| Cubital tunnel syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ulnar neuropathy at elbow |
 | |
| Nerves of the left upper extremity. (Ulnar nerve labeled at center) | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Symptoms | Numbness (fingers) |
| Causes | Nerve entrapment, Tumor |
| Diagnostic method | CBC, Imaging |
| Treatment | NSAIDs, Surgery |
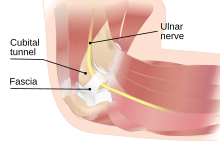
Cubital tunnel syndrome is an entrapment neuropathy, or nerve compression syndrome, a condition caused by compression, traction or friction, of the ulnar nerve at the elbow.[1] Nerve compression is also known as a trapped nerve. The ulnar nerve travels from the shoulder (brachial plexus) down the length of the arm to the hand. Along its course it may become compressed at several sites.[2] At the elbow the ulnar nerve passes through the cubital tunnel. Ulnar nerve compression most commonly occurs at the level of the cubital tunnel.[2] The ulnar nerve provides motor and sensory innervation to the forearm, and hand and its compression can cause the numbness and other symptoms associated with cubital tunnel syndrome. In many cases the cause is unknown.[3]
Cubital tunnel syndrome is an ulnar neuropathy that can be caused not only by compression at the cubital tunnel level itself, but can also be caused by movement of the elbow.[1] The volume of the cubital tunnel may be reduced when being moved from full extension to a lesser degree of flexion. Symptoms may include a claw hand.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Graf, A; Ahmed, AS; Roundy, R; Gottschalk, MB; Dempsey, A (July 2023). "Modern Treatment of Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Evidence and Controversy". Journal of hand surgery global online. 5 (4): 547–560. doi:10.1016/j.jhsg.2022.07.008. PMC 10382899. PMID 37521554.
- ^ a b Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice (Forty-first ed.). New York: Elsevier Limited. p. 952. ISBN 9780702052309.
- ^ "Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Elbow (Cubital Tunnel Syndrome) - OrthoInfo - AAOS". www.orthoinfo.org. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ "Ulnar nerve dysfunction: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
Further reading[edit]
- Fowler, J.R. (2019). Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Diagnosis, Management and Rehabilitation. Springer International Publishing. ISBN 978-3-030-14171-4. Retrieved 2024-06-15.