111.235.90.223 (talk) No edit summary Tags: Reverted possible vandalism Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit Possible vandalism |
PohranicniStraze (talk | contribs) m Reverted edits by 111.235.90.223 (talk) to last version by Potapt Tag: Rollback |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Province of Thailand}} |
{{Short description|Province of Thailand}} |
||
{{Infobox settlement |
|||
| name = Nonthaburi |
| name = Nonthaburi |
||
| native_name = นนทบุรี |
| native_name = นนทบุรี |
||
Revision as of 06:48, 14 October 2021
Nonthaburi
นนทบุรี | |
|---|---|
(left-to-right, top-to-bottom) Leaning Chedi of Wat Paramaiyikawat, Wat Chaloem Phra Kiat Worawihan, Wat Ku, Old Provincial Hall of Nonthaburi, Impact, Mueang Thong Thani, A train of MRT Purple Line | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Nonthaburi Province | |
| Coordinates: 13°51′45″N 100°30′52″E / 13.86250°N 100.51444°E | |
| Founded | 1561 |
| Incorporated into Bangkok | 1943 |
| Separated from Bangkok | 1946 |
| Capital | Nonthaburi |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Suchin Chaichumsak (since October 2019)[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 622 km2 (240 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 75th |
| Population (2018)[3] | |
| • Total | 1,246,295 |
| • Rank | Ranked 16th |
| • Density | 2,003.7/km2 (5,190/sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 2nd |
| Human Achievement Index | |
| • HAI (2017) | 0.6788 "high" Ranked 4th |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 11xxx |
| Calling code | 02 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-12 |
| Vehicle registration | นนทบุรี |
| Website | www |
Nonthaburi (Thai: นนทบุรี, pronounced [nōn.tʰá(ʔ).bū.rīː]) is one of the central provinces (changwat) of Thailand, established by the Act Establishing Changwat Samut Prakan, Changwat Nonthaburi, Changwat Samut Sakhon and Changwat Nakhon Nayok, Buddhist Era 2489 (1946), which came into force on 9 May 1946.[5]
Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise) Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Pathum Thani, Bangkok, and Nakhon Pathom. Nonthaburi is the most densely populated province after Bangkok. The Bang Kwang Central Prison is in the province.
Geography
Nonthaburi is directly northwest of Bangkok on the Chao Phraya River. The province is part of the greater Bangkok Metropolitan Area. In most parts it is as urbanized as the capital,[6] and the boundary between the two provinces is nearly unrecognizable. There is no forest area in the province.[7]
History
Ayutthaya Period
Nonthaburi was established for more than 400 years. It was originally a densely populated village known in the name of "Ban Talat Khwan" which is a fertile land because it is on the bank of the Chao Phraya River and a famous fruit orchard of Ayutthaya.
In 1549, Maha Chakkraphat raised Ban Talat Khwan as Nonthaburi. Nonthaburi was originally located at Bang Kraso today with Wat Hua Muang (Nowadays is an abandoned temple that the government has used as the location of Phra Nang Klao Hospital) as the northern district and there is a temple at the end of the city as the southern area.
In 1636, King Prasat Thong ordered to dig for the southern canal at Tai Mueang Temple go through the front of Khema Temple and became the new Chao Phraya River at present, the former Chao Phraya River is shoal and eventually became a canal.
During the reign of King Narai in 1665, he realized that when the Chao Phraya River changed the walkway makes it easier for the enemy to approach the city, he ordered a fortress to be built at the estuary and moved Nonthaburi to the estuary at the same time.
Rattanakosin period
In 1916, King Rama VI changed the word "city" to "province", Nonthaburi city was renamed to be called Nonthaburi province. In 1942, when the economic downturn occurred after World War II, the government collapsed Nonthaburi to save the budget. By transferring Muang Nonthaburi District and Pak Kret District to Phra Nakhon province (now Bangkok) and transfer Bang Kruai District, Bang Yai District and Bang Bua Thong District up to Thonburi province, until Nonthaburi has been raised as a province again in 1946, districts have returned to the administrative area of the province as it was until now.
Symbols
The provincial seal shows earthenware, a traditional product of Nonthaburi. The provincial flower and tree is the yellow flame tree (Peltophorum pterocarpum).
The provincial slogan translates to "Grand royal mansion, renowned Suan Somdet, Ko Kret's pottery, famous ancient temples, tasty durians, and the beautiful government office". The royal mansion refers to Phra Tamnak Nonthaburi in Mueang Nonthaburi District, the former residence of Prince Maha Vajiralongkorn. Princess Mother Srinagarindra Garden (Suan Somdet) is a water garden with a statue of princess Srinagarindra in the Pak Kret District. The provincial administration building once received an award as the most beautiful such building by the Ministry of Interior.
Agriculture
Nonthaburi Province is renowned for growing the best durians in the country. Durian has been a well-known fruit in this province for 400 years.[8] The fruit is known as "Durian Non" which means durian from Nonthaburi Province.[9] It is also known as the most expensive durian in the world.[8] There are six groups of Nonthaburi durian which are Kop, Luang, Kan Yao, Kampan, Thong Yoi, and miscellaneous.[9] Most durian orchards are near rivers such as the Chao Phraya. This is because the soil next to the river is good for planting which is also good for durian trees.[8] Many durian orchards have disappeared due to flooding and pollution.[9] The price of durian Non depends on its group. Kan Yao is the most expensive, starting from around 10,000 baht up to 20,000 baht (or about US$600) for one durian. The Kan Yao itself is not easy to find in normal markets. The main reason for the high price is because it is rare. The recent flood in 2011 cleared out almost all of the durian trees in Nonthaburi, and only a few trees have been newly planted.[8] Also, residential areas are expanding into agricultural areas.[9]
Health
Nonthaburi's main hospital operated by the Ministry of Public Health is Phra Nang Klao Hospital. It is also the location of the largest psychiatric hospital in Thailand- Srithanya Hospital.
Religion
Administrative divisions

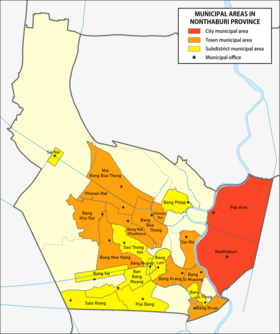
Provincial government
The province is divided into six districts (amphoes).[3] The districts are further subdivided into 52 subdistricts (tambons) and 433 villages (mubans).
Local government
As of 8 September 2020 there are: one Nonthaburi Provincial Administrative Organization - PAO (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and twenty-two municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. The capital Nonthaburi and Pak Kret have city (thesaban nakhon) status. Further ten have town (thesaban mueang) status and ten subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon).[3]
| City municipalities | People | ||||
| 1 | Nonthaburi[10] | 254,375 | 2 | Pak Kret[11] | 190,272 |
| Town municipalities | People | ||||
| 1 | Mai Bang Bua Thong[12] | 54,554 | 6 | Bang Kruai[13] | 44,138 |
| 2 | Bang Bua Thong[14] | 51,420 | 7 | Bang Khu Rat[15] | 40,070 |
| 3 | Bang Rak Pattana[16] | 46,766 | 8 | Bang Si Mueang[17] | 32,880 |
| 4 | Phimon Rat[18] | 46,803 | 9 | Sai Ma[19] | 23,316 |
| 5 | Bang Mae Nang[20] | 45,974 | 10 | Bang Krang[21] | 23,010 |
| Subdistrict mun. | People | ||||
| 1 | Plai Bang[22] | 45,573 | 6 | Bang Yai[22] | 11,620 |
| 2 | Sao Thong Hin[23] | 39,315 | 7 | Bang Si Thong[24] | 11,203 |
| 3 | Sala Klang[25] | 18,582 | 8 | Bang Phlap[26] | 10,417 |
| 4 | Ban Bang Muang[27] | 17,526 | 9 | Bang Muang[22] | 5,843 |
| 5 | Bang Len[28] | 16,050 | 10 | Sai Noi[22] | 2,547 |
The non-municipal areas are administered by 23 Subdistrict Administrative
Organizations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[29]
| Municipalities | Communities | |
| Nonthaburi[30] | 93 | |
| Bang Si Muang[31] | 41 |
Human achievement index 2017
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 10 | 3 | 34 | 3 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |

|
 |

|
|
| 61 | 30 | 1 | 73 |
| Province Nonthaburi, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.6788 is "high", occupies place 4 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the Human achievement index (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[4]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
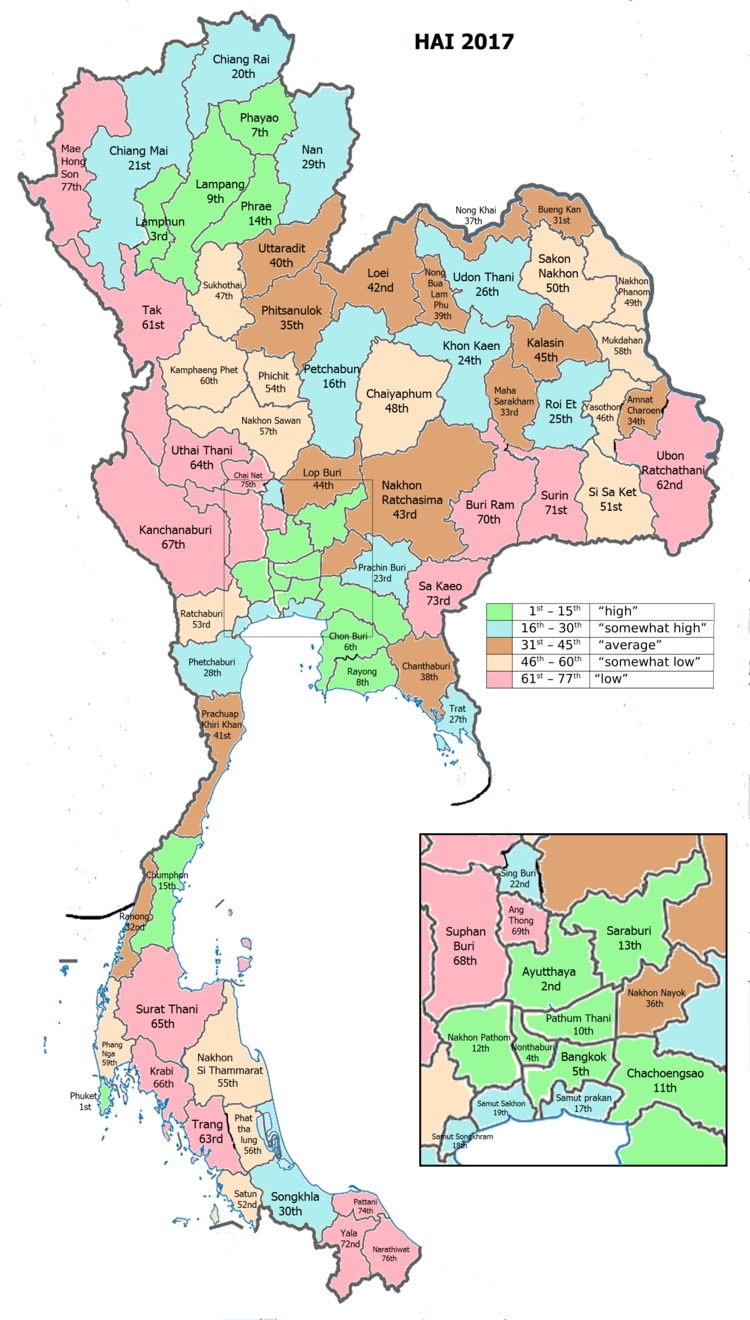
|
See also
References
- ^ "ประกาศสำนักนายกรัฐมนตรี เรื่อง แต่งตั้งข้าราชการพลเรือนสามัญ" [Announcement of the Prime Minister's Office regarding the appointment of civil servants] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 136 (Special 242 Ngor). 11. 28 September 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- ^ Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)[dead link] - ^ a b c "สถิติทางการทะเบียน" [Registration statistics]. bora.dopa.go.th. Department of Provincial Administration (DOPA). December 2019. Retrieved 22 September 2020.
Download จำนวนประชากร ปี พ.ศ.2562 - Download population year 2019
- ^ a b Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- ^ พระราชบัญญัติจัดตั้งจังหวัดสมุทรปราการ จังหวัดนนทบุรี จังหวัดสมุทรสาคร และจังหวัดนครนายก พุทธศักราช ๒๔๘๙ [Act Establishing Changwat Samut Prakan, Changwat Nonthaburi, Changwat Samut Sakhon and Changwat Nakhon Nayok, Buddhist Era 2489 (1946)] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 63 (29 Kor): 315–317. 9 May 1946. Retrieved 2 December 2019.
- ^ "นนทบุรี จูงมือเพื่อนสาว เที่ยวใกล้กรุงเทพ".
- ^ "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ a b c d Gasik, Lindsay. "The Most Expensive Durian In The World; Nonthaburi, Thailand". Year of the Durian. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
- ^ a b c d [1] สำนักบรรณสารสนเทส มสธ. ทุเรียนนนท์ ฝ่ายอุทยานการศึกษา สำนักการศึกษาต่อเนื่อง มหาวิทยาลัยสุโขทัยธรรมาธิราช (Accessed on 9 September 2015)
- ^ "พระราชกฤษฎีกาจัดตั้งเทศบาลนครนนทบุรี จังหวัดนนทบุรี พ.ศ. ๒๕๓๘" [Royal Decree Establish of Nonthaburi city municipality, Nonthaburi province, B.E.2538 (1995)] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 112 (40 Kor): 29–32. 24 September 1995. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ "พระราชกฤษฎีกาจัดตั้งเทศบาลนครปากเกร็ด จังหวัดนนทบุรี พ.ศ. ๒๕๔๓" [Royal Decree Establish of Pak Kret city municipality, Nonthaburi province, B.E.2543 (2000)] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 117 (10 Kor): 25–28. 10 February 2000. Retrieved 10 December 2019, effectively on 20 April 2000
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "ประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย เรื่อง เป็ลี่ยนชี่อองค์การบริหารส่วนตำบลบางบัวทอง อำเภอบาบัวทอง จังหวัดนนทบุรี เป็นใหม่บางบัวทอง และจัดตั้งเทศบาลเมืองใหม่บางบัวทอง" [Notification of the Ministry of Interior Re: Change name of Bang Bua Thong Subdistrict Administrative Organization, Bang Bua Thong district, Nonthaburi province Is Mai Bang Bua Thong and establish as Mai Bang Bua Thong town municipality.] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 137 (Special 204 Ngor): 16–17. 8 September 2020. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
- ^ "พระราชกฤษฎีกาจัดตั้งเทศบาลเมืองบางกรวย พ.ศ. ๒๕๔๕" [Royal Decree Bang Kruai town municipality B.E.2545] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 119 (122 Kor): 5–8. 16 December 2002. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ^ "พระราชกฤษฎีกาจัดตั้งเทศบาลเมืองบางบัวทอง จังหวัดนนทบุรี พ.ศ. ๒๔๘๐" [Royal Decree Establish of Bang Bua Thong town municipality, Nonthaburi province, B.E.2480 (1937)] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 54: 1859–1862. 14 March 1937. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ "ประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย เรื่อง จัดตั้งองค์การบริหารส่วนตำบลบางคูรัด อำเภอบางบัวทอง จังหวัดนนทบุรี เป็นเทศบาลเมืองบางคูรัด" [Notification of the Ministry of Interior Re: Establishment of Bang Khu Rat Subdistrict Administrative Organization, Bang Bua Thong district, Nonthaburi province Is Bang Khu Rat town municipality.] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 136 (Special 33 Ngor): 15. 6 February 2019. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ^ "ประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย เรื่อง จัดตั้งองค์การบริหารส่วนตำบลบางรักพัฒนา อำเภอบางบัวทอง จังหวัดนนทบุรี เป็นเทศบาลเมืองบางรักพัฒนา" [Notification of the Ministry of Interior Re: Establishment of Bang Rak Pattana Subdistrict Administrative Organization, Bang Bua Thong district, Nonthaburi province Is Bang Rak Pattana town municipality.] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 136 (Special 265 Ngor): 5. 25 October 2019. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ^ "ประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย เรื่อง เปลี่ยนแปลงฐานะเทศบาลตำบลบางศรีเมือง อำเภอเมืองนนทบุรี จังหวัดนนทบุรี เป็นเทศบาลเมืองบางศรีเมือง" [Notification of the Ministry of Interior Re: Change status of Bang Si Mueang subdistrict municipality, Mueang Nonthaburi district, Nonthaburi province to Bang Si Mueang town municipality.] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 123 (Special Section 29 Ngor): 5. 23 February 2006. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ "ประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย เรื่อง จัดตั้งองค์การบริหารส่วนตำบลพิมลราช อำเภอบางบัวทอง จังหวัดนนทบุรี เป็นเทศบาลเมืองพิมลราช" [Notification of the Ministry of Interior Re: Establishment of Phimon Rat Subdistrict Administrative Organization, Bang Bua Thong district, Nonthaburi province Is Phimon Rat town municipality.] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 131 (Special 41 Ngor): 5. 4 March 2014. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ^ "ประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย เรื่อง เปลี่ยนแปลงฐานะเทศบาลตำบลไทรม้า อำเภอเมืองนนทบุรี จังหวัดนนทบุรี เป็นเทศบาลเมืองไทรม้า" [Notification of the Ministry of Interior Re: Establishment of Sai Ma Subdistrict Municipality, Mueang Nonthaburi district, Nonthaburi province Is Sai Ma town municipality.] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 137 (Special 172 Ngor): 9–10. 29 July 2020. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ "ประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย เรื่อง จัดตั้งองค์การบริหารส่วนตำบลบางแม่นาง อำเภอบาบัวทอง จังหวัดนนทบุรี เป็นเทศบาลเมืองบางแม่นาง" [Notification of the Ministry of Interior Re: Establishment of Bang Mae Nang Subdistrict Administrative Organization, Bang Bua Thong district, Nonthaburi province Is Bang Mae Nang town municipality.] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 137 (Special 66 Ngor): 8. 20 March 2020. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ "ประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย เรื่อง จัดตั้งองค์การบริหารส่วนตำบลบางกร่าง อำเภอเมืองนนทบุรี จังหวัดนนทบุรี เป็นเทศบาลเมืองบางกร่าง" [Notification of the Ministry of Interior Re: Establishment of Bang Krang Subdistrict Administrative Organization, Mueang Nonthaburi district, Nonthaburi province Is Bang Krang town municipality.] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 137 (Special 132 Ngor): 6. 4 June 2020. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ a b c d "พระราชบัญญัติ เปลี่ยนแปลงฐานะของสุขาภิบาลเป็นเทศบาล พ.ศ.๒๕๔๒" [Royal Decree: Change Sanitation district to Municipality Act B.E. 2542 (1999)] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 116 (9 Kor): 1–4. 24 February 1999. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
Sanitation districts Plai Bang, Bang Yai, Bang Muang and Sai Noi are upgraded to subdistrict municipality, effectively 25 May 1999
- ^ "Number of local government organizations: Summary elevating local authorities". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 12 September 2011. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
No.4.15 Established Sao Thong Hin Subdistrict Administrative Organization (SAO), Bang Yai district, Nonthaburi province is Sao Thong Hin subdistrict municipality.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations: Summary elevating local authorities". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 31 May 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
No.4.28 Established Bang Si Thong Subdistrict Administrative Organization (SAO), Bang Kruai district, Nonthaburi province is Bang Si Thong subdistrict municipality, effectively 5 September 2013.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations: Summary elevating local authorities". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 15 August 2008. Retrieved 12 January 2009.
Established Sala Klang Subdistrict Administrative Organization (SAO), Bang Kruai district, Nonthaburi province is Sala Klang subdistrict municipality.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations: Summary elevating local authorities". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 3 September 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
No.4.119 Established Bang Phlap Subdistrict Administrative Organization (SAO), Pak Kret district, Nonthaburi province is Bang Phlap subdistrict municipality, effectively 6 September 2013.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations: Summary elevating local authorities". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 12 September 2011. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
No.4.25 Established Ban Bang Muang Subdistrict Administrative Organization (SAO), Bang Yai district, Nonthaburi province is Ban Bang Muang subdistrict municipality, effectively 30 September 2011.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations: Summary elevating local authorities". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 29 June 2011. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
No.4.16 Established Bang Len Subdistrict Administrative Organization (SAO), Bang Yai district, Nonthaburi province is Bang Len subdistrict municipality, effectively 30 September 2011.
- ^ Department of Provincial Administration (DOPA), List of 5,324 SAO's information as of date 20 December 2019, 23 SAO's (no.1751-1776) were established in 1995 (9), in 1996 (8) and in 1997 (6).
- ^ "ดูทั้งหมด" [view all]. nakornnont.go.th (in Thai). 2020. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
93 communities.
- ^ "ข้อมูลชุมชน" [Community information]. bangsrimuang.go.th (in Thai). 2020. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
There are 41 communities.








