wild Cats of the World. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago.</ref> (the tail of a tiger is 60–110 cm long). The heaviest wild Siberian tiger on record weighed in at 384 kg,<ref>Graham Batemann: ''Die Tiere unserer Welt Raubtiere'', Deutsche Ausgabe: Bertelsmann Verlag, 1986. <!-- Clubausgabe hatte keine ISBN --></ref> but according to Mazak these giants are not confirmed via reliable references.<ref name = "der-tiger"/> Females are smaller - the size difference between male and female tigers tends to be more pronounced in the larger subspecies of tiger, with males weighing up to 1.7 times as much as the females<ref>Matthiessen, Peter. 2000. Tigers in the Snow, p. 47. The Harvill Press, London.</ref>. Consequently, females of the Siberian and Bengal subspecies weigh only between 100 and 181 kg. Island-dwelling tigers, such as the Sumatran subspecies, are much smaller than mainland tigers, with males usually weighing only 100–140 kg and females 75–110 kg. The extinct [[Bali Tiger]] was even smaller, with a weight of 90–100 kg in males and 65–80 kg in females.<ref name="der-tiger"/> |
||
Tigers have rusty-reddish to brown-rusty coats, a whitish medial and ventral area, and stripes that vary from brown or gray to pure black. The form and density of stripes differs between subspecies, but most tigers have over 100 stripes. The pattern of stripes is unique to each animal, and thus could potentially be used to identify individuals, much in the same way as [[fingerprint]]s are used to identify people. This is not, however, a preferred method of identification, due to the difficulty of recording the stripe pattern of a wild tiger. It seems likely that the function of stripes is [[camouflage]], serving to hide these animals from their prey. The stripe pattern is found on a tiger's skin and if shaved, its distinctive camouflage pattern would be preserved. Male tigers have wider forepaw pads than females. This difference is often used by biologists in determining the gender of tigers when observing their tracks.<ref name = "Tigersnow"/> |
Tigers have rusty-reddish to brown-rusty coats, a whitish medial and ventral area, and stripes that vary from brown or gray to pure black. The form and density of stripes differs between subspecies, but most tigers have over 100 stripes. The pattern of stripes is unique to each animal, and thus could potentially be used to identify individuals, much in the same way as [[fingerprint]]s are used to identify people. This is not, however, a preferred method of identification, due to the difficulty of recording the stripe pattern of a wild tiger. It seems likely that the function of stripes is [[camouflage]], serving to hide these animals from their prey. The stripe pattern is found on a tiger's skin and if shaved, its distinctive camouflage pattern would be preserved. Male tigers have wider forepaw pads than females. This difference is often used by biologists in determining the gender of tigers when observing their tracks.<ref name = "Tigersnow"/> |
||
Like most cats, tigers are believed to have some degree of [[color vision]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.buschgardens.org/infobooks/Tiger/sensetiger.html|title=Tigers: Senses |publisher=Busch Gardens Animal Information Database|accessdate=2006-06-22 }}</ref> |
Like most cats, tigers are believed to have some degree of [[color vision]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.buschgardens.org/infobooks/Tiger/sensetiger.html|title=Tigers: Senses |publisher=Busch Gardens Animal Information Database|accessdate=2006-06-22 }}</ref> |
||
The nine subspecies of tiger (living and extinct) tend to vary in size, colour, fur length and stripe pattern. The following is a description of each of the subspecies of tiger, in order of descending size.<ref>All tiger weights and lengths, with the exception of the Malayan tiger, are from Tiger Territory: [http://www.lairweb.org.nz/tiger]</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Siberian Tiger sf.jpg|thumb|left|Siberian tiger]] |
|||
'''Siberian tiger''' |
|||
Male Siberian tigers weigh between 180 and 306 kg on average, whereas females are smaller, at 100-167 kg. Lengths for Siberian tigers range between 2.7 and 3.3 m for males and 2.4 and 2.75 for females. As animals that have adapted to a cold climate, Siberian tigers tend to have much thicker and longer fur than other subspecies, with a thicker layer of fat beneath. This tends to make the Siberian tiger appear larger than it really is, since in winter this fur can reach 21 inches (46.2 cm) in length<ref>[http://www.lairweb.org.nz/tiger/amur4.html]</ref>, although it is still the largest tiger subspecies, with an average (male) weight of about 227 kg<ref>Sunquist, Mel and Fiona Sunquist. 2002. Wild Cats of the World. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago</ref>. Their fur tends to be pale gold, with fewer and paler stripes than Bengal tigers. |
|||
[[Image:Panthera tigris tigris.jpg|thumb|right|Bengal tiger]] |
|||
'''Bengal tiger''' |
|||
Bengal tigers are the second largest tiger subspecies, although tigers in the extreme northern parts of their range may equal Siberian tigers in size, with an average (male) weight of about 236 kg. Generally, however, male Bengal tigers range between 180 and 248 kg, whereas females range between 100 and 160 kg. Total body lengths for males range from 2.7 to 3.1 m, and lengths for females range from 2.4 to 2.65 m. Bengal tigers are perhaps the most recognisable of the tiger subspecies, with typical reddish background colouring with an overlay of black or dark brown stripes. Bengal tigers actually vary more in their colouring than other tiger subspecies, since white and golden tabby tigers invariably are at least part Bengal. |
|||
[[Image:Caspian tiger.JPG|thumb|left|Caspian tiger]] |
|||
'''Caspian tiger''' |
|||
Now extinct, Caspian tigers were relatively large and stocky tigers, rivalling Bengal tigers in size. Weights for males were between 169 and 240 kg and weights for females were between 85 and 135 kg. Total body lengths were 2.64 - 2.95 m and 2.41 - 2.59 m for males and females respectively. The ground colour of their fur was similar to that of Bengal tigers, but their stripes were paler, tending to be dark brown or grey in hue. Also, the stripe patterns were tighter and narrower. Their fur was relatively long, particularly in winter. |
|||
[[Image:Panthera tigris corbetti.jpg|thumb|left|Indochinese tiger]] |
|||
'''Indochinese tiger''' |
|||
Indochinese tigers look similar to Bengal tigers in terms of their stripe pattern, but tend to be smaller and darker, with averages weights of 150 - 195 kg and 100 - 130 kg, and lengths of 2.57 - 2.84 m and 2.31 - 2.64 m for males and females respectively. |
|||
[[Image:Panthera tigris amoyensis.jpg|thumb|right|South China tiger]] |
|||
'''South China tiger''' |
|||
South China tiger males range between 130 and 175 kg, and tigresses between 100 and 115 kg. Average lengths are 2.3 - 2.6 m for males and 2.2 - 2.4 m for females. Their stripes are quite short and broad, and spaced further apart than those of Bengal tigers. |
|||
[[Image:Tiger in the water.jpg|180px|thumb|left|Malayan tiger]] |
|||
'''Malayan tiger''' |
|||
Male Malayan tigers weigh an average of 120 kg with an average length of 2.35 m, whereas female Malayan tigers weigh an average of 100 kg with an average length of 2 m. Thus, Malayan tigers are the smallest of the mainland tiger subspecies, and the second smallest living tiger subspecies. Malayan tigers look very similar to Indochinese tigers, but are smaller in stature. |
|||
[[Image:Sumatran tiger.JPG|thumb|right|Sumatran tiger]] |
|||
'''Sumatran tiger''' |
|||
Sumatran tigers are the smallest living subspecies of tiger. Males range from 100 to 140 kg with a total body length of between 2.2 and 2.55 m, and females range from 75 to 110 kg with a total body length of 2.15 to 2.3 m. They are also notable for having a larger facial ruff than other tiger subspecies (particularly males), as well as very long whiskers. They are also darker with a greater number of stripes than Bengal tigers.<ref>[http://www.lairweb.org.nz/tiger/sumatran4.html]</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Panthera tigris sondaica 01.jpg|left|thumb|A photograph of a Javan tiger.]] |
|||
'''Javan tiger''' |
|||
Male Javan tigers weighed between 100 and 141 kg, and females between 75 and 115 kg. Whereas male Javan tigers are thought to have measured about 2.46 m from nose to tail tip, the length of female Javan tigers is not known, although they were smaller than the males. Overall, Javan tigers were similar to Sumatran tigers in size and appearance, although their stripes were closer together. They had the longest cheek whiskers of any subspecies of tiger. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
'''Bali tiger''' |
|||
With males weighing just 90 - 100 kg, and females 65 - 80 kg, Bali tigers were the smallest of all tiger subspecies. Male lengths ranged from 2.2 to 2.31 m, and female lengths from 1.9 to 2.11 m. Their fur was a deep orange, with darker and fewer stripes than other subspecies. They also had unusual bar-shaped patterns on their forehead<ref>[http://www.lairweb.org.nz/tiger/bali2.html]</ref>. |
|||
====White tigers==== |
====White tigers==== |
||
[[Image:Singapore Zoo Tigers.jpg|thumb |
[[Image:Singapore Zoo Tigers.jpg|thumb|230px|A pair of white tigers at the [[Singapore Zoo]]]] |
||
{{main|White tiger}} |
{{main|White tiger}} |
||
| Line 145: | Line 98: | ||
{{main|Golden tabby}} |
{{main|Golden tabby}} |
||
In addition, another recessive gene may create a very unusual "golden tabby" colour variation, sometimes known as "strawberry". Golden tabby tigers have light gold fur, pale legs and faint orange stripes. Their fur tends to be much thicker than normal.<ref>[http://www.lairweb.org.nz/tiger/tabby.html]</ref> There are extremely few golden tabby tigers in captivity, around 30 in all. Like white tigers, strawberry tigers are invariably at least part Bengal. Both white and golden tabby tigers tend to be larger than average Bengal tigers. |
In addition, another recessive gene may create a very unusual "golden tabby" colour variation, sometimes known as "strawberry". Golden tabby tigers have light gold fur, pale legs and faint orange stripes. Their fur tends to be much thicker than normal.<ref>[http://www.lairweb.org.nz/tiger/tabby.html]</ref> There are extremely few golden tabby tigers in captivity, around 30 in all. Like white tigers, strawberry tigers are invariably at least part Bengal. Both white and golden tabby tigers tend to be larger than average Bengal tigers. |
||
====Other colour variations==== |
====Other colour variations==== |
||
There are also unconfirmed reports of a [[Maltese Tiger|"blue" or slate-coloured tiger]], and largely or totally [[Black tiger (animal)|black tigers]], and these are assumed, if real, to be intermittent mutations rather than distinct species.<ref name="nz" /> |
There are also unconfirmed reports of a [[Maltese Tiger|"blue" or slate-coloured tiger]], and largely or totally [[Black tiger (animal)|black tigers]], and these are assumed, if real, to be intermittent mutations rather than distinct species.<ref name="nz" /> |
||
| Line 337: | Line 289: | ||
[[Category:Tigers| ]] |
[[Category:Tigers| ]] |
||
[[Category:Mammals of Asia]] |
[[Category:Mammals of Asia]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Mammals of Indonesia]] |
||
[[Category:Fauna of Southeast Asia]] |
|||
[[Category:Fauna of the Indian Subcontinent]] |
|||
[[Category:Megafauna of Eurasia]] |
|||
[[Category:National symbols of India]] |
[[Category:National symbols of India]] |
||
[[Category:EDGE Species]] |
[[Category:EDGE Species]] |
||
Revision as of 13:08, 15 August 2008
| Tiger | |
|---|---|

| |
| A Bengal Tiger (P. tigris tigris) in India's Bandhavgarh reserve. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | P. tigris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Panthera tigris (Linnaeus, 1758)
| |

| |
| Historical distribution of tigers (pale yellow) and 2006 (green).[2] | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Tigris striatus Severtzov, 1858 | |
The tiger (Panthera tigris) is a member of the Felidae family; the largest and the most powerful of the four "big cats" in the genus Panthera.[3] Native to much of eastern and southern Asia, the tiger is an apex predator and an obligate carnivore. Reaching up to 4 metres (13 ft) in total length and weighing up to 300 kilograms (660 pounds), the larger tiger subspecies are comparable in size to the biggest extinct felids.[4][5] Aside from their great bulk and power, their most recognizable feature is the pattern of dark vertical stripes that overlays near-white to reddish-orange fur, with lighter underparts. The largest subspecies of tiger is the Siberian tiger.
Highly adaptable, tigers range from the Siberian taiga, to open grasslands, to tropical mangrove swamps. They are territorial and generally solitary animals, often requiring large contiguous areas of habitat that support their prey demands. This, coupled with the fact that they are endemic to some of the more densely populated places on earth, has caused significant conflicts with humans. Of the nine subspecies of modern tiger, three are extinct and the remaining six are classified as endangered, some critically so. The primary direct causes are habitat destruction and fragmentation, and hunting. Their historical range, which once reached from Mesopotamia and the Caucasus through most of South and East Asia, has been radically reduced. While all surviving species are under formal protection, poaching, habitat destruction and inbreeding depression continue to be threats.
Nonetheless, tigers are among the most recognizable and popular of the world's charismatic megafauna. They have featured prominently in ancient mythology and folklore, and continue to be depicted in modern films and literature. Tigers appear on many flags and coats of arms, as mascots for sporting teams, and as the national animal of several Asian nations.
Naming and etymology
The word "tiger" is taken from the Greek word "tigris", which is possibly derived from a Persian source meaning "arrow", a reference to the animal's speed and also the origin for the name of the River Tigris.[6][7] In American English, "Tigress" was first recorded in 1611. It was one of the many species originally described, as Felis tigris, by Linnaeus in his 18th century work, Systema Naturae.[8] The generic component of its scientific designation, Panthera tigris, is often presumed to derive from Greek pan- ("all") and ther ("beast"), but this may be a folk etymology. Although it came into English through the classical languages, panthera is probably of East Asian origin, meaning "the yellowish animal," or "whitish-yellow".[9]
A group of tigers[10] is rare (see below), but when seen together is termed a 'streak' or an 'ambush'.
Range
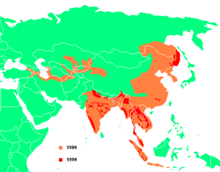
In the historical past tigers were widespread in Asia, from the Caucasus and the Caspian Sea, to Siberia and Indonesia. During the 19th century the striped cats completely vanished from western Asia, and became restricted to isolated pockets in the remaining parts of their range. Today, this fragmented relic range extends from India in the west to China and Southeast Asia in the east. The northern limit is close to the Amur River in south eastern Siberia. The only large island inhabited by tigers today is Sumatra. Tigers vanished from Java during the second half of the 19th century, and in Borneo are known only from fossil remains.
Taxonomy and evolution
The oldest remains of a tiger-like cat, called Panthera palaeosinensis, have been found in China and Java. This species lived about 2 million years ago, at the beginning of the Pleistocene, and was smaller than a modern tiger. The earliest fossils of true tigers are known from Java, and are between 1.6 and 1.8 million years old. Distinct fossils from the early and middle Pleistocene were also discovered in deposits from China, and Sumatra. A subspecies called the Trinil tiger (Panthera tigris trinilensis) lived about 1.2 million years ago and is known fossils found at Trinil in Java.[11]
Tigers first reached India and northern Asia in the late Pleistocene, reaching eastern Beringia (but not the American Continent), and Japan, and Sakhalin. Fossils found in Japan indicate that the local tigers were, like the surviving island subspecies, smaller than the mainland forms. This may be due to the phenomenon in which body size is related to environmental space (see insular dwarfism), or perhaps the availability of prey. Until the Holocene, tigers also lived in Borneo.
Subspecies
There are nine recent subspecies of tiger, three of which are extinct, and one of which is almost certain to become extinct in the near future.[3] Their historical range (severely diminished today) ran through Russia, Siberia, Iran, Afghanistan, India, China, and southeast Asia, including the Indonesian islands. The surviving subspecies, in descending order of wild population, are:

- The Bengal tiger or the Royal Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris tigris) is found in parts of India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Burma. It lives in varied habitats: grasslands, subtropical and tropical rainforests, scrub forests, wet and dry deciduous forests, and mangroves. Males in the wild usually weigh 205 to 227 kg (450–500 lb), while the average female will weigh about 141 kg.[12] However, the northern Indian and the Nepalese Bengal tigers are somewhat bulkier than those found in the south of the Indian Subcontinent, with males averaging around 236 kg (520 lb).[13] While conservationists already believed the population to be below 2,000,[14] the most recent audit by the Indian Government's National Tiger Conservation Authority has estimated the number at just 1,411 wild tigers (1165-1657 allowing for statistical error), a drop of 60% in the past decade.[15] Since 1972, there has been a massive wildlife conservation project, known as Project Tiger, to protect the Bengal tiger. The project is considered as one of the most successful wildlife conservation programs[citation needed], though at least one Tiger Reserve (Sariska Tiger Reserve) has lost its entire tiger population to poaching.[16]

- The Indochinese tiger (Panthera tigris corbetti), also called Corbett's tiger, is found in Cambodia, China, Laos, Burma, Thailand, and Vietnam. These tigers are smaller and darker than Bengal tigers: Males weigh from 150–190 kg (330–420 lb) while females are smaller at 110–140 kg (242–308 lb). Their preferred habitat is forests in mountainous or hilly regions. Estimates of the Indochinese tiger population vary between 1,200 to 1,800, with only several hundred left in the wild. The largest current population is in Malaysia, where illegal poaching is strictly controlled, but all existing populations are at extreme risk from habitat fragmentation and inbreeding. In Vietnam, almost three-quarters of the tigers killed provide stock for Chinese pharmacies.
- The Malayan tiger (Panthera tigris malayensis), exclusively found in the southern part of the Malay Peninsula, was not considered a subspecies in its own right until 2004. The new classification came about after a study by Luo et al. from the Laboratory of Genomic Diversity Study,[17] part of the National Cancer Institute of the United States. Recent counts showed there are 600–800 tigers in the wild, making it the third largest tiger population, behind the Bengal tiger and the Indochinese tiger. The Malayan tiger is the smallest of the mainland tiger subspecies, and the second smallest living subspecies, with males averaging about 120 kg and females about 100 kg in weight. The Malayan tiger is a national icon in Malaysia, appearing on its coat of arms and in logos of Malaysian institutions, such as Maybank.

- The Sumatran tiger (Panthera tigris sumatrae) is found only on the Indonesian island of Sumatra, and is critically endangered.[18] It is the smallest of all living tiger subspecies, with adult males weighing between 100–130 kg (220–286 lb) and females 70–90 kg (154–198 lb). Their small size is an adaptation to the thick, dense forests of the Sumatra island where they reside, as well as the smaller-sized prey. The wild population is estimated at between 400 and 500, seen chiefly in the island's national parks. Recent genetic testing has revealed the presence of unique genetic markers, indicating that it may develop into a separate species,[specify] if it does not go extinct.[19] This has led to suggestions that Sumatran tigers should have greater priority for conservation than any other subspecies. While Habitat destruction is the main threat to the existing tiger population (logging continues even in the supposedly protected national parks), 66 tigers were recorded as being shot and killed between 1998 and 2000, or nearly 20% of the total population.

- The Siberian tiger (Panthera tigris altaica), also known as the Amur, Manchurian, Altaic, Korean or North China tiger, is confined to the Amur-Ussuri region of Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsk Krai in far eastern Siberia, where it is now protected. Considered the largest subspecies, with an average weight of around 227 kg (500 lb) for males,[20] the Amur tiger is also noted for its thick coat, distinguished by a paler golden hue and fewer stripes. A six-month old Siberian tiger can be as big as a fully grown leopard. The last two censuses (1996 and 2005) found 450–500 Amur tigers within their single, and more or less continuous, range making it one of the largest undivided tiger populations in the world.
- The South China tiger (Panthera tigris amoyensis), also known as the Amoy or Xiamen tiger, is the most critically endangered subspecies of tiger and is listed as one of the 10 most endangered species in the world.[21][clarification needed] It will almost certainly become extinct.[citation needed] One of the smaller tiger subspecies, the length of the South China tiger ranges from 2.2–2.6 m (87–104 in) for both males and females. Males weigh between 127 and 177 kg (280–390 lb) while females weigh between 100 and 118 kg (220–260 lb). From 1983 to 2007, no South China tigers were sighted.[22] In 2007 a farmer spotted a tiger and handed in photographs to the authorities as proof.[23][22] In 1977, the Chinese government passed a law banning the killing of wild tigers, but this may have been too late to save the subspecies. There are currently 59 known captive South China tigers, all within China, but these are known to be descended from only six animals. Thus, the genetic diversity required to maintain the subspecies may no longer exist. Currently, there are breeding efforts to reintroduce these tigers to the wild by 2008.
Extinct subspecies
- The Balinese tiger (Panthera tigris balica) was limited to the island of Bali. These tigers were hunted to extinction—the last Balinese tiger is thought to have been killed at Sumbar Kima, West Bali on 27 September 1937; this was an adult female. No Balinese tiger was ever held in captivity. The tiger still plays an important role in Balinese Hindu religion.
- The Javan tiger (Panthera tigris sondaica) was limited to the Indonesian island of Java. It now seems likely that this subspecies became extinct in the 1980s, as a result of hunting and habitat destruction, but the extinction of this subspecies was extremely probable from the 1950s onwards (when it is thought that fewer than 25 tigers remained in the wild). The last confirmed specimen was sighted in 1979, but there were a few reported sightings during the 1990s.[24][25]

- The Caspian tiger or Persian tiger (Panthera tigris virgata) appears to have become extinct in the wild in the late 1950s,[26][27] with the last reliable sighting in 1968, though it is thought that such a tiger was last shot dead in the south-eastern-most part of Turkey in 1970. Historically, it ranged through Afghanistan, Iran, Iraq, Pakistan, the former Soviet Union, and Turkey.[26] The Caspian tiger was a large subspecies and reached nearly the dimensions of the Bengal Tiger. The heaviest confirmed weight of a male was 240 kg. The ground colour was comparable to that of the Indian subspecies, but differed especially in the tight, narrow, striping pattern. The stripes were dark grey or brown, rather than black. Especially during the winter, the fur was relatively long. The Caspian tiger was one of two subspecies of tiger (along with the Bengal) that was used by the Romans to battle gladiators and other animals, including the Barbary Lion. The Romans traveled far to capture exotic beasts for the arena. There are still occasional reported sightings of the Caspian Tiger in the wild.[27]
Hybrids
Hybridization among the big cats, including the tiger, was first conceptualized in the 19th century, when zoos were particularly interested in the pursuit of finding oddities to display for financial gain.[28] Lions have been known to breed with tigers (most often the Amur and Bengal subspecies) to create hybrids called ligers and tigons.[29] Such hybrids were once commonly bred in zoos, but this is now discouraged due to the emphasis on conserving species and subspecies. Hybrids are still bred in private menageries and in zoos in China.
The liger is a cross between a male lion and a tigress.[30] Because the lion sire passes on a growth-promoting gene, but the corresponding growth-inhibiting gene from the female tiger is absent, ligers grow far larger than either parent. They share physical and behavioural qualities of both parent species (spots and stripes on a sandy background). Male ligers are sterile, but female ligers are often fertile. Males have about a 50% chance of having a mane, but, even if they do, their manes will be only around half the size of that of a pure lion. Ligers are typically between 10 to 12 feet in length, and can be between 800 and 1,000 pounds or more.[30]
The less common tigon is a cross between the lioness and the male tiger.[31]
Biology and behaviour
Physical characteristics
Tigers are the heaviest cats found in the wild,[32] but the subspecies differ markedly in size, tending to increase proportionally with latitude, as predicted by Bergmann's Rule. Large male Siberian Tigers (Panthera tigris altaica) can reach a total length of 3.5 m and a weight of 306 kilograms.[33] Apart from those exceptional large individuals, male Siberian tigers usually have a head and body length of 190–220 cm and an average weight of 227 kg[34] (the tail of a tiger is 60–110 cm long). The heaviest wild Siberian tiger on record weighed in at 384 kg,[35] but according to Mazak these giants are not confirmed via reliable references.[33] Females are smaller - the size difference between male and female tigers tends to be more pronounced in the larger subspecies of tiger, with males weighing up to 1.7 times as much as the females[36]. Consequently, females of the Siberian and Bengal subspecies weigh only between 100 and 181 kg. Island-dwelling tigers, such as the Sumatran subspecies, are much smaller than mainland tigers, with males usually weighing only 100–140 kg and females 75–110 kg. The extinct Bali Tiger was even smaller, with a weight of 90–100 kg in males and 65–80 kg in females.[33]
Tigers have rusty-reddish to brown-rusty coats, a whitish medial and ventral area, and stripes that vary from brown or gray to pure black. The form and density of stripes differs between subspecies, but most tigers have over 100 stripes. The pattern of stripes is unique to each animal, and thus could potentially be used to identify individuals, much in the same way as fingerprints are used to identify people. This is not, however, a preferred method of identification, due to the difficulty of recording the stripe pattern of a wild tiger. It seems likely that the function of stripes is camouflage, serving to hide these animals from their prey. The stripe pattern is found on a tiger's skin and if shaved, its distinctive camouflage pattern would be preserved. Male tigers have wider forepaw pads than females. This difference is often used by biologists in determining the gender of tigers when observing their tracks.[37]
Like most cats, tigers are believed to have some degree of color vision.[38]
White tigers

There is a well-known mutation that produces the white tiger, technically known as chinchilla albinistic,[39] an animal which is rare in the wild, but widely bred in zoos due to its popularity. Breeding of white tigers will often lead to inbreeding (as the trait is recessive). Many initiatives have taken place in white and orange tiger mating in an attempt to remedy the issue, often mixing subspecies in the process. Furthermore, such inbreeding has led to white tigers having a greater likelihood of being born with physical defects, such as crossed eyes, cleft palates and scoliosis (curvature of the spine).[40][41] Even apparently healthy white tigers generally do not live as long as their orange counterparts.
Recordings of white tigers were first made in the early 19th century.[42] They can only occur when both parents carry the rare gene found in white tigers; this gene has been calculated to occur in only one in every 10,000 births. The white tiger is not a separate sub-species, but only a colour variation; since the only white tigers that have been observed in the wild have been Bengal tigers[43] (and all white tigers in captivity are at least part Bengal), it is commonly thought that the recessive gene that causes the white colouring is probably carried only by Bengal tigers, although the reasons for this are not known.[44][45] Nor are they in any way more endangered than tigers are generally, this being a common misconception. Another misconception is that white tigers are albinos, despite the fact that pigment is evident in the white tiger's stripes. They are distinct not only because of their white hue; they also have blue eyes and pink noses.
Golden tabby tigers

In addition, another recessive gene may create a very unusual "golden tabby" colour variation, sometimes known as "strawberry". Golden tabby tigers have light gold fur, pale legs and faint orange stripes. Their fur tends to be much thicker than normal.[46] There are extremely few golden tabby tigers in captivity, around 30 in all. Like white tigers, strawberry tigers are invariably at least part Bengal. Both white and golden tabby tigers tend to be larger than average Bengal tigers.
Other colour variations
There are also unconfirmed reports of a "blue" or slate-coloured tiger, and largely or totally black tigers, and these are assumed, if real, to be intermittent mutations rather than distinct species.[39]
Territorial behavior
Adult tigers are fiercely territorial. The size of a tiger's home range mainly depends on prey abundance, and, in the case of male tigers, on access to females. A tigress may have a territory of 20 square kilometres while the territories of males are much larger, covering 60–100 km². While females can at times be aggressive towards other females, their territories can overlap and they do tolerate each other. Males, however, are usually intolerant of other males within their territory. Because of their aggressive nature, territorial disputes can be violent, and may end in the death of one of the males. To identify his territory, the male marks trees by spraying of urine and anal gland secretions, as well as marking trails with scat. Males show a grimacing face, called the Flehmen response, when identifying a female's reproductive condition by sniffing their urine markings.
Male tigers can mingle easily with females in their territories, and will even share kills. George Schaller observed a male tiger share a kill with two females and four cubs. Females are often reluctant to let males near their cubs, but Schaller saw that these females made no effort to protect or keep their cubs from the male. This suggests that the male might have been the father of the cubs. In contrast to male lions, male tigers will allow the females and cubs to feed on the kill first. Females will also share kills, even more so than the males. They are also much more tolerant of sharing kills with individuals of the same sex.[47]
Tigers have been studied in the wild using a variety of techniques. The populations of tigers were estimated in the past using plaster casts of their pugmarks. This method was found faulty[48] and attempts were made to use camera trapping instead. Newer techniques based on DNA from their scat are also being evaluated. Radio collaring has also been a popular approach to tracking them for study in the wild.

Hunting and diet
In the wild, tigers mostly feed on larger and medium sized animals. Sambar, gaur, domestic buffalo, chital, boar, and nilgai are the tiger's favored prey in India. Sometimes, they also prey on leopards, pythons, sloth bears and crocodiles. In Siberia the main prey species are Mandchurian elk, wild boar, Sika Deer, roe deer, and musk deer. In Sumatra Rusa Deer, wild boar, and Malayan Tapir are preyed on. In the former Caspian tiger's range, prey included Saiga Antelope, camels, Caucasian Wisent, yak, and wild horses. Like many predators, they are opportunistic and will eat much smaller prey, such as monkeys, peafowls, hares, and fish.
Adult elephants are too large to serve as common prey, but conflicts between tigers and elephants do sometimes take place. A case where a tiger killed an adult Indian Rhinoceros has been observed.[49] Young elephant and rhino calves are occasionally taken. Tigers also sometimes prey on domestic animals such as dogs, cows, horses, and donkeys. These individuals are termed cattle-lifters or cattle-killers in contrast to typical game-killers.
Old tigers, or those wounded and rendered incapable of catching their natural prey, have turned into man-eaters; this pattern has recurred frequently across India. An exceptional case is that of the Sundarbans, where healthy tigers prey upon fishermen and villagers in search of forest produce, humans thereby forming a minor part of the Tiger's diet.[50]


Tigers hunt alone and ambush their prey as other cats do, overpowering them from any angle, using their body size and strength to knock large prey off balance. Even with their great masses, tigers can reach speeds of about 49-65 kilometres per hour (35-40 miles per hour). When hunting large prey, tigers prefer to bite the throat and use their muscled forelimbs to hold onto the prey, bringing it to the ground. The tiger remains latched onto the neck until its prey dies of strangulation.[51] With small prey, the tiger bites the nape, often breaking the spinal cord, piercing the windpipe, or severing the jugular vein or common carotid artery.[52] Though rarely observed, some tigers have been recorded to kill prey by swiping with their paws, which are powerful enough to smash the skulls of domestic cattle,[53] and break the backs of sloth bears.[54]
In the wild, tigers can leap as high as 5 m (16 ft) and as far as 9–10 m (30–33 ft), making them one of the highest-jumping mammals, just slightly behind cougars in ability.[citation needed]
They have been reported to carry domestic livestock weighing 50 kg (110 lb) while easily jumping over fences 2 m (6 ft 6 in) high.[citation needed] Their heavily muscled forelimbs are used to hold tightly onto the prey and to avoid being dislodged, especially by large prey such as gaurs. Gaurs and water buffalos weighing over a ton have been killed by tigers weighing about a sixth as much.[55]
Tigers will occasionally eat vegetation for dietary fiber, the fruit of the Slow Match Tree being favoured.[53]

Interspecific predatory relationships
Tigers may kill such formidable predators as leopards, pythons and even crocodiles on occasion,[56][57][58] although predators typically avoid one another. When seized by a crocodile, a tiger will strike at the reptile's eyes with its paws.[53] Leopards dodge competition from tigers by hunting in different times of the day and hunting different prey.[49] With relatively abundant prey, tigers and leopards were seen to successfully coexist without competitive exclusion or inter-species dominance hierarchies that may be more common to the savanna.[59] Tigers have been known to suppress wolf populations in areas where the two species coexist.[60][61] Dhole packs have been observed to attack and kill tigers in disputes over food, though not usually without heavy losses.[54] Siberian Tigers and Brown Bears can be competitors and usually avoid confrontation; however, tigers will kill bear cubs and even some adults on occasion. Bears (Asiatic Black Bears and Brown Bears) make up 5-8% of the Tiger's diet in the Russian Far East.[33] Some bears emerging from hibernation will try to steal tigers' kills, although the tiger will mostly defend its kill.[37] Sloth Bears are quite aggressive and will sometimes drive younger aged tigers away from their kills, although in most of cases Bengal tigers prey on sloth bears.[33]
Reproduction
A female is only receptive for a few days and mating is frequent during that time period. A pair will copulate frequently and noisily, like other cats. The gestation period is 16 weeks and 3–4 cubs of about 1 kg (2 lb) each are born. The females rear them alone. Wandering male tigers may kill cubs to make the female receptive. At 8 weeks, the cubs are ready to follow their mother out of the den. The cubs become independent around 18 months of age, but it is not until they are around 2–2½ years old that they leave their mother. The cubs reach sexual maturity by 3–4 years of age. The female tigers generally own territory near their mother, while males tend to wander in search of territory, which they acquire by fighting and eliminating another male. Over the course of her life, a female tiger will give birth to an approximately equal number of male and female cubs. Tigers breed well in captivity, and the captive population in the United States may rival the wild population of the world.[47]
Habitat
Typical tiger country has three main features: It will always have good cover, it will always be close to water and plenty of prey. Bengal Tigers live in all types of forests, including Wet, Evergreen, semi-evergreen of Assam and eastern Bengal; the mangrove forest of Ganges Delta; The deciduous forest of Nepal and thorn forests of the Western Ghats. Compared to the lion, the tiger prefers more dense vegetation, for which its camouflage is ideally suited, and where a single predator is not at a disadvantage compared to a pride. Among the big cats, only the tiger and jaguar are strong swimmers; tigers are often found bathing in ponds, lakes, and rivers. Unlike other cats, which tend to avoid water, tigers actively seek it out. During the extreme heat of the day, they are often to be found cooling off in pools. Tigers are excellent swimmers, better than the jaguar and can swim up to 4 miles. Tigers are often to be found carrying their dead prey across lakes.
Conservation efforts
Poaching for fur and destruction of habitat have greatly reduced tiger populations in the wild. A century ago, it is estimated there were over 100,000 tigers in the world but the population has dwindled to between 7,000 and 5,000 tigers.[62] Some estimates suggest the population is even lower, with some at less than 2,500 mature breeding individuals, with no subpopulation containing more than 250 mature breeding individuals.[1] The threat of extinction is mitigated somewhat by the presence of some 20,000 tigers currently in captivity, although parts of the captive population, such as the 4-5,000 animals in China's commercial tiger farms, are of low genetic diversity.
India
India harbors the largest population of wild tigers in the world, along with one of the highest human populations. A major concerted conservation effort known as Project Tiger has been underway since 1973, spearheaded by Indira Gandhi. The fundamental accomplishment has been the establishment of over 25 well-monitored tiger reserves in reclaimed land where human development is categorically forbidden. The program has been credited with tripling the number of wild Bengal tigers from roughly 1,200 in 1973 to over 3,500 in the 1990s, though the reports of the Indian government are occasionally met with some skepticism.[citation needed] A recently passed tribal Bill, which allows tribal populations to reside inside designated tiger sanctuaries, may have impacts on the continuing success of the program.[citation needed]
A tiger census carried out over 2007, whose report was published on February 12, 2008 stated that the wild tiger population in India has come down to approximately 1,411. It is noted in the report that the decrease of tiger population can be attributed directly to poaching.[63]
Russia
The Siberian tiger was on the brink of extinction with only about 40 animals in the wild in the 1940s. Under the Soviet Union, anti-poaching controls were strict and a network of protected zones (zapovedniks) were instituted, leading to a rise in the population to several hundred. Poaching again became a problem in the 1990s, when the economy of Russia collapsed, local hunters had access to a formerly sealed off lucrative Chinese market, and logging in the region increased. While an improvement in the local economy has led to greater resources being invested in conservation efforts, an increase of economic activity has led to an increased rate of development and deforestation. The major obstacle in preserving the species is the enormous territory individual tigers require (up to 450 km2 needed by a single female).[32] Current conservation efforts are led by local governments and NGO's in consort with international organizations, such as the World Wide Fund and the Wildlife Conservation Society.[32] Currently, there are about 400-550 animals in the wild.
Tibet
In Tibet, tiger and leopard pelts have traditionally been used in various ceremonies and costumes. In January 2006 the Dalai Lama preached a ruling against using, selling, or buying wild animals, their products, or derivatives. It has yet to be seen whether this will result in a long-term slump in the demand for poached tiger and leopard skins.[64][65][66]
Rewilding
The first attempt at rewilding was by Indian conservationist Billy Arjan Singh, who reared a zoo-born tigress named Tara, and released her in the wilds of Dudhwa National Park in 1978. This was soon followed by a large number of people being eaten by a tigress who was later shot. Government officials claim that this tigress was Tara, an assertion hotly contested by Singh and conservationists. Later on, this rewilding gained further disrepute when it was found that the local gene pool had been sullied by Tara's introduction as she was partly Siberian tiger, a fact not known at the time of release, ostensibly due to poor record-keeping at Twycross Zoo, where she had been raised.[67][68][69][70][71][72][73][74][75][76]
Save China's Tigers
The organisation Save China's Tigers, working with the Wildlife Research Centre of the State Forestry Administration of China and the Chinese Tigers South Africa Trust, secured an agreement on the reintroduction of Chinese tigers into the wild. The agreement, which was signed in Beijing on 26 November 2002, calls for the establishment of a Chinese tiger conservation model through the creation of a pilot reserve in China where indigenous wildlife, including the South China Tiger, will be reintroduced. A number of Chinese tiger cubs will be selected from zoos in China and sent to a 300 square kilometer reserve near the town of Philippolis in South Africa, where they will be taught to hunt for themselves. The offspring of the trained tigers will be released into the pilot reserves in China, while the original animals will stay in South Africa to continue breeding.[77] A second Chinese tiger rehabilitation project is also being run in Fujian, China.[78]
China will conduct the work of surveying land, restoring habitat and prey within the pilot reserve. [79]
Relation with humans

Tiger as prey
The tiger has been one of the Big Five game animals of Asia. Tiger hunting took place on a large scale in the early nineteenth and twentieth centuries, being a recognised and admired sport by the British in colonial India as well as the maharajas and aristocratic class of the erstwhile princely states of pre-independence India. Tiger hunting was done by some hunters on foot; others sat up on machans with a goat or buffalo tied out as bait; yet others on elephant-back.[80] In some cases, villagers beating drums were organised to drive the animals into the killing zone. Elaborate instructions were available for the skinning of tigers and there were taxidermists who specialised in the preparation of tiger skins.
Man-eating tigers

Although humans are not regular prey for tigers, they have killed more people than any other cat, particularly in areas where population growth, logging, and farming have put pressure on tiger habitats. Most man-eating tigers are old and missing teeth, acquiring a taste for humans because of their inability to capture preferred prey.[81] Almost all tigers that are identified as man-eaters are quickly captured, shot, or poisoned. Unlike man-eating leopards, even established man-eating tigers will seldom enter human settlements, usually remaining at village outskirts.[82] Nevertheless, attacks in human villages do occur.[83] Man-eaters have been a particular problem in India and Bangladesh, especially in Kumaon, Garhwal and the Sundarbans mangrove swamps of Bengal, where some healthy tigers have been known to hunt humans.
Traditional Asian medicine

Many people in China have a belief that various tiger parts have medicinal properties, including as pain killers and aphrodisiacs.[84] There is no scientific evidence to support these beliefs. The use of tiger parts in pharmaceutical drugs in China is already banned, and the government has made some offenses in connection with tiger poaching punishable by death. Furthermore, all trade in tiger parts is illegal under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora and a domestic trade ban has been in place in China since 1993. Still, there are a number of tiger farms in the country specializing in breeding the cats for profit. It is estimated that between 4,000 and 5,000 captive-bred, semi-tame animals live in these farms today.[85][86]
As pets
The Association of Zoos and Aquariums estimates that up to 12,000 tigers are being kept as private pets in the USA, significantly more than the world's entire wild population.[87] 4,000 are believed to be in captivity in Texas alone.[87]
In Brian De Palma's remake of Scarface, starring Al Pacino, Pacino's character, Tony Montana, aspires to obtaining all the exterior trappings of the American Dream, which in the character's opinion included keeping a pet tiger on his property.
Part of the reason for America's enormous tiger population relates to legislation. Only nineteen states have banned private ownership of tigers, fifteen require only a licence, and sixteen states have no regulations at all.[87]
The success of breeding programmes at American zoos and circuses led to an overabundance of cubs in the 1980s and 90s, which drove down prices for the animals.[87] The SPCA estimate there are now 500 lions, tigers and other big cats in private ownership just in the Houston area.[87]

Cultural depictions
The tiger replaces the lion as King of the Beasts in cultures of eastern Asia,[88] representing royalty, fearlessness and wrath.[89] Its forehead has a marking which resembles the Chinese character 王, which means "king"; consequently, many cartoon depictions of tigers in China and Korea are drawn with 王 on their forehead.[citation needed]
Of great importance in Chinese myth and culture, the tiger is one of the 12 Chinese zodiac animals. Also in various Chinese art and martial art, the tiger is depicted as an earth symbol and equal rival of the Chinese dragon- the two representing matter and spirit respectively. In fact, the Southern Chinese martial art Hung Ga is based on the movements of the Tiger and the Crane. In Imperial China, a tiger was the personification of war and often represented the highest army general (or present day defense secretary),[89] while the emperor and empress were represented by a dragon and phoenix, respectively. The White Tiger (Chinese: 白虎; pinyin: Bái Hǔ) is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. It is sometimes called the White Tiger of the West (西方白虎), and it represents the west and the autumn season.[89]
In Buddhism, it is also one of the Three Senseless Creatures, symbolizing anger, with the monkey representing greed and the deer lovesickness.[89]
The Tungusic people considered the Siberian tiger a near-deity and often referred to it as "Grandfather" or "Old man". The Udege and Nanai called it "Amba". The Manchu considered the Siberian tiger as Hu Lin, the king.[37]
The widely worshiped Hindu goddess Durga, an aspect of Devi-Parvati, is a ten-armed warrior who rides the tigress (or lioness) Damon into battle. In southern India the god Aiyappa was associated with a tiger.[90]
The weretiger replaces the werewolf in shapeshifting folklore in Asia;[91] in India they were evil sorcerers while in Indonesia and Malaysia they were somewhat more benign.[92]
The tiger continues to be a subject in literature; both Rudyard Kipling, in The Jungle Book, and William Blake, in Songs of Experience, depict the tiger as a menacing and fearful animal. In The Jungle Book, the tiger, Shere Khan, is the wicked mortal enemy of the protagonist, Mowgli. However, other depictions are more benign: Tigger, the tiger from A. A. Milne's Winnie-the-Pooh stories, is cuddly and likable. In the Man Booker Prize winning novel "Life of Pi," the protagonist, Pi Patel, sole human survivor of a ship wreck in the Pacific Ocean, befriends another survivor: a large Bengal Tiger. The famous comic strip Calvin and Hobbes features Calvin and his stuffed tiger, Hobbes. A tiger is also featured on the cover of the popular cereal Frosted Flakes (also marketed as "Frosties") bearing the name "Tony the Tiger".

The Tiger is the national animal of Bangladesh, Nepal, India[93] (Bengal Tiger)[94] Malaysia (Malayan Tiger), North Korea and South Korea (Siberian Tiger).
World's favourite animal
In a poll conducted by Animal Planet, the Tiger was voted the world's favourite animal, narrowly beating man's best friend, the dog. More than 50,000 viewers from 73 countries voted in the poll. The tiger received 21 percent of the vote, the dog 20, the dolphin 13, the horse 10, the lion 9, the snake 8, followed by the elephant, the chimpanzee, the orangutan and the whale.[95][96][97][98]
Animal behaviourist Candy d'Sa, who worked with Animal Planet on the list, said: "We can relate to the tiger, as it is fierce and commanding on the outside, but noble and discerning on the inside".[95]
Callum Rankine, international species officer at the World Wildlife Federation conservation charity, said the result gave him hope. "If people are voting tigers as their favourite animal, it means they recognise their importance, and hopefully the need to ensure their survival," he said.[95]
Gallery
-
Picture of Felis tigris (Panthera tigris) subspecies unknown
-
Dervish with a lion and a tiger. Mughal painting, c. 1650
-
Bengal tiger
-
Sumatran tiger
-
Siberian Tiger
-
Siberian tiger
-
Bengal tiger cooling off at Bandhavghar, India
-
Vibrissae of a Tiger at Chester Zoo
See also
- Black tiger (animal)
- Maltese Tiger
- Project Tiger, India
- Siegfried & Roy, two famous tamers of tigers
- Tiger Temple, a Buddhist temple in Thailand famous for its tame tigers
Cited references
- ^ a b Template:IUCN2006 Database entry includes justification for why this species is endangered.
- ^ Save The Tiger Fund | Wild Tiger Conservation
- ^ a b "Encyclopaedia Britannica Online - Tiger (Panthera tigris)".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Cat Specialist Group.
- ^ "BBC Wildfacts – Tiger".
- ^ Liddell, Henry George and Robert Scott (1980). A Greek-English Lexicon (Abridged Edition). United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-910207-4.
- ^ Tiger at the Online Etymology Dictionary
- ^ Template:La icon Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I. Editio decima, reformata. Holmiae. (Laurentii Salvii). pp. p. 824.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ ""Panther"". Online Etymology Dictionary. Douglas Harper. Retrieved 2007-07-05.
- ^ ""WIKI Answers article on 'Group of tigers'"".
- ^ Van den Hoek Ostende. 1999. Javan Tiger - Ruthlessly hunted down. 300 Pearls - Museum highlights of natural diversity. Downloaded on August 11, 2006.
- ^ Sunquist, Mel and Fiona Sunquist. 2002. Wild Cats of the World. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago
- ^ Sunquist, Mel and Fiona Sunquist. 2002. Wild Cats of the World. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago
- ^ Task force says tigers under siege
- ^ Wade, Matt (February 15, 2008), "Threat to a national symbol as India's wild tigers vanish", The Age (Melbourne), p. 9
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "No tigers found in Sariska: CBI". DeccanHerald.com. Retrieved 2007-07-20. (Archive).
- ^ "Laboratory of Genomic Diversity LGD".
- ^ Template:IUCN2006 Database entry includes a brief justification of why this subspecies is critically endangered and the criteria used.
- ^ Cracraft J., Feinstein J., Vaughn J., Helm-Bychowski K. (1998) Sorting out tigers (Panthera tigris) Mitochondrial sequences, nuclear inserts, systematics, and conservation genetics. Animal Conservation 1: 139–150.
- ^ Sunquist, Mel and Fiona Sunquist. 2002. Wild Cats of the World. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago
- ^ www.china.org.cn Retrieved on 6 October 2007
- ^ a b 绝迹24年华南虎重现陕西 村民冒险拍下照片
- ^ BBC NEWS | World | Asia-Pacific | Rare China tiger seen in the wild
- ^ Bambang M. 2002. In search of 'extinct' Javan tiger. The Jakarta Post (October 30).
- ^ Harimau jawa belum punah! (Indonesian Javan Tiger website)
- ^ a b "The Caspian Tiger - Panthera tigris virgata".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "The Caspian Tiger at www.lairweb.org.nz".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "History of big cat hybridisation".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Guggisberg, C. A. W. (1975). Wild Cats of the World. New York: Taplinger Publishing. ISBN 0-8008-8324-1.
- ^ a b Markel, Scott (2003). Sequence Analysis in a Nutshell: a guide to common tools and databases. Sebastopol, California: O'Reily. ISBN 0-596-00494-X.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "tigon - Encyclopædia Britannica Article".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c "WWF – Tigers – Ecology". Cite error: The named reference "WWF" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b c d e Template:De icon Vratislav Mazak: Der Tiger. Nachdruck der 3. Auflage von 1983. Westarp Wissenschaften Hohenwarsleben, 2004 ISBN 3 894327596 Cite error: The named reference "der-tiger" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Sunquist, Mel and Fiona Sunquist. 2002. Wild Cats of the World. University Of Chicago Press, Chicago.
- ^ Graham Batemann: Die Tiere unserer Welt Raubtiere, Deutsche Ausgabe: Bertelsmann Verlag, 1986.
- ^ Matthiessen, Peter. 2000. Tigers in the Snow, p. 47. The Harvill Press, London.
- ^ a b c Matthiessen, Peter (2001). Tigers In The Snow. North Point Press. ISBN 0865475962.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Tigers: Senses". Busch Gardens Animal Information Database. Retrieved 2006-06-22.
- ^ a b "White tigers".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ The white tiger today and the unusual white lion, [1]
- ^ White Tigers, [2]
- ^ "White Tiger Facts".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ White Tigers, [3]
- ^ Snow Tigers, [4]
- ^ The white tiger today and the unusual white lion, [5]
- ^ [6]
- ^ a b "Zoogoer - Tiger, Panthera tigris".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Karanth, K.U., Nichols, J.D., Seidensticker, J., Dinerstein, E., Smith, J.L.D., McDougal, C., Johnsingh, A.J.T., Chundawat, R.S. (2003) Science deficiency in conservation practice: the monitoring of tiger populations in India. Animal Conservation (61): 141-146 Full text
- ^ a b "Sympatric Tiger and Leopard: How two big cats coexist in the same area". Ecology.info
- ^ Man-eaters. The tiger and lion, attacks on humans
- ^ Schaller. G The Deer and the Tiger: A Study of Wildlife in India 1984, University Of Chicago Press
- ^ Sankhala 1997, p. 23.
- ^ a b c Perry, Richard (1965). The World of the Tiger. pp. pp.260. ASIN: B0007DU2IU.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ a b Mills, Stephen (2004). Tiger. pp. pp.168. ISBN 1552979490.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ Sankhala 1997, p. 17.
- ^ Tiger – BangaliNET.com
- ^ Tiger – Oakland Zoo
- ^ Sunquist, Fiona & Mel Sunquist. 1988. Tiger Moon. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
- ^ Karanth, K. Ullas (2000). "Behavioural correlates of predation by tiger (Panthera tigris), leopard (Panthera pardus) and dhole (Cuon alpinus) in Nagarahole, India". Journal of Zoology. 250: 255–265. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2000.tb01076.x. Retrieved 2008-06-05.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "The IUCN-Reuters Media Awards 2000". IUCN. Retrieved 2007-08-17.
- ^ "Amur Tiger". Save The Tiger Fund. Retrieved 2007-08-17.
- ^ Big Cat Recuse - Tiger
- ^ [7].
- ^ Simon Denyer (March 6, 2006). "Dalai Lama offers Indian tigers a lifeline". iol.co.za. Retrieved 2007-07-20.
- ^ Justin Huggler (February 18, 2006). "Fur flies over tiger plight". New Zealand Herald. Tibet.com. Retrieved 2007-07-20.
- ^ "Dalai Lama campaigns for wildlife". BBC News. April 6, 2005. Retrieved 2007-07-20.
- ^ Indian tiger isn't 100 per cent “swadeshi (Made in India)”; by Pallava Bagla; Indian Express Newspaper; November 19, 1998
- ^ Tainted Royalty, Wildlife: Royal Bengal Tiger, a controversy arises over the purity of the Indian tiger after DNA samples show Siberian tiger genes. By Subhadra Menon. India Today, November 17, 1997
- ^ The Tale of Tara, 4: Tara's Heritage from Tiger Territory website
- ^ Genetic pollution in wild Bengal tigers, Tiger Territory website
- ^ Interview with Billy Arjan Singh: Dudhwa's Tiger man, October 2000, Sanctuary Asia Magazine, sanctuaryasia.com
- ^ Mitochondrial DNA sequence divergence among big cats and their hybrids by Pattabhiraman Shankaranarayanan* and Lalji Singh*, *Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, Uppal Road, Hyderabad 500 007, India, Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics, CCMB Campus, Uppal Road, Hyderabad 500 007, India
- ^ Central Zoo Authority of India (CZA), Government of India
- ^ "Indians Look At Their Big Cats' Genes", Science, Random Samples, Volume 278, Number 5339, Issue of 31 October 1997, 278: 807 (DOI: 10.1126/science.278.5339.807b) (in Random Samples),The American Association for the Advancement of Science
- ^ BOOKS By & About Billy Arjan Singh
- ^ Book - Tara : The Cocktail Tigress/Ram Lakhan Singh. Edited by Rahul Karmakar. Allahabad, Print World, 2000, xxxviii, 108 p., ills., $22. ISBN 81-7738-000-1. A book criticizing Billy Arjan Singh's release of hand reared hybrid Tigress Tara in the wild at Dudhwa National Park in India
- ^ FAQs | Save China's Tigers
- ^ Xinhua - English
- ^ FAQs | Save China's Tigers
- ^ vide Royal Tiger (nom-de-plume) in The Manpoora Tiger - about a Tiger Hunt in Rajpootanah. (1836) Bengal Sporting Magazine, Vol IV. reproduced in The Treasures of Indian Wildlife
- ^ Man-eaters. The tiger and lion, attacks on humans
- ^ Man-eaters. The tiger and lion, attacks on humans
- ^ Increasing tiger attacks trigger panic around Tadoba-Andhari reserve
- ^ BBC NEWS | Programmes | From Our Own Correspondent | Beijing's penis emporium
- ^ WWF: Chinese tiger farms must be investigated
- ^ WWF: Breeding tigers for trade soundly rejected at cites
- ^ a b c d e Lloyd, J & Mitchinson, J: "The Book of General Ignorance". Faber & Faber, 2006.
- ^ Tiger Culture | Save China's Tigers
- ^ a b c d Cooper, JC (1992). Symbolic and Mythological Animals. London: Aquarian Press. pp. 226–27. ISBN 1-85538-118-4. Cite error: The named reference "Cooper92" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Balambal, V (1997). "19. Religion - Identity - Human Values - Indian Context". Bioethics in India: Proceedings of the International Bioethics Workshop in Madras: Biomanagement of Biogeoresources, 16-19 Jan. 1997. Eubios Ethics Institute. Retrieved 2007-10-08.
- ^
Summers, Montague (1966). The Werewolf. University Books. p. 21.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^
Encyclopædia Britannica. 1910–1911.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)CS1 maint: date format (link) - ^ National Animal Panthera tigris, Tiger is the national animal of India Govt. of India website,
- ^ "National Symbols of India". High Commission of India, London. Retrieved 2007-10-25.
- ^ a b c Tiger tops dog as world's favourite animal
- ^ Pers® - The Tiger is the World's Favorite Animal
- ^ CBBC Newsround | Animals | Tiger 'is our favourite animal'
- ^ Endangered tiger earns its stripes as the world's most popular beast | Independent, The (London) | Find Articles at BNET.com
References
- Brakefield, T. (1993). Big cats kingdom of might, Voyageur press.
- Dr. Tony Hare. (2001) Animal Habitats P. 172 ISBN 0-8160-4594-1
- Kothari, Ashok S. & Chhapgar, Boman F. (eds). 2005. The Treasures of Indian Wildlife. Bombay Natural History Society and Oxford University Press, Mumbai.
- Mazák, V. (1981). Panthera tigris. (PDF). Mammalian Species, 152: 1-8. American Society of Mammalogists.
- Nowak, Ronald M. (1999) Walker's Mammals of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-5789-9
- Template:Harvard reference Abridged German translation of Return of the Tiger, Lustre Press, 1993.
- Seidensticker, John. (1999) Riding the Tiger. Tiger Conservation in Human-dominated Landscapes Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521648351
External links
- 21st Century Tiger: information about tigers and conservation projects
- Save China's Tigers: information about tigers and the South China Tiger rewilding project in Africa
- Save The Tiger Fund
- Sundarbans Tiger Project: research and conservation of tigers in the largest remaining mangrove forest in the world
- Tiger Canyons Homepage: information about tigers and the Crossbred Tiger Rewilding project
- Tigers in Crisis
- WWF – Tigers
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA








