Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
consistent citation formatting |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Drugbox |
{{Drugbox |
||
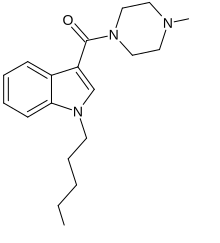
| IUPAC_name = (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-(1-pentylindol-3-yl)methanone |
| IUPAC_name = (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-(1-pentylindol-3-yl)methanone |
||
| image = MEPIRAPIM_structure. |
| image = MEPIRAPIM_structure.svg |
||
<!--Clinical data--> |
<!--Clinical data--> |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''MEPIRAPIM''' is an [[indole]]-based [[cannabinoid]] which differs from [[JWH-018]] by having a 4-methylpiperazine group in place of the naphthyl group<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.caymanchem.com/app/template/Product.vm/catalog/15388 | title=MEPIRAPIM | publisher=Cayman Chemical | access-date=23 June 2015}}</ref> and has been used as an active ingredient in [[synthetic cannabis]] products. It was first identified in Japan in 2013, alongside [[FUBIMINA]].<ref name="Uchiyama_2014">{{cite journal | title=Two new synthetic cannabinoids, AM-2201 benzimidazole analog (FUBIMINA) and (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)(1-pentyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (MEPIRAPIM), and three phenethylamine derivatives, 25H-NBOMe 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl analog, 25B-NBOMe, and 2C-N-NBOMe, identified in illegal products | journal=Forensic Toxicology | vauthors=Uchiyama N, Shimokawa Y, Matsuda S, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y | date=January 2014 | volume=32 | issue=1 | pages=105–115 | doi=10.1007/s11419-013-0217-2| s2cid=32599561 }}</ref> MEPIRAPIM acts as a [[T-type calcium channel ]]inhibitor and is only minimally active at the central CB1 receptor.<ref>{{ |
'''MEPIRAPIM''' is an [[indole]]-based [[cannabinoid]] which differs from [[JWH-018]] by having a 4-methylpiperazine group in place of the naphthyl group<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.caymanchem.com/app/template/Product.vm/catalog/15388 | title=MEPIRAPIM | publisher=Cayman Chemical | access-date=23 June 2015}}</ref> and has been used as an active ingredient in [[synthetic cannabis]] products. It was first identified in Japan in 2013, alongside [[FUBIMINA]].<ref name="Uchiyama_2014">{{cite journal | title=Two new synthetic cannabinoids, AM-2201 benzimidazole analog (FUBIMINA) and (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)(1-pentyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (MEPIRAPIM), and three phenethylamine derivatives, 25H-NBOMe 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl analog, 25B-NBOMe, and 2C-N-NBOMe, identified in illegal products | journal=Forensic Toxicology | vauthors=Uchiyama N, Shimokawa Y, Matsuda S, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y | date=January 2014 | volume=32 | issue=1 | pages=105–115 | doi=10.1007/s11419-013-0217-2| s2cid=32599561 }}</ref> MEPIRAPIM acts as a [[T-type calcium channel ]]inhibitor and is only minimally active at the central CB1 receptor.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kevin RC, Mirlohi S, Manning JJ, Boyd R, Cairns EA, Ametovski A, Lai F, Luo JL, Jorgensen W, Ellison R, Gerona RR, Hibbs DE, McGregor IS, Glass M, Connor M, Bladen C, Zamponi GW, Banister SD | display-authors = 6 | title = Putative Synthetic Cannabinoids MEPIRAPIM, 5F-BEPIRAPIM (NNL-2), and Their Analogues Are T-Type Calcium Channel (Ca<sub>V</sub>3) Inhibitors | journal = ACS Chemical Neuroscience | volume = 13 | issue = 9 | pages = 1395–1409 | date = May 2022 | pmid = 35442021 | doi = 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00822 | s2cid = 248264685 }}</ref> |
||
==Legality== |
==Legality== |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
Sweden's public health agency suggested to classify MEPIRAPIM as hazardous substance on November 10, 2014.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se/nyheter-och-press/nyhetsarkiv/2014/november/cannabinoider-foreslas-bli-klassade-som-halsofarlig-vara/ | title=Cannabinoider föreslås bli klassade som hälsofarlig vara | access-date=29 June 2015}}</ref> |
Sweden's public health agency suggested to classify MEPIRAPIM as hazardous substance on November 10, 2014.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se/nyheter-och-press/nyhetsarkiv/2014/november/cannabinoider-foreslas-bli-klassade-som-halsofarlig-vara/ | title=Cannabinoider föreslås bli klassade som hälsofarlig vara | access-date=29 June 2015}}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
== See also == |
||
* [[APICA (synthetic cannabinoid drug)|APICA]] |
* [[APICA (synthetic cannabinoid drug)|APICA]] |
||
* [[AM-2201]] |
* [[AM-2201]] |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
* [[THJ-2201]] |
* [[THJ-2201]] |
||
==References== |
== References == |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
[[Category:Designer drugs]] |
[[Category:Designer drugs]] |
||
[[Category:Piperazines]] |
[[Category:Piperazines]] |
||
{{cannabinoid-stub}} |
{{cannabinoid-stub}} |
||
Latest revision as of 05:17, 29 May 2023
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H27N3O |
| Molar mass | 313.445 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
MEPIRAPIM is an indole-based cannabinoid which differs from JWH-018 by having a 4-methylpiperazine group in place of the naphthyl group[1] and has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products. It was first identified in Japan in 2013, alongside FUBIMINA.[2] MEPIRAPIM acts as a T-type calcium channel inhibitor and is only minimally active at the central CB1 receptor.[3]
Legality[edit]
Sweden's public health agency suggested to classify MEPIRAPIM as hazardous substance on November 10, 2014.[4]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "MEPIRAPIM". Cayman Chemical. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- ^ Uchiyama N, Shimokawa Y, Matsuda S, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (January 2014). "Two new synthetic cannabinoids, AM-2201 benzimidazole analog (FUBIMINA) and (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)(1-pentyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (MEPIRAPIM), and three phenethylamine derivatives, 25H-NBOMe 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl analog, 25B-NBOMe, and 2C-N-NBOMe, identified in illegal products". Forensic Toxicology. 32 (1): 105–115. doi:10.1007/s11419-013-0217-2. S2CID 32599561.
- ^ Kevin RC, Mirlohi S, Manning JJ, Boyd R, Cairns EA, Ametovski A, et al. (May 2022). "Putative Synthetic Cannabinoids MEPIRAPIM, 5F-BEPIRAPIM (NNL-2), and Their Analogues Are T-Type Calcium Channel (CaV3) Inhibitors". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 13 (9): 1395–1409. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00822. PMID 35442021. S2CID 248264685.
- ^ "Cannabinoider föreslås bli klassade som hälsofarlig vara". Retrieved 29 June 2015.