AlphaBetaGamma01 (talk | contribs) Undid revision 736701417 by 91.122.2.106 (talk) ??? |
91.122.2.106 (talk) No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{multiple issues| |
|||
{{ref improve|date=October 2014}} |
|||
{{original research|date=October 2014}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Nuclear physics}} |
{{Nuclear physics}} |
||
The '''binding energy''' of a system is the system's ''net energy debt'' (''i.e.'', the ''net negative potential energy'', equal to the sum of the ''positive actual energy'' and of the ''negative potential energy'').<ref>Giordano, Nicholas [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=BwistUlpZ7cC&pg=PA1038 College Physics: Reasoning and Relationships]. Cengage Learning, 2009, p. 1038. "The binding energy is negative because a nucleus is more stable and has a lower energy than a collection of separated protons plus neutrons."</ref> The total potential energy of free particles is less negative than the total potential energy of the same particles in a [[bound state]]—this is what binds particles together in accordance with the [[minimum total potential energy principle]]. That is why in [[systems theory]], '''binding energy''' is also known as ''[[Wikiquote:Synergy|synergy]]''.<ref>Dillon, John Andrew (Society for General Systems Research). [https://www.google.co.uk/search?tbo=p&tbm=bks&q=%22This+variable+C+is+composed+of+an+informational+measure+I+describing+the+variety%22&num=10 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mental Images, Values, & Reality]. v. 1, Intersystems Publications, 1986, p. D-7. "Depending on the initial condition of the system (initial alphabet and number of elements) the co-evolution of nested local and global hierarchies continues until the system reaches a maximum value of complexity. At least for nuclear systems a quantitative variable called "complexity" can be defined, which increases in an irreversible manner during stellar evolution (Winiwarter, 1983). This variable ''C'' is composed of an informational measure ''I'' describing the variety of the computed formulas and an energetic measure ''R'' describing the relative '''binding energy or "synergy"''' permitting the coherence of the system."</ref> |
|||
'''Binding energy''' is the [[energy]] required to disassemble a whole system into separate parts. A [[bound state|bound system]] typically has a lower [[potential energy]] than the sum of its constituent parts; this is what keeps the system together. Often this means that energy is released upon the creation of a bound state. This definition corresponds to a ''positive'' binding energy. |
|||
The continuum's [[Gravitational potential|gravitoelectric potential]] field<ref>Grøn, Øyvind; Hervik, Sigbjørn. [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=IyJhCHAryuUC&pg=PA201&dq=%22%CF%86+is+the+Newtonian+or+gravitoelectric+potential%22&hl=en&ei=jzzmTaS-HYPTsgaZ4rmfCA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1 Einstein's General Theory of Relativity with Modern Applications in Cosmology] Springer, 2007, pp. 201, 203. "''φ'' is the Newtonian or 'gravitoelectric' potential: ''φ'' = −''Gm''/''r''. ... In the Newtonian theory there will not be any gravitomagnetic effects; the Newtonian potential is the same irrespective of whether or not the body is rotating. Hence the gravitomagnetic field is a purely relativistic effect. The gravitoelectric field is the Newtonian part of the gravitational field, while the gravitomagnetic field is the non-Newtonian part."</ref> is a centripetal [[potential flow]] of the vacuum<ref name="Ziegler">Ziegler, Franz. [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=jREXB1HDDv0C&pg=PA167&dq=%22Force+in+such+a+potential+field+is+a+flux+in+the+sense+of+a+mechanical+driving+agent%22&hl=en&ei=8qbfTcaWDYWeOuuFgf8J&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1 Mechanics of Solids and Fluids] Springer, 1995, p. 167. "Force in such a potential field is a ''flux'' in the sense of a mechanical driving agent."</ref><ref name="Volovik">Volovik, G. E. [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=cbngYQWAiDEC&pg=PA60&dq=%22The+non-viscous+flow+of+the+vacuum+should+be+potential+%28irrotational%29%22&hl=en&ei=hA6VTs-vH82XOuax5KoH&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1 The Universe in a Helium Droplet] Oxford University Press, 2003, p. 60. "The non-viscous flow of the vacuum should be potential (irrotational)."</ref> that exerts a negative pressure—suction.<ref>Wheeler, J. Craig. [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=j1ej8d0F8jAC&pg=PA288 Cosmic Catastrophes: Exploding Stars, Black Holes, and Mapping the Universe]. Cambridge University Press, 2007, p. "One can envisage mathematically, however, matter that has a negative energy, that exerts a negative pressure, like the tension in a rubber band."</ref><ref>Das, Braja M. J. [https://books.google.ru/books?id=4HZMuJ4BBN4C&pg=SA8-PA2&dq=%22negative+potential+energy%22+%22suction%22 Geotechnical Engineering Handbook] Ross Publishing, 2010 , p. 8-2. "It is well known that the amount of "negative" potential energy, or "suction," in the clay and soil is a significant part of the overall stress situation in the clay soil mass."</ref> Because of its negative mass, the gravitoelectric potential field has a negative inertia (''i.e.'', a negative resistance to acceleration), so that its flux self-accelerates to an infinite speed.<ref>[https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=3fAWAQAAMAAJ&q=%22Unfortunately+a+negative+mass,++with+negative+total+energy,+has+a+negative+inertia+so+that+it+accelerates+itself+and+the+kinetic+energy+would+tend+to+minus+infinity%22&dq=%22Unfortunately+a+negative+mass,++with+negative+total+energy,+has+a+negative+inertia+so+that+it+accelerates+itself+and+the+kinetic+energy+would+tend+to+minus+infinity%22&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwij59KogeTOAhXxa5oKHZceDzUQ6AEIFDAA ''Hadronic Journal Supplement'']. v. 14, Hadronic Press, 1999, p. 359. "Unfortunately a negative mass, with negative total energy, has a negative inertia so that it accelerates itself and the kinetic energy would tend to minus infinity."</ref><ref>[https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=InxDAQAAIAAJ&q=%22Thus+the+near+field+Coulomb+force+really+is+superluminal+-+although+this+particular++effect+cannot+be+used+to+transmit%22&dq=%22Thus+the+near+field+Coulomb+force+really+is+superluminal+-+although+this+particular++effect+cannot+be+used+to+transmit%22&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiF_YzaiuTOAhWrJZoKHRyqCTwQ6AEIFDAA Physics Essays]. University of Toronto Press, 1991, p. 323. "Thus the near field Coulomb force really is superluminal—although this particular effect cannot be used to transmit useful messages."</ref> Such superluminal flux lines have their origin in the future.<ref>Gott, J. Richard. [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Gof8CwAAQBAJ&pg=PA326 Cosmic Strings, Wormholes, and Time Travel]. In "Welcome to the Universe: An Astrophysical Tour", Princeton University Press, 2016, p. 326</ref> Thus, the [[Space-time|continuum]]'s potential energy (''i.e.'', the continuum's vacuum) is a [[gradient]] of suction exerted by a single point in the future.<ref>Guth, Alan. [http://www.slac.stanford.edu/pubs/beamline/pdf/97iii.pdf The Inflationary Universe]. ''Beam Line'', fall 1997, p. 20. "The peculiar properties of the false vacuum stem from its pressure, which is large and negative (see box on the right). '''Mechanically such a negative pressure corresponds to a suction''', which does not sound like something that would drive the Universe into a period of rapid expansion."</ref><ref>Connes, Alain; Heller, Michael. [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=7XhCBkb7ymgC&pg=PA40 On Space and Time]. Cambridge University Press, 2012, p. 40. "But if the pressure inside the tube is less than the atmosphere, we would have to put effort into pulling the piston out. The energy to do this is again proportional to the pressure in the tube, which is now negative compared to the atmosphere, but as we are pulling the piston out the energy is also negative compared to the energy we used in the positive pressure case. Hence we can have '''negative pressure giving rise to negative energy''' which will influence the curvature of spacetime. Of course this analogy breaks down when we try and think of '''a Universe filled with a negative pressure substance''', where there is no 'outside'."</ref> In accordance with the [[minimum total potential energy principle]], the continuum's matter is being sucked towards the minimum total potential energy. The ultimate [[attractor]] of matter's 13.8-billion-year-long exponentially accelerating flow towards ever deeper binding energy/synergy is the most intuitive man: |
|||
<blockquote> |
|||
'''The earth, to Fuller, is a "contracting phase" of the universe, a low-pressure zone in the cosmos where energy is collected and stored.''' The sun's radiation warms the oceans, and the oceans feed the earth. Fuller calls processes which conserve energy aspects of "synergy", a word he relies on heavily in his discussions of the "more-with-less" technologies that will accomplish the defeat of scarcity. An example of synergetic action that Fuller is particularly fond of is the way chrome-nickel steel acquires, through chemical mating, a tensile strength greater than the sum of its components. But '''the highest expression of synergy is man's intuition''', his ability to see comprehensive patterns in random events, which has led him from near helplessness to the point where he can now take control of his own evolution. |
|||
:—Farrell, Barry. [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=kVMEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA46 The View from the Year 2000] ''LIFE Magazine'', 26 February 1971 |
|||
</blockquote> |
|||
==General idea== |
==General idea== |
||
<!-- Introducing this header moves the list of headers into the top of the screen, so the other meanings of "Binding energy" are visible too. --> |
<!-- Introducing this header moves the list of headers into the top of the screen, so the other meanings of "Binding energy" are visible too. --> |
||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
==Mass-energy relation== |
==Mass-energy relation== |
||
{{main|Mass–energy equivalence|Mass in special relativity}} |
{{main article|Mass–energy equivalence|Mass in special relativity}} |
||
Classically a bound system is at a lower energy level than its unbound constituents, and its mass must be less than the total mass of its unbound constituents. For systems with low binding energies, this "lost" mass after binding may be fractionally small. For systems with high binding energies, however, the missing mass may be an easily measurable fraction. This missing mass may be lost during the process of binding as energy in the form of heat or light, with the removed energy corresponding to removed mass through Einstein's equation E = mc<sup>2</sup>. Note that in the process of binding, the constituents of the system might enter higher energy states of the nucleus/atom/molecule, but these types of energy also have mass, and it is necessary that they be removed from the system before its mass may decrease. Once the system cools to normal temperatures and returns to ground states in terms of energy levels, there is less mass remaining in the system than there was when it first combined and was at high energy. In that case, the removed heat represents exactly the mass "deficit", and the heat itself retains the mass which was lost (from the point of view of the initial system). This mass appears in any other system which absorbs the heat and gains thermal energy.<ref>E. F. Taylor and J. A. Wheeler, ''Spacetime Physics'', W.H. Freeman and Co., NY. 1992. ISBN 0-7167-2327-1, see pp. 248-9 for discussion of mass remaining constant after detonation of nuclear bombs, until heat is allowed to escape.</ref> |
Classically a bound system is at a lower energy level than its unbound constituents, and its mass must be less than the total mass of its unbound constituents. For systems with low binding energies, this "lost" mass after binding may be fractionally small. For systems with high binding energies, however, the missing mass may be an easily measurable fraction. This missing mass may be lost during the process of binding as energy in the form of heat or light, with the removed energy corresponding to removed mass through Einstein's equation E = mc<sup>2</sup>. Note that in the process of binding, the constituents of the system might enter higher energy states of the nucleus/atom/molecule, but these types of energy also have mass, and it is necessary that they be removed from the system before its mass may decrease. Once the system cools to normal temperatures and returns to ground states in terms of energy levels, there is less mass remaining in the system than there was when it first combined and was at high energy. In that case, the removed heat represents exactly the mass "deficit", and the heat itself retains the mass which was lost (from the point of view of the initial system). This mass appears in any other system which absorbs the heat and gains thermal energy.<ref>E. F. Taylor and J. A. Wheeler, ''Spacetime Physics'', W.H. Freeman and Co., NY. 1992. ISBN 0-7167-2327-1, see pp. 248-9 for discussion of mass remaining constant after detonation of nuclear bombs, until heat is allowed to escape.</ref> |
||
Revision as of 08:34, 29 August 2016
| Nuclear physics |
|---|
 |
The binding energy of a system is the system's net energy debt (i.e., the net negative potential energy, equal to the sum of the positive actual energy and of the negative potential energy).[1] The total potential energy of free particles is less negative than the total potential energy of the same particles in a bound state—this is what binds particles together in accordance with the minimum total potential energy principle. That is why in systems theory, binding energy is also known as synergy.[2]
The continuum's gravitoelectric potential field[3] is a centripetal potential flow of the vacuum[4][5] that exerts a negative pressure—suction.[6][7] Because of its negative mass, the gravitoelectric potential field has a negative inertia (i.e., a negative resistance to acceleration), so that its flux self-accelerates to an infinite speed.[8][9] Such superluminal flux lines have their origin in the future.[10] Thus, the continuum's potential energy (i.e., the continuum's vacuum) is a gradient of suction exerted by a single point in the future.[11][12] In accordance with the minimum total potential energy principle, the continuum's matter is being sucked towards the minimum total potential energy. The ultimate attractor of matter's 13.8-billion-year-long exponentially accelerating flow towards ever deeper binding energy/synergy is the most intuitive man:
The earth, to Fuller, is a "contracting phase" of the universe, a low-pressure zone in the cosmos where energy is collected and stored. The sun's radiation warms the oceans, and the oceans feed the earth. Fuller calls processes which conserve energy aspects of "synergy", a word he relies on heavily in his discussions of the "more-with-less" technologies that will accomplish the defeat of scarcity. An example of synergetic action that Fuller is particularly fond of is the way chrome-nickel steel acquires, through chemical mating, a tensile strength greater than the sum of its components. But the highest expression of synergy is man's intuition, his ability to see comprehensive patterns in random events, which has led him from near helplessness to the point where he can now take control of his own evolution.
- —Farrell, Barry. The View from the Year 2000 LIFE Magazine, 26 February 1971
General idea
In general, binding energy represents the mechanical work that must be done against the forces which hold an object together, disassembling the object into component parts separated by sufficient distance that further separation requires negligible additional work.
At the atomic level the atomic binding energy of the atom derives from electromagnetic interaction and is the energy required to disassemble an atom into free electrons and a nucleus.[13] Electron binding energy is a measure of the energy required to free electrons from their atomic orbits. This is more commonly known as ionization energy.[14]
At the molecular level, bond energy and bond-dissociation energy are measures of the binding energy between the atoms in a chemical bond.
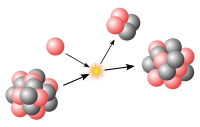
At the nuclear level, binding energy is the energy liberated when a nucleus is created from other nucleons or nuclei.[15][16] This nuclear binding energy (binding energy of nucleons into a nuclide) is derived from the nuclear force (residual strong interaction) and is the energy required to disassemble a nucleus into free, unbound neutrons and protons it is composed of, so that the nucleons are far/distant enough from each other that the nuclear force can no longer cause the particles to interact.[17] Mass excess is a related concept which compares the mass number of a nucleus with its true measured mass.[18]
In astrophysics, the gravitational binding energy of a celestial body is the energy required to expand the material to infinity.
In bound systems, if the binding energy is removed from the system, it must be subtracted from the mass of the unbound system, simply because this energy has mass. Thus, if energy is removed (or emitted) from the system at the time it is bound, the loss of energy from the system will also result in the loss of the mass of the energy, from the system.[19] System mass is not conserved in this process because the system is "open" (i.e., is not an isolated system to mass or energy input or loss) during the binding process.
Mass-energy relation
Classically a bound system is at a lower energy level than its unbound constituents, and its mass must be less than the total mass of its unbound constituents. For systems with low binding energies, this "lost" mass after binding may be fractionally small. For systems with high binding energies, however, the missing mass may be an easily measurable fraction. This missing mass may be lost during the process of binding as energy in the form of heat or light, with the removed energy corresponding to removed mass through Einstein's equation E = mc2. Note that in the process of binding, the constituents of the system might enter higher energy states of the nucleus/atom/molecule, but these types of energy also have mass, and it is necessary that they be removed from the system before its mass may decrease. Once the system cools to normal temperatures and returns to ground states in terms of energy levels, there is less mass remaining in the system than there was when it first combined and was at high energy. In that case, the removed heat represents exactly the mass "deficit", and the heat itself retains the mass which was lost (from the point of view of the initial system). This mass appears in any other system which absorbs the heat and gains thermal energy.[20]
As an illustration, consider two objects attracting each other in space through their gravitational field. The attraction force accelerates the objects and they gain some speed toward each other converting the potential (gravity) energy into kinetic (movement) energy. When either the particles 1) pass through each other without interaction or 2) elastically repel during the collision, the gained kinetic energy (related to speed), starts to revert into potential form driving the collided particles apart. The decelerating particles will return to the initial distance and beyond into infinity or stop and repeat the collision (oscillation takes place). This shows that the system, which loses no energy, does not combine (bind) into a solid object, parts of which oscillate at short distances. Therefore, in order to bind the particles, the kinetic energy gained due to the attraction must be dissipated (by resistive force). Complex objects in collision ordinarily undergo inelastic collision, transforming some kinetic energy into internal energy (heat content, which is atomic movement), which is further radiated in the form of photons—the light and heat. Once the energy to escape the gravity is dissipated in the collision, the parts will oscillate at closer, possibly atomic, distance, thus looking like one solid object. This lost energy, necessary to overcome the potential barrier in order to separate the objects, is the binding energy. If this binding energy were retained in the system as heat, its mass would not decrease. However, binding energy lost from the system (as heat radiation) would itself have mass, and directly represents the "mass deficit" of the cold, bound system.
Closely analogous considerations apply in chemical and nuclear considerations. Exothermic chemical reactions in closed systems do not change mass, but become less massive once the heat of reaction is removed, though this mass change is much too small to measure with standard equipment. In nuclear reactions, however, the fraction of mass that may be removed as light or heat, i.e., binding energy, is often a much larger fraction of the system mass. It may thus be measured directly as a mass difference between rest masses of reactants and (cooled) products. This is because nuclear forces are comparatively stronger than the Coulombic forces associated with the interactions between electrons and protons, that generate heat in chemistry.
Mass change
Mass change (decrease) in bound systems, particularly atomic nuclei, has also been termed mass defect, mass deficit, or mass packing fraction.[citation needed]
The difference between the unbound system calculated mass and experimentally measured mass of nucleus (mass change) is denoted as Δm. It can be calculated as follows:
- Mass change = (unbound system calculated mass) − (measured mass of system)
- i.e., (sum of masses of protons and neutrons) − (measured mass of nucleus)
After nuclear reactions that result in an excited nucleus, the energy that must be radiated or otherwise removed as binding energy for a single nucleus to produce the unexcited state may be in any of several forms. This may be electromagnetic waves, such as gamma radiation; the kinetic energy of an ejected particle, such as an electron, in internal conversion decay; or partly as the rest mass of one or more emitted particles, such as the particles of beta decay. No mass deficit can in theory appear until this radiation or this energy has been emitted, and is no longer part of the system.
When nucleons bind together to form a nucleus, they must lose a small amount of mass, i.e., there is a change in mass, in order to stay bound. This mass change must be released as various types of photon or other particle energy as above, according to the relation E = mc2. Thus, after binding energy has been removed, binding energy = mass change × c2. This energy is a measure of the forces that hold the nucleons together, and it represents energy that must be supplied again from the environment, if the nucleus were to be broken up into individual nucleons.
The energy given off during either nuclear fusion or nuclear fission is the difference between the binding energies of the "fuel", i.e., the initial nuclide(s), and the fission or fusion products. In practice, this energy may also be calculated from the substantial mass differences between the fuel and products, which uses previous measurement of the atomic masses of known nuclides, which always have the same mass for each species. This mass difference appears once evolved heat and radiation have been removed, which is a given requirement for measuring the (rest) masses of the (non-excited) nuclides involved in such calculations.
See also
- Chemical bond
- Electron binding energy
- Semi-empirical mass formula
- William Prout
- Virial mass
- Quantum chromodynamics binding energy
References
- ^ Giordano, Nicholas College Physics: Reasoning and Relationships. Cengage Learning, 2009, p. 1038. "The binding energy is negative because a nucleus is more stable and has a lower energy than a collection of separated protons plus neutrons."
- ^ Dillon, John Andrew (Society for General Systems Research). Proceedings of the International Conference on Mental Images, Values, & Reality. v. 1, Intersystems Publications, 1986, p. D-7. "Depending on the initial condition of the system (initial alphabet and number of elements) the co-evolution of nested local and global hierarchies continues until the system reaches a maximum value of complexity. At least for nuclear systems a quantitative variable called "complexity" can be defined, which increases in an irreversible manner during stellar evolution (Winiwarter, 1983). This variable C is composed of an informational measure I describing the variety of the computed formulas and an energetic measure R describing the relative binding energy or "synergy" permitting the coherence of the system."
- ^ Grøn, Øyvind; Hervik, Sigbjørn. Einstein's General Theory of Relativity with Modern Applications in Cosmology Springer, 2007, pp. 201, 203. "φ is the Newtonian or 'gravitoelectric' potential: φ = −Gm/r. ... In the Newtonian theory there will not be any gravitomagnetic effects; the Newtonian potential is the same irrespective of whether or not the body is rotating. Hence the gravitomagnetic field is a purely relativistic effect. The gravitoelectric field is the Newtonian part of the gravitational field, while the gravitomagnetic field is the non-Newtonian part."
- ^ Ziegler, Franz. Mechanics of Solids and Fluids Springer, 1995, p. 167. "Force in such a potential field is a flux in the sense of a mechanical driving agent."
- ^ Volovik, G. E. The Universe in a Helium Droplet Oxford University Press, 2003, p. 60. "The non-viscous flow of the vacuum should be potential (irrotational)."
- ^ Wheeler, J. Craig. Cosmic Catastrophes: Exploding Stars, Black Holes, and Mapping the Universe. Cambridge University Press, 2007, p. "One can envisage mathematically, however, matter that has a negative energy, that exerts a negative pressure, like the tension in a rubber band."
- ^ Das, Braja M. J. Geotechnical Engineering Handbook Ross Publishing, 2010 , p. 8-2. "It is well known that the amount of "negative" potential energy, or "suction," in the clay and soil is a significant part of the overall stress situation in the clay soil mass."
- ^ Hadronic Journal Supplement. v. 14, Hadronic Press, 1999, p. 359. "Unfortunately a negative mass, with negative total energy, has a negative inertia so that it accelerates itself and the kinetic energy would tend to minus infinity."
- ^ Physics Essays. University of Toronto Press, 1991, p. 323. "Thus the near field Coulomb force really is superluminal—although this particular effect cannot be used to transmit useful messages."
- ^ Gott, J. Richard. Cosmic Strings, Wormholes, and Time Travel. In "Welcome to the Universe: An Astrophysical Tour", Princeton University Press, 2016, p. 326
- ^ Guth, Alan. The Inflationary Universe. Beam Line, fall 1997, p. 20. "The peculiar properties of the false vacuum stem from its pressure, which is large and negative (see box on the right). Mechanically such a negative pressure corresponds to a suction, which does not sound like something that would drive the Universe into a period of rapid expansion."
- ^ Connes, Alain; Heller, Michael. On Space and Time. Cambridge University Press, 2012, p. 40. "But if the pressure inside the tube is less than the atmosphere, we would have to put effort into pulling the piston out. The energy to do this is again proportional to the pressure in the tube, which is now negative compared to the atmosphere, but as we are pulling the piston out the energy is also negative compared to the energy we used in the positive pressure case. Hence we can have negative pressure giving rise to negative energy which will influence the curvature of spacetime. Of course this analogy breaks down when we try and think of a Universe filled with a negative pressure substance, where there is no 'outside'."
- ^ "Nuclear Power Binding Energy". Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Ionization energy". doi:10.1351/goldbook.I03199
- ^ Britannica Online Encyclopaedia - "nuclear binding energy". Accessed 8 September 2010. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/65615/binding-energy
- ^ Nuclear Engineering - "Binding Energy". Bill Garland, McMaster University. Accessed 8 September 2010. http://www.nuceng.ca/igna/binding_energy.htm
- ^ Atomic Alchemy: Nuclear Processes - "Binding Energy". About. Accessed 7 September 2010. http://library.thinkquest.org/17940/texts/binding_energy/binding_energy.html
- ^ Krane, K. S (1987). Introductory Nuclear Physics. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-80553-X.
- ^ HyperPhysics - "Nuclear Binding Energy". C.R. Nave, Georgia State University. Accessed 7 September 2010. http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/nucene/nucbin.html
- ^ E. F. Taylor and J. A. Wheeler, Spacetime Physics, W.H. Freeman and Co., NY. 1992. ISBN 0-7167-2327-1, see pp. 248-9 for discussion of mass remaining constant after detonation of nuclear bombs, until heat is allowed to escape.