Content deleted Content added
templated cites |
templated cite |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''CUMYL-FUBINACA''' ('''SGT-149''') is an [[indazole]]-3-carboxamide based [[synthetic cannabinoid]] receptor agonist, with an EC<sub>50</sub> of 1.8nM for human [[CB1 receptor|CB<sub>1</sub> receptors]] and 23.7nM for human [[CB2 receptor|CB<sub>2</sub> receptors]], giving it around 13x selectivity for CB<sub>1</sub>.<ref>{{cite |
'''CUMYL-FUBINACA''' ('''SGT-149''') is an [[indazole]]-3-carboxamide based [[synthetic cannabinoid]] receptor agonist, with an EC<sub>50</sub> of 1.8nM for human [[CB1 receptor|CB<sub>1</sub> receptors]] and 23.7nM for human [[CB2 receptor|CB<sub>2</sub> receptors]], giving it around 13x selectivity for CB<sub>1</sub>.<ref>{{cite patent | url= https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2014167530A1 | country = WO | number = 2014167530 | title = Cannabinoid compounds | pubdate = 11 April 2013 | inventor = Bowden MW, Williamson PB }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Longworth M, Banister SD, Boyd R, Kevin RC, Connor M, McGregor IS, Kassiou M | title = Pharmacology of Cumyl-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoid New Psychoactive Substances (NPS) CUMYL-BICA, CUMYL-PICA, CUMYL-5F-PICA, CUMYL-5F-PINACA, and Their Analogues | journal = ACS Chemical Neuroscience | volume = 8 | issue = 10 | pages = 2159–2167 | date = October 2017 | pmid = 28792725 | doi = 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00267 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Banister SD, Connor M | title = The Chemistry and Pharmacology of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist New Psychoactive Substances: Evolution | journal = Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology | year = 2018 | volume = 252 | pages = 191–226 | pmid = 30105473 | doi = 10.1007/164_2018_144 | isbn = 978-3-030-10560-0 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Krishna Kumar K, Shalev-Benami M, Robertson MJ, Hu H, Banister SD, Hollingsworth SA, Latorraca NR, Kato HE, Hilger D, Maeda S, Weis WI, Farrens DL, Dror RO, Malhotra SV, Kobilka BK, Skiniotis G | display-authors = 6 | title = Structure of a Signaling Cannabinoid Receptor 1-G Protein Complex | journal = Cell | volume = 176 | issue = 3 | pages = 448–458.e12 | date = January 2019 | pmid = 30639101 | doi = 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.040 | pmc = 6461403 | doi-access = free }}</ref> It has been sold online as a [[designer drug]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Thornton SL, Darracq MA, Gugelmann HM, Armenian P | title = Surface internet marketplace presence and availability of NPS sold as research chemicals: a snapshot study. | journal = Toxicology Communications | date = 2019 | volume = 3 | issue = 1 | pages = 67-74 | doi = 10.1080/24734306.2019.1648067 }}</ref> |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 03:38, 20 June 2022
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
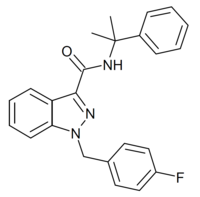
| Formula | C24H22FN3O |
| Molar mass | 387.458 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
CUMYL-FUBINACA (SGT-149) is an indazole-3-carboxamide based synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist, with an EC50 of 1.8nM for human CB1 receptors and 23.7nM for human CB2 receptors, giving it around 13x selectivity for CB1.[1][2][3][4] It has been sold online as a designer drug.[5]
See also
References
- ^ WO 2014167530, Bowden MW, Williamson PB, "Cannabinoid compounds", published 11 April 2013
- ^ Longworth M, Banister SD, Boyd R, Kevin RC, Connor M, McGregor IS, Kassiou M (October 2017). "Pharmacology of Cumyl-Carboxamide Synthetic Cannabinoid New Psychoactive Substances (NPS) CUMYL-BICA, CUMYL-PICA, CUMYL-5F-PICA, CUMYL-5F-PINACA, and Their Analogues". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 8 (10): 2159–2167. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00267. PMID 28792725.
- ^ Banister SD, Connor M (2018). "The Chemistry and Pharmacology of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist New Psychoactive Substances: Evolution". Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 252: 191–226. doi:10.1007/164_2018_144. ISBN 978-3-030-10560-0. PMID 30105473.
- ^ Krishna Kumar K, Shalev-Benami M, Robertson MJ, Hu H, Banister SD, Hollingsworth SA, et al. (January 2019). "Structure of a Signaling Cannabinoid Receptor 1-G Protein Complex". Cell. 176 (3): 448–458.e12. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.040. PMC 6461403. PMID 30639101.
- ^ Thornton SL, Darracq MA, Gugelmann HM, Armenian P (2019). "Surface internet marketplace presence and availability of NPS sold as research chemicals: a snapshot study". Toxicology Communications. 3 (1): 67–74. doi:10.1080/24734306.2019.1648067.