m link Hainan Island Operation |
Solbin~enwiki (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
Hainan was historically part of [[Guangdong Province]] and [[Guangxi Province]], being as such, it was the Ch'iung-yai or Qiongya [[Circuit (political division)|Circuit]] (瓊崖道) in 1912 (the establishment of the [[Republic of China]]). In 1921, it was planned to become a [[Special administrative region (Republic of China)|Special Administrative Region]] (瓊崖特別行政區); in 1944, it became Hainan Special Administrative Region with 16 [[counties]] containing the [[South China Sea Islands]]. |
Hainan was historically part of [[Guangdong Province]] and [[Guangxi Province]], being as such, it was the Ch'iung-yai or Qiongya [[Circuit (political division)|Circuit]] (瓊崖道) in 1912 (the establishment of the [[Republic of China]]). In 1921, it was planned to become a [[Special administrative region (Republic of China)|Special Administrative Region]] (瓊崖特別行政區); in 1944, it became Hainan Special Administrative Region with 16 [[counties]] containing the [[South China Sea Islands]]. |
||
[[Image:Hainan people 02.JPG|thumb|right|250px|Hainan indigenous people {{Who|date=November 2009}}]] |
|||
During the 1920s and 30s, Hainan was a hotbed of [[Communist Party of China|Communist]] activity, especially after a bloody crackdown in [[Shanghai]], the [[Republic of China]] in 1927 drove many [[Communists]] into hiding. The Communists and the Li natives fought a vigorous [[guerrilla]] campaign against the [[Hainan Island Operation|Japanese occupation of Hainan]] (1939-45), but in retaliation over one third of the male population were killed by the Japanese. [[Feng Baiju]] led the [[Hainan Independent Column]] of fighters throughout the 1930s and 1940s. After the Japanese surrender in 1945 the [[Guomindang|Nationalist Party (KMT)]] re-established control. Hainan was one of the last areas of China controlled by the Republic of China. From March to May 1950, the [[Landing Operation on Hainan Island]] captured the island for the [[Communist Party of China|Chinese communists]]. [[Feng Baiju]] and his column of guerrilla fighters played an essential role in scouting for the landing operation and coordinated their own offensive from their jungle bases on the island. This allowed the Hainan takeover to be successful where the [[Battle of Kuningtou|Jinmen]] and [[Battle of Dengbu Island|Dengbu]] assaults had failed in the previous fall. The takeover was made possible by the presence of a local guerrilla force that was lacking on [[Jinmen]], [[Dengbu]], and [[Taiwan]]. Hence, while many observers of the Chinese civil war thought that the fall of Hainan to the Communists would be followed shortly by the fall of Taiwan, the lack of any communist guerrilla force on Taiwan and its sheer distance from the mainland made this impossible, as did the arrival of the [[United States Seventh Fleet|US 7th fleet]] in the [[Taiwan Strait]] after the outbreak of the [[Korean War]] in June. |
During the 1920s and 30s, Hainan was a hotbed of [[Communist Party of China|Communist]] activity, especially after a bloody crackdown in [[Shanghai]], the [[Republic of China]] in 1927 drove many [[Communists]] into hiding. The Communists and the Li natives fought a vigorous [[guerrilla]] campaign against the [[Hainan Island Operation|Japanese occupation of Hainan]] (1939-45), but in retaliation over one third of the male population were killed by the Japanese. [[Feng Baiju]] led the [[Hainan Independent Column]] of fighters throughout the 1930s and 1940s. After the Japanese surrender in 1945 the [[Guomindang|Nationalist Party (KMT)]] re-established control. Hainan was one of the last areas of China controlled by the Republic of China. From March to May 1950, the [[Landing Operation on Hainan Island]] captured the island for the [[Communist Party of China|Chinese communists]]. [[Feng Baiju]] and his column of guerrilla fighters played an essential role in scouting for the landing operation and coordinated their own offensive from their jungle bases on the island. This allowed the Hainan takeover to be successful where the [[Battle of Kuningtou|Jinmen]] and [[Battle of Dengbu Island|Dengbu]] assaults had failed in the previous fall. The takeover was made possible by the presence of a local guerrilla force that was lacking on [[Jinmen]], [[Dengbu]], and [[Taiwan]]. Hence, while many observers of the Chinese civil war thought that the fall of Hainan to the Communists would be followed shortly by the fall of Taiwan, the lack of any communist guerrilla force on Taiwan and its sheer distance from the mainland made this impossible, as did the arrival of the [[United States Seventh Fleet|US 7th fleet]] in the [[Taiwan Strait]] after the outbreak of the [[Korean War]] in June. |
||
[[Image:Haikou skyline 6 - 2009 09 07.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Haikou. A view south from Bin Hai road]] |
[[Image:Haikou skyline 6 - 2009 09 07.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Haikou. A view south from Bin Hai road]] |
||
| Line 297: | Line 297: | ||
== Transportation == |
== Transportation == |
||
[[Image:Hainan 1.JPG|thumb|180px|Sanya|right]] |
|||
[[Image:HainanSanya7.jpg|thumb|right|Sanya street]] |
|||
Before 1950 there were practically no transportation links with the interior of the island. The first roads were built in the early 20th century, but no major road construction was undertaken in the mountains until the 1950s. Parallel north–south roads along the east and west coasts and through the interior of the island constitute most of Hainan's road network. The freight-handling facilities of the island's ports have been improved, and Haikou has an international airport, the [[Haikou Meilan International Airport]]. |
Before 1950 there were practically no transportation links with the interior of the island. The first roads were built in the early 20th century, but no major road construction was undertaken in the mountains until the 1950s. Parallel north–south roads along the east and west coasts and through the interior of the island constitute most of Hainan's road network. The freight-handling facilities of the island's ports have been improved, and Haikou has an international airport, the [[Haikou Meilan International Airport]]. |
||
Revision as of 17:11, 28 January 2010
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | East Asia |
| Area rank | 42nd |
| Administration | |
China | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | approx. 8,180,000 |
Hainan (Chinese: 海南; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Hái-lâm, pinyin: , jyutping: literal meaning: "South of the Sea") is the smallest province of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Although the province comprises some two hundred islands scattered among three archipelagos off the southern coast, all but three percent of its land mass is on Hainan Island (Hainan Dao), from which the province takes its name. To say "Hainan" in China usually refers to Hainan Island itself. The PRC government claims Hainan's territories to extend to the southern Spratly Islands, Paracel Islands and other disputed marine territory. Hainan is also the largest Special Economic Zone laid out by Chinese leader Deng Xiaoping in the late 1980s.
Hainan Island is located in the South China Sea, separated from Guangdong's Leizhou Peninsula to the north by a shallow and narrow strait. It has an area of 33,920 square kilometers and is China's southernmost province. For centuries Hainan was part of Guangdong province, but in 1988 this resource-rich tropical island became a separate province. The capital is Haikou.
There are 8 major cities and 10 counties on Hainan and the Xisha Islands in the south of Sanya City.[1]
The major cities of Hainan Island are (going clockwise): Haikou, Wenchang, Qionghai, Wanning, Wuzhishan (or five finger Mountain), Sanya, Dongfang, Danzhou.
And its counties are (going in the clock circle way): Ding'an, Tunchang, Qiongzhong, Lingshui, Baoting, Ledong, Baisha, Changjiang, Lingao and Chengmai.
History
Hainan Island was called the Pearl Cliffs (珠崖 Zhūyá), Fine Jade Cliffs (瓊崖 Qióngyá), and the Fine Jade Land (瓊州 Qióngzhōu). The latter two gave rise to the province's abbreviation, Qióng (琼 in Simplified Chinese), referring to the greenery cover on the island.
Hainan first enters written Chinese history in 110 BC, when the Han Dynasty established a military garrison there. The Han people started the movement around that time together with the military and officials to Hainan Island from Mainland China. Among them, there are offspring of those who were banished to Hainan for political reasons. Most of them moved to Hainan Island from places like Guangdong, Fujian and Guangxi in the southern part of Mainland China.
Li people are the original inhabitants of Hainan. They are believed to be the descendants of the ancient Yue tribes of China, who settled on the island more than 3,000 years ago.[citation needed]
The Li ethnic group of China mainly inhabits the nine cities and counties in the middle and southern part of Hainan - the cities of Sanya, Tongza and Dongfang, the Li autonomous counties of Baisha, Lingshui, Ledong, Changjiang, and the 'Li and Miao Autonomous Counties of Qiongzhong and Baoting'. Some others reside elsewhere on Hainan with other ethnic groups in Danzhou, Wanning, Qionghai and Tunchang.
The area inhabited by the Li ethnic group totals 18,700 square kilometers, about 55 percent of the province's total.[2]

In Eastern Wu of the Three Kingdoms Period, Hainan was the Zhuya Commandery (珠崖郡).
Under the Song Dynasty, Hainan came under the control of Guangxi Province, and for the first time large numbers of Han Chinese arrived, settling mostly in the north. Under the Yuan Dynasty (AD 1206-1368) it became an independent province, but was placed under Guangdong Province during the Ming Dynasty in 1370. In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, large numbers of Han from Fujian and Guangdong began migrating to Hainan, pushing the Li into the highlands in the southern half of the island. In the eighteenth century, the Li rebelled against the government, which responded by bringing in mercenaries from the Miao people regions of Guizhou Province. Many of the Miao settled on the island and their descendants live in the western highlands to this day.
In 1906, the Chinese Republican leader Sun Yat-sen proposed that Hainan become a separate province.
Hainan was historically part of Guangdong Province and Guangxi Province, being as such, it was the Ch'iung-yai or Qiongya Circuit (瓊崖道) in 1912 (the establishment of the Republic of China). In 1921, it was planned to become a Special Administrative Region (瓊崖特別行政區); in 1944, it became Hainan Special Administrative Region with 16 counties containing the South China Sea Islands.
During the 1920s and 30s, Hainan was a hotbed of Communist activity, especially after a bloody crackdown in Shanghai, the Republic of China in 1927 drove many Communists into hiding. The Communists and the Li natives fought a vigorous guerrilla campaign against the Japanese occupation of Hainan (1939-45), but in retaliation over one third of the male population were killed by the Japanese. Feng Baiju led the Hainan Independent Column of fighters throughout the 1930s and 1940s. After the Japanese surrender in 1945 the Nationalist Party (KMT) re-established control. Hainan was one of the last areas of China controlled by the Republic of China. From March to May 1950, the Landing Operation on Hainan Island captured the island for the Chinese communists. Feng Baiju and his column of guerrilla fighters played an essential role in scouting for the landing operation and coordinated their own offensive from their jungle bases on the island. This allowed the Hainan takeover to be successful where the Jinmen and Dengbu assaults had failed in the previous fall. The takeover was made possible by the presence of a local guerrilla force that was lacking on Jinmen, Dengbu, and Taiwan. Hence, while many observers of the Chinese civil war thought that the fall of Hainan to the Communists would be followed shortly by the fall of Taiwan, the lack of any communist guerrilla force on Taiwan and its sheer distance from the mainland made this impossible, as did the arrival of the US 7th fleet in the Taiwan Strait after the outbreak of the Korean War in June.

On 1 May 1950, under the PRC, the Special Administrative Region became an Administrative Region Office (海南行政区公署), a branch of the Guangdong provincial government. On October 1, 1984, it became the Hainan Administrative Region (海南行政区), with a People's Government, and finally as province separate from Guangdong four years later.
The Communists resumed development of the island along the lines established by the Japanese, but the results were limited by the island's isolation, its humid and typhoon-prone climate, and its continuing reputation as a place of danger and exile by mainland Chinese. With China's shift in economic policy at the end of the 1970s, Hai-nan became a focus of attention.
In 1988, when the island was made a separate province, it was designated a Special Economic Zone in an effort to increase investment.
During the mid-1980s, when Hainan was still part of the Guangdong Province, a fourteen-month episode of marketing zeal by Hainan Special District Administrator Lei Yu[3] put Hainan's pursuit of provincial status under a cloud. It involved the duty-free imports from Hong Kong of 90,000 Japanese-made cars and trucks at a cost of C¥ 4.5 billion (US$ 1.5 billion), and exporting them– with the help of local naval units– to the mainland, making 150% profits. By comparison, only 10,000 vehicles were imported into Hainan since 1950. In addition, it involved further consignments of 2.9 million TV sets, 252,000 videocassette recorders & 122,000 motorcycles. The money was taken from the 1983 central government funds destined for the construction of the island's transportation infrastructure (roads, railways, airports, harbours) over the next ten years.[citation needed]
The central government funds were deemed insufficient by the Hainan authorities for the construction of the island's other infrastructures (water works, power stations, telecommunications, etc.) and had taken a very liberal interpretation of the economic and trade regulations for Hainan and thirteen coastal cities; the regulations did not mention on prohibiting the re-selling of second-hand goods. Some of the proceeds, from unsold units, were later retrieved by the central government to re-finance the special district.
Geography



Hainan, separated by the Qiongzhou Strait (瓊州海峽) from the Leizhou Peninsula (雷州半島) of Guangdong, is the largest island administered by the People's Republic of China. The size of Hainan is comparable to the size of Belgium. The PRC, however, regard it as the second largest island, since Taiwan is considered the largest. To the west of Hainan is the Gulf of Tonkin. Wuzhi Mountain (1,876 m) is the highest mountain on the island.
In the official PRC territorial claim, Hainan Province includes not just one island, but also some two hundred South China Sea Islands. Whilst the containment of the South China Sea Islands means that Hainan Province has a very large water body, it has a disproportionally small land area. James Shoal (曾母暗沙 Zengmu Ansha), which is presently marked by the PRC, signifies the country's southernmost border. But the Malaysians also claim it is on their continental shelf.
Climate
Hainan has a tropical moist monsoonal climate. Its annual temperature change is less than 15 degrees Celsius. The coldest months are January and February when the temperatures drop to 16 to 21 degrees Celsius; the hottest months are July and August, and the temperatures are 25 to 29 degrees Celsius. Except for the mountainous regions in the central part of the island, the daily average temperature in Hainan is above 10 degrees Celsius, and the integrated temperature during the growing season of the crops reaches eight thousand to nine thousand degree Celsius-days. The summer in the north is hot and, for more than 20 days in a year, the temperature can be higher than 35 degrees Celsius. The average annual precipitation is 1500 to 2000 mm and can be as high as 2400 mm in central and eastern areas, and as low as 900 mm in the coastal areas of the southwest. The eastern part of Hainan lies in the path of typhoons, and 70% of the annual precipitation is derived from typhoons and the summer rainy season. Major flooding occurs due to the typhoons and they can cause many problems for the local residents.
Rivers and lakes
Most of the rivers in Hainan originate in the central area of the island and flow radially in different directions. The Nandu River in the northern part of the island is 314 km long, and its tributary, the Xinwu River, is 109 km long, the Changhua River in the west is 230 km long, and the Wanquan River in the east is 162 km long. Evaporation during the dry season around the coastal areas greatly reduces the flow of the rivers.
There are very few natural lakes in Hainan. There is a well-known artificial reservoir, the Songtao Reservoir, in the central-north area.
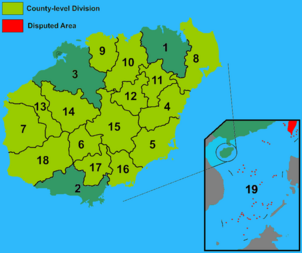
Subdivisions
Hainan Province uses a slightly different administrative system than the other provinces of China. Most other provinces are divided entirely into prefecture-level divisions, each of which is then divided entirely into county-level divisions. County-level divisions generally do not come directly under the province. In Hainan, nearly all county-level divisions (the four districts excepted) come directly under the province. This method of division is due to Hainan's relatively sparse population of around 8 million people.
Politics
The politics of Hainan is structured in a dual party-government system like all other governing institutions in mainland China.
The Governor of Hainan is the highest ranking official in the People's Government of Hainan. However, in the province's dual party-government governing system, the Governor has less power than the Hainan Communist Party of China Provincial Committee Secretary or CPC Party Chief.
Government
Even while Hainan was a part of Guangdong it had a considerable amount of local autonomy; the southern half of the island was an autonomous prefecture. Hainan's elevation to provincial level in 1988 increased its accountability to the central government, but by designating the new province a special economic zone the central government expressed its intent to allow Hainan maximum flexibility in devising programs to facilitate foreign investment and economic growth. Administratively, the province has been divided into five economic major districts.
Economy
Hainan's economy is predominantly agricultural, and more than a half of the island's exports are agricultural products. Hainan's elevation to province-level status (1988), however, was accompanied by its designation as China's largest "special economic zone", the intent being to hasten the development of the island's plentiful resources.
Prior to this, the province had a reputation for being a "Wild West" area, largely untouched by industrialisation; even today there are relatively few factories in the province. Tourism plays an important part of Hainan's economy, thanks largely to its tropical beaches and lush forests.
The central government has encouraged foreign investment in Hainan and has allowed the island to rely to a large extent on market forces.
Hainan's industrial development largely has been limited to the processing of its mineral and agricultural products, particularly rubber and iron ore. Since the 1950s, machinery, farm equipment, and textiles have been manufactured in the Haikou area for local consumption. A major constraint on industrial expansion has been an inadequate supply of electricity. Much of the island's generating capacity is hydroelectric, and it is subject to seasonal fluctuations in stream and river flows.
Its nominal GDP for 2009 was 164.7 billion yuan (US$24 billion), making it the 4th smallest in all of the PRC and contributes just 0.5% to the entire country's economy. Its GDP per capita was 19,166 yuan (US$2,805).
Economic and Technological Development Zones
- Haikou Free Trade Zone
- Haikou New & Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
- Sanya Yalong Bay National Resort
- Yangpu Economic Development Zone
Military
Hainan is home to the People's Liberation Army Navy strategic nuclear submarine naval harbor 18°13′16″N 109°41′10″E / 18.221°N 109.686°E[4]. The naval harbor is estimated to be 60 ft high, built into hillsides around a military base. The caverns are capable of hiding up to 20 nuclear submarines from spy satellites. The harbor houses nuclear ballistic missile submarines and is large enough to accommodate aircraft carriers. The US Department of Defence has estimated that China will have five Type 094 nuclear submarines operational by 2010 with each capable of carrying 12 JL-2 intercontinental ballistic missile. Two 950 metre piers and three smaller ones would be enough to accommodate two carrier strike groups or amphibious assault ships.
Natural resources
Hainan has commercially exploitable reserves of more than 30 minerals. Iron, first mined by the Japanese during their occupation of the island in World War II, is the most important. Also important are titanium, manganese, tungsten, bauxite, molybdenum, cobalt, copper, gold, and silver. There are large deposits of lignite and oil shale on the island, and significant offshore finds of oil and natural gas have been discovered. Virgin forests in the interior mountains contain more than 20 commercially valuable species, including teak and sandalwood.
Agriculture

Paddy rice is cultivated extensively in the northeastern lowlands and in the southern mountain valleys. Leading crops other than rice include coconuts, palm oil, sisal, tropical fruits (including pineapples, of which Hainan is China's leading producer), black pepper, coffee, tea, cashews, and sugarcane. In the early 20th century Chinese emigrants returning from then British Malaya, introduced rubber trees to the island; after 1950, state farms were developed, and Hainan now produces a significant amount of China's rubber.
Fishing
Marine products contribute a significant share to the provincial economy. Shrimps, scallops, and pearls are raised in shallow bays and basins for local use and export. Grouper, Spanish mackerel, and tuna constitute the bulk of the catch from the rich offshore fishing grounds.
Transportation
Before 1950 there were practically no transportation links with the interior of the island. The first roads were built in the early 20th century, but no major road construction was undertaken in the mountains until the 1950s. Parallel north–south roads along the east and west coasts and through the interior of the island constitute most of Hainan's road network. The freight-handling facilities of the island's ports have been improved, and Haikou has an international airport, the Haikou Meilan International Airport.
Railroad ferry link was established in early 2000s connecting the island's railroad network to the mainland.[5] In 2005, Ministry of Communications allocated 20 million yuan (US$2.4 million) to set up a committee to research and study the possibility of a bridge or tunnel link connecting the island to the mainland.[6]
Construction of a new railway linking Haikou and Sanya began in 2007. The entire length will be 302 kilometers and will have 14 stops. The travel time between Haikou and Sanya is expected to be approximately 80 minutes. The railway is projected to cost over 18 billion yuan and is scheduled for completion in 2010.[7]
Culture and education
Hainan has always been on the fringe of the Chinese cultural sphere. Traditionally, the island was a place of exile for criminals and disgraced officials. As a frontier region celebrated by such exiled poets as Su Dongpo, Hainan acquired an air of mystery and romance. The influx of large numbers of mainlanders after 1950 - particularly in the 1970s, when young Chinese from southern Guangdong were assigned to state farms to help develop Hainan, and in the 1980s, when thousands more came to take advantage of the economic opportunities offered - has perpetuated the frontier atmosphere on the island. The level of primary and secondary education has improved since 1949, but facilities for higher education remain somewhat inadequate.[citation needed]
Universities
- South China Tropical Agricultural University (华南热带农业大学, merged into Hainan University on Aug 14, 2007)
- Hainan University (海南大学)
- Hainan Normal University (海南师范大学)
- Qiongzhou University (琼州大学)
- Hainan Medical Institute (海南医学院)
- Haikou College of Economics (海口经济学院)
Demographics

(Link to entire map including key).
In 2000, the ethnic groups of Hainan included the Han Chinese, known as the Hainanese, who currently make a majority (84% of the population); the Li (Hlai) (14.7% of the population); the Miao (Hmong) (0.7%) and the Zhuang (0.6%). The Li are the largest indigenous group on the island in terms of population. Also found on the island are the Utsuls, descendants of Cham refugees, who are classified as Hui by the Chinese government.
Although they are indigenous to the island and do not speak a Chinese language, the Limgao (Ong-Be) people near the capital (8% of the population) are counted as Han Chinese.
There are 90,000 Buddhist Hainanese, and 6,500 Muslims. Most, if not all, of the Muslims are Utsuls living near Sanya. Because Hainan was a point in the travel route of missionaries, there are many Christians: 35,000 Protestants and 4,100 Catholics.
Languages
The Han Chinese of Hainan speak a variant of the Min Nan Chinese language, known as Hainanese. In addition, the national standard Putonghua is understood and spoken by most people, and Standard Cantonese is understood by many local Hainanese. The Li people have their own language, as do the Miao and Zhuang. The latter three groups would usually speak Standard Mandarin as a second language.
The villagers in Huihui and Huixin can all speak their native language Cham fluently. The adults have quite high literacy skills in Chinese. Most of the adults speak several Chinese dialects, and some also speak Li. In old Yacheng City and its vicinity as well as for several dozen miles west of Huihui and Huixin, the so-called military speech (the official language of the southwest among the northern Chinese dialects) is spoken. In Yanglan Village to the northeast, two Yue dialects, both closely related to Cantonese, are spoken: the Mai dialect and the Danzhou dialect, spoken in Haipo Village in the south, which is the same dialect as the dialect spoken in Danzhou in Dan Country in the northern part of the island. From the east to the west along the seashore, the Hainanese dialect is used. In Sanya City itself one sometimes finds speakers of Mandarin Chinese and Cantonese.
The general public can also use Mandarin Chinese to communicate with mainlanders. When Chams interact with the Hainanese dialect speakers from within Hainan Province, they use the Hainanese dialect, though youngsters generally use Mandarin Chinese. Not many can communicate in Li when interacting with the Li, so the Hainanese dialect or Mandarin is often used. In the market place and within the Sanya Municipality, the Cham speakers use Cham among themselves, and when they interact with speakers of other languages, they mostly use the Hainanese dialect. However, in the market places near the government seat of Yanglan Township, the Chams either use the Hainanese dialect or the Mai dialect. Some of the Cham speakers also speak the Danzhou dialect, a Cantonese dialect [8].
Notables
The poet Su Shi (1036-1101) popularized Hainan's isolation and exoticism when he was exiled there under the Song dynasty. The Dongpo Academy was built on the site of the residence where he lived in exile.
Hai Rui (1514-1587) was a famous Chinese official of the Ming dynasty. His name has come down in history as a model of honesty and integrity in office.
The most famous native of Hainan is Chinese-American Methodist minister, Charlie Soong (Sòng Jiāshù), father of the Shanghai born Soong sisters: Soong Ai-ling, wife of H. H. Kung (once China's richest man); Soong Ching-ling, wife of Sun Yat-Sen; and Soong Mei-ling, wife of former ROC President Chiang Kai-shek.
Food
Hainan cuisine is said to be "lighter, with mild seasonings." A lot of local taste is mixed with the Han Chinese taste. Seafood predominates the menu, as shrimp, crab, fish and other sea life are widely available.
Wenchang Chicken is a dish known throughout the province of Hainan. Although there are many varieties of this dish, the name is usually used to define a type of large, free-range chicken from Wenchang city, located on the east coast of the province. As opposed to battery chickens, its meat has more texture and is somewhat drier.
Hainan chicken rice is a famous dish in Southeast Asia bearing the region's name. However, whilst many restaurants use chicken fat to quickly add flavour to the dish, the proper local method is to 'marinate' the rice with chicken soup to add a more full flavour.
Tourism



As Hainan Island is not heavily industrialised, its greenery, together with its beautiful beaches and clean air, make it a popular tourist attraction. The island is accessible through ferry links with Guangdong province, as well as air links. There are two airports, Meilan Airport in Haikou, and Phoenix Airport in Sanya.
In December 2004, the Guangdong-Hainan passenger railway link opened, connecting Guangzhou in Guangdong province on the mainland to Hainan Island. The complete trip, which includes crossing the Qiongzhou Strait by ferry, takes a total of 12 hours. The project cost $583 million US and is expected to greatly enhance Hainan's tourism and economic development. This is important because Hainan currently lags well behind Shenzhen and Zhuhai special economic zones, which border Hong Kong and Macao, respectively.
Hainan Island is often divided into eight regions for tourism purposes: Haikou and area (Haikou, Qiongshan, Ding'an); the Northeast (Wenchang); the Central East Coast (Qionghai, Ding'an); the South East Coast; the South (Sanya); the West Coast (Ledong, Dongfang, Changjiang); the North West (Danzhou, Lingao, Chengmai); and the Central Highlands (Baisha, Qiongzhong, and Wuzhishan/Tongzha).
Haikou is the province's capital and contains interesting historic sites. Also known as Coconut City, Haikou is a major port. The Five Officials Temple (Chinese: 五公祠; pinyin: Wŭgōng cí, 20°0′35.79″N 110°21′17.34″E / 20.0099417°N 110.3548167°E) consists of five traditional temples and halls that were built in honour of five officials of the Tang (618-907) and Song (960-1279) dynasties. These officials were banished to Hainan for periods ranging from 11 days to 11 years for speaking out against what they felt were wrong practices by the Emperors. (It is perhaps significant that the establishment of the Five Officials Temple in the late 19th century coincides with a time when China's territorial integrity was under threat, and that several of the officials honoured here were exiled for espousing aggressive policies on the recapture of the north of China from the Jurchens during the Southern Song dynasty.)
Xiuying Fort Barbette was built in 1891 to defend the southeastern corner of China during the Sino-French War. The Xiuying Fort Barbette covers about a third of an acre. Its five large cannons are still intact and viewable at the site.
The Tomb of Hai Rui (Chinese: 海瑞墓; pinyin: Hǎi Ruì Mù, 20°0′29.66″N 110°17′30.18″E / 20.0082389°N 110.2917167°E) is a key national cultural protection site. Hai Rui was a compassionate and popular official of Hainanese origins who lived during the Ming Dynasty. He was famous for his lifelong honesty and his willingness to speak out on behalf of local people. In later life, Hai Rui was persecuted and fell out of favour with the emperor. His admirers built the Hai Rui Tomb after his death to commemorate his great works. Construction of the tomb began in 1589.
sanya, a popular tourist destination located in Lingshui County, is a state-protected nature reserve for macaques.
Hainan Island has a number of beaches, hot springs. Some top scenic sites include Yalong bay National Resort; Dadonghai Tourist Resort; Qizhi Shan (Seven Finger Mountain), Guantang Hot Spring Resort, Shishan Volcanic Garden; Wanquan River, Baishi Ridge Scenic Zone and Baihua Ridge.
Other attractions in Hainan include:
- Qiong Opera
- Yalong Wan (亞龍灣 Crescent Dragon Bay or Yalong Bay), is a seven kilometre-long beach east of Sanya City.
The province has initiated a visa-upon-arrival policy for foreign tourist groups from twenty-one countries in 2000, in order to attract visitors. It received 380,000 overseas tourists in 2002.
Space centre
- Main article Wenchang Satellite Launch Center.
China announced in October 2007 that it would build its fourth space launch centre, just a week after it fired off its first lunar orbiter. The new launch centre, to be built on the eastern island province of Hainan, is scheduled to be completed in 2012 and starts operating in 2013. The location of the launch centre in Hainan, a low-latitude region, will displace more than 6,000 residents that will be relocated to make way for the space centre, which will occupy 1,200 hectares. The site will be mainly used for launching various kinds of satellites and large space stations. The plan has been approved by the government. A 407-hectare space themed park will also be constructed near the new launch centre.
Miscellaneous topics
- Hainan is a sister province of Jeju-do island-province of South Korea and of the Canadian island-province of Prince Edward Island.
- The novel, Red Detachment of Women, by Liang Xin, was set in Hainan. The novel was first adapted to a feature film in the 1950s, and then a ballet in the 1960s as one of the Eight model plays. Most of the people of that time derived their romanticized image of Hainan Island from the scenes in the ballet, particularly that of the vivid forests of coconut trees, the Five-Finger Mountain (Wuzhi Shan), and the Wanquan River.
- One of the satellite launch centers of China is located in Hainan near the city of Wenchang. It is called Wenchang Satellite Launch Center. It is the closest Chinese launch center to the equator.
- The Hainan Gibbon is one of the world's most endangered primates. Seacology, a non-profit organization in Berkeley, CA, initiated a project to protect the highly endangered Hainan Gibbon in exchange for scholarships for the children of four villages near Bawangling Reserve.
See also
References
- ^ http://www.hainan.gov.cn/code/V3/map
- ^ "Population and People of Hainan Island".
- ^ Subsequently Vice Mayor of Shenzhen SEZ (May 1985 to January 1988), Executive Vice Mayor of Guangzhou (January 1988 to April 1992) and Vice Chairman of Guangxi AR (April 1992 to January 1996).
- ^ ""China Builds Secret Nuclear Submarine Base in South China Sea"". FoxNews.com. 2008-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ "Railway Ferry Service Across Qiongzhou Straits Begins". People's Daily Online. 2003-01-08. Retrieved 2008-08-12.
- ^ Xinhua News Agency (2005-02-03). "Hainan Mulls Bridge/ Tunnel Link to Mainland". China.org.cn. Retrieved 2008-08-12.
- ^ http://english.cri.cn/3126/2006/08/23/269@130061.htm
- ^ Thurgood, Graham. "Sociolinguistics and contact-induced language change: Hainan Cham, Anong, and Phan Rang Cham.". 2006. Tenth International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics, 17-20 January 2006, Palawan, Philippines. Linguistic Society of the Philippines and SIL International.
Further reading
- D'Arcy Brown, Liam (2003). Green Dragon, Sombre Warrior: travels to China's extremes. London: John Murray. ISBN 0-7195-6038-1
External links
- Hainan Government Website
- Template:Wikitravel
- Economic profile for Hainan at HKTDC
- Dr Howard M Scott "Hainan"
- Resources on the Hainanese in the National Library of Singapore
Template:Austronesian-speaking 19°06′24″N 109°34′03″E / 19.10667°N 109.56750°E