172.195.96.244 (talk) →Isomers and production: wikilink to m-Cymene, ref fix |
m added refractive index value Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{redirect|Cymene|the other isomers|Cymenes|the ancient city of Thessaly|Cymene (Thessaly)}} |
{{redirect|Cymene|the other isomers|Cymenes|the ancient city of Thessaly|Cymene (Thessaly)}} |
||
{{chembox |
{{chembox |
||
| verifiedrevid = 414093009 |
| verifiedrevid = 414093009 |
||
| Name = ''p''-Cymene |
| Name = ''p''-Cymene |
||
| ImageFileL1_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} |
| ImageFileL1_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} |
||
| ImageFileL1 = P-Cymol.svg |
| ImageFileL1 = P-Cymol.svg |
||
| ImageNameL1 = Skeletal formula |
| ImageNameL1 = Skeletal formula |
||
| ImageFileR1 = Cymene-3D-balls.png |
| ImageFileR1 = Cymene-3D-balls.png |
||
| ImageNameR1 = Ball-and-stick model |
| ImageNameR1 = Ball-and-stick model |
||
| PIN = 1-Methyl-4-(propan-2-yl)benzene<ref>{{cite book | title = Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book) | publisher = [[Royal_Society_of_Chemistry|The Royal Society of Chemistry]] | date = 2014 | location = Cambridge | pages = 139, 597 | doi = 10.1039/9781849733069-FP001 | isbn = 978-0-85404-182-4}}</ref> |
| PIN = 1-Methyl-4-(propan-2-yl)benzene<ref>{{cite book | title = Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book) | publisher = [[Royal_Society_of_Chemistry|The Royal Society of Chemistry]] | date = 2014 | location = Cambridge | pages = 139, 597 | doi = 10.1039/9781849733069-FP001 | isbn = 978-0-85404-182-4}}</ref> |
||
| OtherNames = ''para''-Cymene<br />4-Isopropyltoluene<br />4-Methylcumene<br />Paracymene |
| OtherNames = ''para''-Cymene<br />4-Isopropyltoluene<br />4-Methylcumene<br />Paracymene |
||
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers |
| Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers |
||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| ChemSpiderID = 7183 |
| ChemSpiderID = 7183 |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
| InChI = 1/C10H14/c1-8(2)10-6-4-9(3)5-7-10/h4-8H,1-3H3 |
| InChI = 1/C10H14/c1-8(2)10-6-4-9(3)5-7-10/h4-8H,1-3H3 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
|Section2={{Chembox Properties |
| Section2 = {{Chembox Properties |
||
| C=10 | H=14 |
| C=10 | H=14 |
||
| Density = 0.857 g/cm<sup>3</sup> |
| Density = 0.857 g/cm<sup>3</sup> |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| Appearance = Colourless liquid |
| Appearance = Colourless liquid |
||
| MagSus = {{val|-1.028|e=-4|u=cm<sup>3</sup>/mol}} |
| MagSus = {{val|-1.028|e=-4|u=cm<sup>3</sup>/mol}} |
||
| RefractIndex = 1.4908 (at 20 °C) <ref>{{cite journal|author1=Pabst, Florian|author2=Blochowicz, Thomas |title=On the intensity of light scattered by molecular liquids - Comparison of experiment and quantum chemical calculations|journal=[[The Journal of Chemical Physics]]|language=en|date=December 2022|volume=157|issue=24|pages=244501|doi=10.1063/5.0133511}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
|Section3={{Chembox Hazards |
| Section3 = {{Chembox Hazards |
||
| GHSPictograms = {{GHS02}}{{GHS08}}{{GHS09}} |
| GHSPictograms = {{GHS02}}{{GHS08}}{{GHS09}} |
||
| GHSSignalWord = Danger |
| GHSSignalWord = Danger |
||
Revision as of 19:15, 1 January 2023
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Methyl-4-(propan-2-yl)benzene[1] | |||
| Other names
para-Cymene
4-Isopropyltoluene 4-Methylcumene Paracymene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 1903377 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.542 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 305912 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2046 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H14 | |||
| Molar mass | 134.222 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.857 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −68 °C (−90 °F; 205 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 177 °C (351 °F; 450 K) | ||
| 23.4 mg/L | |||
| −1.028×10−4 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.4908 (at 20 °C) [2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H226, H304, H411 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P273, P280, P301+P310, P303+P361+P353, P331, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |||
| Flash point | 47 °C (117 °F; 320 K) | ||
| 435 °C (815 °F; 708 K) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
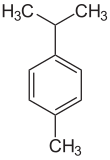
p-Cymene is a naturally occurring aromatic organic compound. It is classified as an alkylbenzene related to a monoterpene. Its structure consists of a benzene ring para-substituted with a methyl group and an isopropyl group. p-Cymene is insoluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents.
Isomers and production
In addition to p-cymene, two less common geometric isomers are o-cymene, in which the alkyl groups are ortho-substituted, and m-cymene, in which they are meta-substituted. p-Cymene is the only natural isomer, as expected from the terpene rule. All three isomers form the group of cymenes.
Cymene is also produced by alkylation of toluene with propylene.[3]
Related compounds
It is a constituent of a number of essential oils, most commonly the oil of cumin and thyme. Significant amounts are formed in sulfite pulping process from the wood terpenes.
p-Cymene is a common ligand for ruthenium. The parent compound is [(η6-cymene)RuCl2]2. This half-sandwich compound is prepared by the reaction of ruthenium trichloride with the terpene α-phellandrene. The osmium complex is also known.[4]
Hydrogenation gives the saturated derivative p-menthane.
References
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. 139, 597. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Pabst, Florian; Blochowicz, Thomas (December 2022). "On the intensity of light scattered by molecular liquids - Comparison of experiment and quantum chemical calculations". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 157 (24): 244501. doi:10.1063/5.0133511.
- ^ Vora, Bipin V.; Kocal, Joseph A.; Barger, Paul T.; Schmidt, Robert J.; Johnson, James A. (2003). "Alkylation". Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0112112508011313.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.
- ^ Bennett, M. A.; Huang, T.-N.; Matheson, T. W.; Smith, A. K. (1982). "(η6-Hexamethylbenzene)Ruthenium Complexes". Inorganic Syntheses. 21: 74–78. doi:10.1002/9780470132524.ch16.