| Jaguar Temporal range: Middle Pleistocene – Recent
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Pantherinae |
| Genus: | Panthera |
| Species: | P. onca
|
| Binomial name | |
| Panthera onca | |
| |
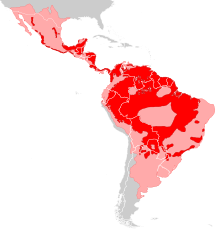
| Current (red) and former range (pink) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The jaguar (Panthera onca) is a large felid species and the only living member of the genus Panthera native to the Americas. The jaguar is the largest cat species in the New World and the third largest in the world. Due to convergent evolution, it closely resembles the leopard but is usually larger and sturdier. It ranges across a variety of forested and open terrains, but its preferred habitat is tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest, swamps, and wooded regions.
The jaguar is largely a solitary, opportunistic, stalk-and-ambush predator at the top of the food chain, adapt at swimming. As a keystone species, it plays an important role in stabilizing ecosystems and regulating prey populations. The jaguar has developed an exceptionally powerful bite, even relative to the other big cats. This allows it to pierce the shells of armored reptiles and to employ an unusual killing method with mammals: it bites directly through the skull of prey between the ears to deliver a fatal blow to the brain.
The jaguar's present range extends from the extreme southwestern United States and Mexico in North America, across much of Central America, and south to Paraguay and northern Argentina in South America. Though there are single cats now living within Arizona, the species has almost become locally extinct in the United States since the early 20th century. It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List, and its numbers are declining. Threats include loss and fragmentation of habitat.
While international trade in jaguars or their body parts is prohibited, the cat is still frequently killed, particularly in conflicts with ranchers and farmers in South America. Although reduced, its range remains large. Given its historical distribution, the jaguar has featured prominently in the mythology of numerous Indigenous peoples of the Americas, including those of the Maya and Aztec civilizations.
Etymology
The word "jaguar" is derived from iaguara, a word in one of the Indigenous languages of Brazil for a wild spotted cat that is larger than a wolf.[2] Onca is derived from the Lusitanian name onça for a spotted cat in Brazil that is larger than a lynx.[3] Indigenous peoples in Guyana call it jaguareté.[4]
The word "panther" is derived from classical Latin panthēra, itself from the ancient Greek pánthēr (πάνθηρ).[5]
Classification
Taxonomy
In 1758, Carl Linnaeus described the jaguar in his work Systema Naturae and gave it the scientific name Felis onca.[6] In the 19th and 20th centuries, several jaguar type specimens formed the basis for descriptions of subspecies.[7] In 1939, Reginald Innes Pocock recognized eight subspecies based on geographic origins and skull morphology of these specimens.[8] Pocock did not have access to sufficient zoological specimens to critically evaluate their subspecific status, but expressed doubt about the status of several. Later consideration of his work suggested only three subspecies should be recognized. The description of P. o. palustris was based on a fossil skull.[9] By 2005, nine subspecies were considered to be valid taxa.[7]
- P. o. onca (Linnaeus, 1758) was a jaguar from Brazil.[6]
- P. o. peruviana (De Blainville, 1843) was a jaguar skull from Peru.[10]
- P. o. hernandesii (Gray, 1857) was a jaguar from Mazatlán in Mexico.[11]
- P. o. palustris (Ameghino, 1888) was a fossil jaguar mandible excavated in the Sierras Pampeanas of Córdova District, Argentina.[12]
- P. o. centralis (Mearns, 1901) was a skull of a male jaguar from Talamanca, Costa Rica.[13]
- P. o. goldmani (Mearns, 1901) was a jaguar skin from Yohatlan in Campeche, Mexico.[13]
- P. o. paraguensis (Hollister, 1914) was a skull of a male jaguar from Paraguay.[14]
- P. o. arizonensis (Goldman, 1932) was a skin and skull of a male jaguar from the vicinity of Cibecue, Arizona.[15]
- P. o. veraecrucis (Nelson and Goldman, 1933) was a skull of a male jaguar from San Andrés Tuxtla in Mexico.[16]
Reginald Innes Pocock placed the jaguar in the genus Panthera and observed that it shares several morphological features with the leopard (P. pardus). He therefore concluded that they are most closely related to each other.[8] Results of morphological and genetic research indicate a clinal north–south variation between populations, but no evidence for subspecific differentiation.[17][18] DNA analysis of 84 jaguar samples from South America revealed that the gene flow between jaguar populations in Colombia was high in the past.[19] Since 2017, the jaguar is therefore considered to be a monotypic taxon.[20]
Evolution

The evolutionary radiation of the Felidae began in the late Miocene between 14.45 to 8.38 million years ago and 16.76 to 6.46 million years ago in Asia.[21][22] The clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa) is the first cat that genetically diverged from the common ancestor of the Felidae.[23][24][25] The genetic lineage of the Panthera is estimated to have diverged between 9.32 to 4.47 million years ago[21] and 11.75 to 0.97 million years ago.[22]
The jaguar is thought to have entered the American continent in the early Pleistocene via Beringia, the land bridge that once spanned the Bering Strait. Results of mitochondrial DNA analysis of 37 jaguars indicate that the species evolved between 510,000 and 280,000 years ago.[17] Fossil remains of the extinct jaguar subspecies Panthera onca augusta and Panthera onca mesembrina excavated in North and South America date to the Pleistocene and are up to 130,000 years old.[26]
| nuclear DNA:[21] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| mitochondrial DNA:[22] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Characteristics
The jaguar is a compact and well-muscled animal. It is the largest cat native to the Americas and the third largest in the world, exceeded in size only by the tiger and the lion.[9][27][28] Its coat is generally a tawny yellow, but ranges to reddish-brown, for most of the body. The ventral areas are white.[15] The fur is covered with rosettes for camouflage in the dappled light of its forest habitat. The spots and their shapes vary between individual jaguars: rosettes may include one or several dots. The spots on the head and neck are generally solid, as are those on the tail, where they may merge to form a band.[9] Jaguars living in forests are often darker and considerably smaller than those living in open areas, possibly due to the smaller numbers of large, herbivorous prey in forest areas.[29]
While the jaguar closely resembles the leopard, it is generally more robust, with stockier limbs and a squarer head. The rosettes on a jaguar's coat are larger, darker, fewer in number and have thicker lines with a small spot in the middle.[30] It has powerful jaws with the third-highest bite force of all felids, after the tiger and the lion.[31] However, in a comparative study of bite force adjusted for body size, the jaguar ranks as the top felid, alongside the clouded leopard and ahead of the tiger and lion.[32] A 100 kg (220 lb) jaguar can bite with a force of 4.939 kilonewtons (1,110 pounds-force) with the canine teeth and 6.922 kN (1,556 lbf) at the carnassial notch.[33]
Its size and weight vary considerably: weights are normally in the range of 56–96 kg (123–212 lb). Exceptionally big males have been recorded to weigh as much as 158 kg (348 lb).[34][35] The smallest females weigh about 36 kg (79 lb).[34] It is sexually dimorphic with females typically 10–20% smaller than males. The length, from the nose to the base of the tail, varies from 1.12 to 1.85 m (3 ft 8 in to 6 ft 1 in). The tail is the shortest of any big cat, at 45 to 75 cm (18 to 30 in) in length.[34][36] Its muscular legs are shorter than the legs of other Panthera species with a similar body weight.[30] The jaguar stands 63 to 76 cm (25 to 30 in) tall at the shoulders. This short and stocky limb structure makes the jaguar adept at climbing, crawling, and swimming.[37]
Further variations in size have been observed across regions and habitats, with size tending to increase from north to south. Jaguars in the Chamela-Cuixmala Biosphere Reserve on the Pacific coast of central Mexico weighed around 50 kg (110 lb), about the size of a female cougar.[38] Jaguars in Venezuela and Brazil are much larger with average weights of about 95 kg (209 lb) in males and of about 56–78 kg (123–172 lb) in females.[9]
Color variation
Melanistic jaguars are informally known as black panthers. The black morph is less common than the spotted one.[39] Melanism in the jaguar is caused by deletions in the melanocortin 1 receptor gene and inherited through a dominant allele.[40]
Melanistic jaguars had been documented in Central and South America, in the southern portion of their range. In 2004, the first black jaguar was recorded in the northern portion of their range, in the Sierra Madre Occidental area of Mexico.[41] Black jaguars were also recorded in Costa Rica's Alberto Manuel Brenes Biological Reserve and in the mountains of the Cordillera de Talamanca.[42][43]
Distribution and habitat
At present, the jaguar's range extends from Mexico through Central America to South America, including much of Amazonian Brazil. The countries included in this range are Argentina, Belize, Bolivia, Colombia, Costa Rica (particularly on the Osa Peninsula), Ecuador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, the United States and Venezuela. It is now locally extinct in El Salvador and Uruguay.[1]
The jaguar prefers dense forest and typically inhabits dry deciduous forests, tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, rainforests and cloud forests in Central and South America; open, seasonally flooded wetlands, dry grassland and historically also oak forests in the United States. It has been recorded at elevations up to 3,800 m (12,500 ft), but avoids montane forests. It favours riverine habitat and swamps with dense vegetation cover.[29] It has lost habitat most rapidly in drier regions such as the Argentine pampas, the arid grasslands of Mexico and the southwestern United States.[1]
In 1919, sightings of jaguars were reported to have occurred in the Monterey, California region.[44] In 1999, its historic range at the turn of the 20th century was estimated at 19,000,000 km2 (7,300,000 sq mi) stretching from the southern United States through Central America to southern Argentina. By the turn of the 21st century, its global range had decreased to about 8,750,000 km2 (3,380,000 sq mi), most of it in the southern United States, northern Mexico, northern Brazil, and southern Argentina.[45] Occasional sightings were reported in Arizona,[46] New Mexico and Texas.[47]
Ecology and behavior
Ecological role
The adult jaguar is an apex predator, meaning it is at the top of the food chain and is not preyed upon in the wild. The jaguar has also been termed a keystone species, as it is assumed that it controls the population levels of prey such as herbivorous and granivorous mammals, and thus maintains the structural integrity of forest systems.[38][48][49]

However, accurately determining what effect species like the jaguar have on ecosystems is difficult, because data must be compared from regions where the species is absent as well as its current habitats, while controlling for the effects of human activity. It is accepted that mid-sized prey species undergo population increases in the absence of the keystone predators, which has been hypothesized to have cascading negative effects.[50] However, field work has shown this may be natural variability and the population increases may not be sustained. Thus, the keystone predator hypothesis is not accepted by all scientists.[51]
The jaguar also coexists with other predators. The jaguar and the cougar are often sympatric (related species sharing overlapping territory) and have often been studied in conjunction. The cougar is the next-largest cat in South America, but is usually larger than the jaguar in Central or North America.[38] In northern Mexico, the jaguar and cougar were found to almost always live in the same areas with neither species having areas where it was the only one of the two living.[52] A study in central Mexico found that the favorite prey of both species was white-tailed deer, with it making up 54% and 66% of jaguar and cougar's prey by biomass, respectively.[38] Therefore, in Mexico and Central America, where cougars are usually equal to or slightly larger than the jaguar in size, neither would be considered to dominant over the other.[52]
In South America, however, where the jaguar is larger than the cougar, the jaguar tends to take larger prey, usually over 22 kg (49 lb) and the cougar smaller prey, usually between 2 and 22 kg (4 and 49 lb), which reduces the cougar's average size.[53] This situation may be advantageous to the cougar. Its broader prey niche, including its ability to take smaller prey, may give it an advantage over the jaguar in human-altered landscapes;[38] while both are classified as near-threatened species, the cougar has a significantly larger current distribution. Depending on the availability of prey, the cougar and jaguar may even share it.[52]
Hunting and diet


Like all cats, the jaguar is an obligate carnivore, feeding only on meat. An analysis of 53 studies documenting the diet of the jaguar across its distribution revealed that its prey ranges in weight from 1–130 kg (2.2–286.6 lb); it prefers prey weighing 45–85 kg (99–187 lb), with capybara (Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris) and giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) being significantly preferred. When available, it also preys on marsh deer (Blastocerus dichotomus), southern tamandua (Tamandua tetradactyla), collared peccary (Pecari tajacu) and black agouti (Dasyprocta fuliginosa).[27] In floodplains, jaguars opportunistically take reptiles such as turtles and caimans. Consumption of reptiles appears to be more frequent in jaguars than in other big cats.[54] The jaguar also preys on livestock in cattle ranching areas where wild prey is scarce.[55][56]
The jaguar has an exceptionally powerful bite.[31] Its bite force allows it to pierce the shells of turtles[57] and to employ an unusual killing method: it bites mammalian prey directly through the skull between the ears to deliver a fatal bite to the brain.[58] Although the jaguar bites into the throat of South American tapir (Tapirus terrestris) and other large prey until the victim suffocates, it kills capybara by piercing its canine teeth through the temporal bones of its skull, breaking its zygomatic arch and mandible and penetrating its brain, often through the ears.[59] This has been hypothesized to be an adaptation to "cracking open" turtle shells; armored reptiles may have formed an abundant prey base for the jaguar following the late Pleistocene extinctions.[57] However, this is disputed as even in areas were jaguars prey on reptiles, they are taken relatively infrequently in comparison to their abundance and mammals still dominate the cat's diet.[54]
The activity patterns of the jaguar coincides with the activity of its main prey species.[60] Camera trap studies revealed that the jaguar primarily exhibits a crepuscular–nocturnal activity pattern. However, jaguars living in thickly forested regions of the Amazon Rainforest and the Pantanal are largely active by day, whereas jaguars in the Atlantic forest are primarily active by night.[61] The jaguar may hunt during the day if game is available and is a relatively energetic feline, spending as much as 50–60 percent of its time active.[29]
The jaguar uses a stalk-and-ambush strategy when hunting, rather than chasing prey. The cat will walk slowly down forest paths, listening for and stalking prey before rushing or ambushing. The jaguar attacks from cover and usually from a target's blind spot with a quick pounce; the species' ambushing abilities are considered nearly peerless in the animal kingdom by both indigenous people and field researchers and are probably a product of its role as an apex predator in several different environments. The ambush may include leaping into water after prey, as a jaguar is quite capable of carrying a large kill while swimming; its strength is such that carcasses as large as a heifer can be hauled up a tree to avoid flood levels. After killing prey, the jaguar will drag the carcass to a thicket or other secluded spot. It begins eating at the neck and chest, rather than the midsection. The heart and lungs are consumed, followed by the shoulders.[62]
The daily food requirement of a 34 kg (75 lb) animal, at the extreme low end of the species' weight range, has been estimated at 1.4 kg (3 lb).[63] In the wild, consumption is naturally more erratic; wild cats expend considerable energy in the capture and kill of prey, and they may consume up to 25 kg (55 lb) of meat at one feeding, followed by periods of famine.[64]
Social activity

The jaguar is solitary except for females with cubs. In 1977, groups consisting of a male, female and cubs as well as of two females and of two males were sighted several times in a study area in the Paraguay River valley. A radio-collared female moved in a home range of 25–38 km2 (9.7–14.7 sq mi), which partly overlapped with another female. The home range of the male in this study area overlapped with several females.[65]
The size of home ranges depends on level of deforestation and human population density. The home ranges of females vary from 15.3 km2 (5.9 sq mi) in the Pantanal to 53.6 km2 (20.7 sq mi) in the Amazon to 233.5 km2 (90.2 sq mi) in the Atlantic Forest. Male jaguar home ranges vary from 25 km2 (9.7 sq mi) in the Pantanal to 180.3 km2 (69.6 sq mi) in the Amazon to 581.4 km2 (224.5 sq mi) in the Atlantic Forest and 807.4 km2 (311.7 sq mi) in the Cerrado.[66] The jaguar uses scrape marks, urine, and feces to mark its territory.[67][68]
Fights between males occur, but are rare, and avoidance behavior has been observed in the wild.[67] Due to structure of the larynx, the jaguar is capable of roaring.[69][70] The jaguar roars to warn territorial and mating competitors; intensive bouts of counter-calling between individuals have been observed in the wild.[57] The female jaguar prustens when approached by the male, possibly to signal tranquility and passivity.[71][72]
Reproduction and life cycle

In captivity, the female jaguar reaches sexual maturity at the age of about 2.5 years. Estrus lasts 7–15 days with an estrus cycle of 41.8 to 52.6 days. During estrus, she exhibits increased restlessness with rolling and prolonged vocalizations.[73] She is an induced ovulator, but can also ovulate spontaneously.[74] Gestation lasts 91 to 111 days.[75] The male is sexually mature at the age of three to four years.[76] His mean ejaculate volume is 8.6±1.3 ml.[77] Generation length of the jaguar is 9.8 years.[78]
Females range more widely than usual during courtship. Breeding pairs separate after mating, and females provide all parenting. They give birth to two cubs, sometimes up to four. After birth, females do not tolerate the presence of the father; there is a risk of infanticide.[62]
The young are born with closed eyes, but open them after two weeks. Cubs are weaned at the age of three months, but remain in the birth den for six months before leaving to accompany their mother on hunts.[79] Jaguars remain with their mothers for up to two years. They appear to rarely live beyond 11 years but captive individuals may live 22 years.[9]
Attacks on humans
The evolutionary food sources of jaguars did not include large primates, so they do not normally see humans as prey. [80] Experts have cited them as the least likely of all big cats to kill and eat humans, and the majority of attacks come when it has been cornered or wounded.[81] However, such behavior appears to be more frequent whenever humans enter jaguar habitat, and decrease access to prey.[82] When the Spanish conquistadors arrived in the Americas, they feared jaguars. However, at this time, the jaguar's chief prey was the capybara in South America, and the peccary further north. Charles Darwin reported that the Indigenous peoples of the Americas stated that their people did not need to fear the jaguar, as long as capybaras were abundant.[83]
Threats

The jaguar is threatened by loss and fragmentation of habitat, illegal killing in retaliation for livestock depredation and for the illegal trade in jaguar body parts. It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List, as the jaguar population has probably declined by 20–25% since the mid-1990s. Deforestation is a major threat to the jaguar across its range.[1] In 2002, it was estimated that the range of the jaguar had declined to about 46% of its range in the early 20th century.[45] In 2018, it was estimated that its range had declined by 55% in the last century. The only remaining stronghold is the Amazon rainforest, a region that is rapidly being fragmented by deforestation.[84]
In Mexico, the jaguar is primarily threatened by poaching. Its habitat is fragmented in northern Mexico, in the Gulf of Mexico and in the Yucatán Peninsula, caused by changes in land use, construction of roads and tourism infrastructure.[85] In Venezuela, the jaguar was extirpated in about 26% of its range in the country since 1940, foremost in dry savannas and unproductive scrubland in the northeastern region.[86]
The international trade of jaguar skins boomed between the end of the Second World War and the early 1970s.[87] Significant declines occurred in the 1960s, as more than 15,000 jaguars were yearly killed for their skins in the Brazilian Amazon alone; the trade in jaguar skins decreased since 1973 when the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species was enacted.[88] Interview surveys with 533 people in the northwestern Bolivian Amazon revealed that local people killed jaguars out of fear, in retaliation and for trade.[89] Between August 2016 and August 2019, jaguar skins and body parts were seen for sale in tourist markets in the Peruvian cities of Lima, Iquitos and Pucallpa.[90] Human-wildlife conflict, opportunistic hunting and hunting for trade in domestic markets are key drivers for killing jaguars in Belize and Guatemala.[91]
Conservation
The jaguar is listed on CITES Appendix I, which means that all international trade in jaguars or their body parts is prohibited. Hunting jaguars is prohibited in Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, French Guiana, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Suriname, the United States, and Venezuela. Hunting jaguars is restricted in Guatemala and Peru.[1] In Ecuador, hunting jaguars is prohibited, and it is classified as threatened with extinction.[92] In Guyana, it is protected as an endangered species, and hunting it is illegal.[93] Jaguars are occasionally sighted in Arizona and New Mexico.[94][95][96]
Jaguar Conservation Units

Jaguar conservation is complicated because of the species' large range spanning 18 countries with different policies and regulations. Specific areas of high importance for jaguar conservation, so-called "Jaguar Conservation Units" (JCU) were determined in 2000. These are large areas inhabited by at least 50 jaguars. Each unit was assessed and evaluated on the basis of size, connectivity, habitat quality for both jaguar and prey, and jaguar population status. That way, 51 Jaguar Conservation Units were determined in 36 geographic regions as priority areas for jaguar conservation including:[45]
- the Sierra Madre of Mexico
- the Selva Maya tropical forests extending over Mexico, Belize, and Guatemala
- the Chocó-Darién moist forests from Honduras, Panama to Colombia
- Sierra de Tamaulipas
- Venezuelan Llanos
- northern Cerrado and Amazon basin in Brazil
- Misiones Province in Argentina
In August 2012, the USFWS set aside 3,392.20 km2 (838,232 acres) in Arizona and New Mexico for the protection of the jaguar.[97]
Recent studies underlined that to maintain the robust exchange across the jaguar gene pool necessary for maintaining the species, it is important that jaguar habitats are interconnected. The Paseo del Jaguar project (Path of the Jaguar), has been established to connect several jaguar hotspots.[98] In 1986, the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary was established in Belize as the world's first protected area for jaguar conservation.[99]
Work employing GPS telemetry in 2003 and 2004 found densities of only six to seven jaguars per 100 km2 in the critical Pantanal region, compared with 10 to 11 using traditional methods; this suggests the widely used sampling methods may inflate the actual numbers of cats.[100]
Approaches

In setting up protected reserves, efforts generally also have to be focused on the surrounding areas, as jaguars are unlikely to confine themselves to the bounds of a reservation, especially if the population is increasing in size. Human attitudes in the areas surrounding reserves and laws and regulations to prevent poaching are essential to make conservation areas effective.[101]
To estimate population sizes within specific areas and to keep track of individual jaguars, camera trapping and wildlife tracking telemetry are widely used, and feces may be sought out with the help of detector dogs to study jaguar health and diet.[100][102] Current conservation efforts often focus on educating ranch owners and promoting ecotourism.[103] The jaguar is generally defined as an umbrella species – its home range and habitat requirements are sufficiently broad that, if protected, numerous other species of smaller range will also be protected.[104] Umbrella species serve as "mobile links" at the landscape scale, in the jaguar's case through predation. Conservation organizations may thus focus on providing viable, connected habitat for the jaguar, with the knowledge other species will also benefit.[103]
Ecotourism setups are being used to generate public interest in charismatic animals such as the jaguar, while at the same time generating revenue that can be used in conservation efforts. Audits done in Africa have shown that ecotourism has helped in African cat conservation. As with large African cats, a key concern in jaguar ecotourism is the considerable habitat space the species requires, so if ecotourism is used to aid in jaguar conservation, some considerations need to be made as to how existing ecosystems will be kept intact, or how new ecosystems that are large enough to support a growing jaguar population will be put into place.[105]
In culture and mythology
In pre-Columbian Central and South America, the jaguar was a symbol of power and strength. In the Andes, a jaguar cult disseminated by the early Chavín culture became accepted over most of today's Peru by 900 BC. The later Moche culture of northern Peru used the jaguar as a symbol of power in many of their ceramics.[106][107][108] In the religion of the Muisca in Altiplano Cundiboyacense, the jaguar was considered a sacred animal, and people dressed in jaguar skins during religious rituals.[109] The skins were traded with peoples in the Orinoquía Region.[110] The name of Muisca rulers Nemequene was derived from the Chibcha words nymy and quyne, meaning "force of the jaguar".[111][112]
In Mesoamerica, the Olmec—an early and influential culture of the Gulf Coast of Mexico roughly contemporaneous with the Chavín—developed a distinct "Olmec were-jaguar" motif of sculptures and figurines showing stylised jaguars or humans with jaguar characteristics. In the later Maya civilization, the jaguar was believed to facilitate communication between the living and the dead and to protect the royal household. The Maya saw these powerful felines as their companions in the spiritual world, and a number of Maya rulers bore names that incorporated the Mayan word for jaguar (b'alam in many of the Mayan languages). Balam (Jaguar) remains a common Maya surname, and it is also the name of Chilam Balam, a legendary author to whom are attributed 17th and 18th-centuries Maya miscellanies preserving much important knowledge. The Aztec civilization shared this image of the jaguar as the representative of the ruler and as a warrior. The Aztecs formed an elite warrior class known as the Jaguar warrior. In Aztec mythology, the jaguar was considered to be the totem animal of the powerful deity Tezcatlipoca.[113][114] Remains of jaguar bones were discovered in a burial site in Guatemala, which indicates that Mayans kept jaguars as pets.[115]
A conch shell gorget depicting a jaguar was found in a burial mound in Benton County, Missouri. The gorget shows evenly-engraved lines and measures 104 mm × 98 mm (4.1 in × 3.9 in).[116] Rock drawings made by the Hopi, Anasazi and Pueblo all over the desert and chaparral regions of the American Southwest show an explicitly spotted cat, presumably a jaguar, as it is drawn much larger than an ocelot.[47]
The jaguar is also used as a symbol in contemporary culture. It is the national animal of Guyana, and is featured in its Coat of arms of Guyana.[117] The flag of the Department of Amazonas features a black jaguar silhouette leaping towards a hunter.[118] The crest of the Argentine Rugby Union features a jaguar.[119]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e Quigley, H.; Foster, R.; Petracca, L.; Payan, E.; Salom, R. & Harmsen, B. (2017). "Panthera onca". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T15953A123791436.
- ^ Marcgraf, G. (1648). "Iaguara Brasiliensibus". Historia Naturalis Brasiliae. Auspicio et Beneficio. Vol. Historia Rerum Naturalium Brasiliae. Lugdun Batavorum, Amstelodam: Franciscus Hackius et Lud. Elzevirius. p. 235.
- ^ Ray, J. (1693). "Pardus an Lynx brasiliensis, Jaguara". Synopsis Methodica Animalium Quadrupedum et Serpentini Generis. Vulgarium Notas Characteristicas, Rariorum Descriptiones integras exhibens. London: S. Smith & B. Walford. p. 168.
- ^ Labat, J.B. (1731). "Once, espèce de Tigre". Voyage du chevalier Des Marchais en Guinée, isles voisines, et à Cayenne, fait en 1725, 1726 & 1727. Vol. Tome III. Amsterdam: La Compagnie. p. 285.
- ^ Liddell, H. G. & Scott, R. (1940). "πάνθηρ". A Greek-English Lexicon (Revised and augmented ed.). Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- ^ a b Linnaeus, C. (1758). "Felis onca". Systema naturæ per regna tria naturæ, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. Tomus I (Decima, reformata ed.). Holmiae: Laurentius Salvius. p. 42.
- ^ a b Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Species Panthera onca". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 546–547. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b Pocock, R. I. (1939). "The races of jaguar (Panthera onca)". Novitates Zoologicae. 41: 406–422.
- ^ a b c d e Seymour, K. L. (1989). "Panthera onca" (PDF). Mammalian Species. 340 (340): 1–9. doi:10.2307/3504096. JSTOR 3504096. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 June 2010. Retrieved 27 December 2009.
- ^ Blainville, H. M. D. de (1843). "F. leo nubicus". Ostéographie ou description iconographique comparée du squelette et du système dentaire des mammifères récents et fossils pour servir de base à la zoologie et la géologie (in French). Vol. Tome II. Paris: J. B. Baillière et Fils. p. Plate VIII.
- ^ Gray, J. E. (1857). "Notice of a new species of jaguar from Mazatlan, living in the gardens of the Zoological Society". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. 25: 278.
- ^ Ameghino, F. (1888). "Formación Pampeana". Los Mamíferos fósiles de la República Argentina (in Spanish). Buenos Aires: Pablo E. Coni é hijos. pp. 473–493.
- ^ a b Mearns, E. A. (1901). "The American Jaguars". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 14: 137–143.
- ^ Hollister, N. (1915). "Two new South American jaguars". Proceedings of the United States National Museum. 48 (2069): 169–170. doi:10.5479/si.00963801.48-2069.169.
- ^ a b Goldman, E. A. (1932). "The jaguars of North America". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 45: 143–146.
- ^ Nelson, E. W. & Goldman, E. A. (1933). "Revision of the jaguars". Journal of Mammalogy. 14 (3): 221–240. doi:10.2307/1373821. JSTOR 1373821.
- ^ a b Eizirik, E.; Kim, J. H.; Menotti-Raymond, M.; Crawshaw P. G. Jr.; O'Brien, S. J. & Johnson, W. E. (2001). "Phylogeography, population history and conservation genetics of jaguars (Panthera onca, Mammalia, Felidae)". Molecular Ecology. 10 (1): 65–79. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2001.01144.x. PMID 11251788. S2CID 3916428.
- ^ Larson, S. E. (1997). "Taxonomic re-evaluation of the jaguar". Zoo Biology. 16 (2): 107–120. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2361(1997)16:2<107::AID-ZOO2>3.0.CO;2-E.
- ^ Ruiz-Garcia, M.; Payan, E.; Murillo, A. & Alvarez, D. (2006). "DNA microsatellite characterization of the jaguar (Panthera onca) in Colombia". Genes & Genetic Systems. 81 (2): 115–127. doi:10.1266/ggs.81.115. PMID 16755135.
- ^ Kitchener, A. C.; Breitenmoser-Würsten, C.; Eizirik, E.; Gentry, A.; Werdelin, L.; Wilting, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Abramov, A. V.; Christiansen, P.; Driscoll, C.; Duckworth, J. W.; Johnson, W.; Luo, S.-J.; Meijaard, E.; O'Donoghue, P.; Sanderson, J.; Seymour, K.; Bruford, M.; Groves, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Nowell, K.; Timmons, Z. & Tobe, S. (2017). "A revised taxonomy of the Felidae: The final report of the Cat Classification Task Force of the IUCN Cat Specialist Group" (PDF). Cat News. Special Issue 11: 70–71.
- ^ a b c Johnson, W. E.; Eizirik, E.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Murphy, W. J.; Antunes, A.; Teeling, E. & O'Brien, S. J. (2006). "The Late Miocene radiation of modern Felidae: A genetic assessment". Science. 311 (5757): 73–77. Bibcode:2006Sci...311...73J. doi:10.1126/science.1122277. PMID 16400146. S2CID 41672825.
- ^ a b c Li, G.; Davis, B. W.; Eizirik, E. & Murphy, W. J. (2016). "Phylogenomic evidence for ancient hybridization in the genomes of living cats (Felidae)". Genome Research. 26 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1101/gr.186668.114. PMC 4691742. PMID 26518481.
- ^ Janczewski, D. N.; Modi, W. S.; Stephens, J. C. & O'Brien, S. J. (1996). "Molecular evolution of mitochondrial 12S RNA and cytochrome b sequences in the pantherine lineage of Felidae". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 12 (4): 690–707. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040232. PMID 7544865.
- ^ Johnson, W. E. & O'Brien, S. J. (1997). "Phylogenetic reconstruction of the Felidae using 16S rRNA and NADH-5 mitochondrial genes". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 44 (S1): S98–S116. Bibcode:1997JMolE..44S..98J. doi:10.1007/PL00000060. PMID 9071018. S2CID 40185850.
- ^ Yu, L. & Zhang, Y. P. (2005). "Phylogenetic studies of pantherine cats (Felidae) based on multiple genes, with novel application of nuclear beta-fibrinogen intron 7 to carnivores". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 35 (2): 483–495. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.01.017. PMID 15804417.
- ^ Arias-Alzate, A.; González-Maya, J.F.; Arroyo-Cabrales, J. & Martínez-Meyer, E. (2017). "Wild felid range shift due to climatic constraints in the Americas: A bottleneck explanation for extinct felids?" (PDF). Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 24 (4): 427–438. doi:10.1007/s10914-016-9350-0.
- ^ a b Hayward, M. W.; Kamler, J. F.; Montgomery, R. A. & Newlove, A. (2016). "Prey Preferences of the Jaguar Panthera onca Reflect the Post-Pleistocene Demise of Large Prey". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 3: 148. doi:10.3389/fevo.2015.00148.
- ^ Hope, M. K. & Deem, S. L. (2006). "Retrospective Study of Morbidity and Mortality of Captive Jaguars (Panthera onca) in North America: 1982–2002" (PDF). Zoo Biology. 25 (6): 501–512. doi:10.1002/zoo.20112.
- ^ a b c Nowell, K. & Jackson, P. (1996). "Jaguar, Panthera onca (Linnaeus, 1758)" (PDF). Wild Cats. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group. pp. 118–122.
- ^ a b Gonyea, W.J. (1976). "Adaptive differences in the body proportions of large felids". Acta Anatomica. 96: 81–96. doi:10.1159/000144663. PMID 973541.
- ^ a b Wroe, S.; McHenry, C. & Thomason, J. (2006). "Bite club: comparative bite force in big biting mammals and the prediction of predatory behavior in fossil taxa". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 272 (1563): 619–625. doi:10.1098/rspb.2004.2986. PMC 1564077. PMID 15817436.
- ^ Christiansen, P. (2007). "Canine morphology in the larger Felidae: implications for feeding ecology". Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 91 (4): 573–592. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.2007.00819.x.
- ^ Hartstone-Rose, A.; Perry, J. M. G. & Morrow, C. J. (2012). "Bite Force Estimation and the Fiber Architecture of Felid Masticatory Muscles". The Anatomical Record: Advances in Integrative Anatomy and Evolutionary Biology. 295 (8): 1336–1351. doi:10.1002/ar.22518. PMID 22707481. S2CID 35304260.
- ^ a b c Nowak, R.M. (1999). Walker's Mammals of the World. Vol. 2. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 831. ISBN 978-0-8018-5789-8.
- ^ Burnie, D. & Wilson, D.E. (2001). Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide to the World's Wildlife. New York City: Dorling Kindersley. ISBN 978-0-7894-7764-4.
- ^ Boitani, L. (1984). Simon and Schuster's Guide to Mammals. New York: Touchstone. ISBN 978-0-671-43727-5.
- ^ "All about Jaguars: Ecology". Wildlife Conservation Society. Archived from the original on 29 May 2009. Retrieved 11 August 2006.
- ^ a b c d e Nuanaez, R.; Miller, B. & Lindzey, F. (2000). "Food habits of jaguars and pumas in Jalisco, Mexico". Journal of Zoology. 252 (3): 373–379. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2000.tb00632.x.
- ^ Brown, D.E. & Lopez-Gonzalez, C.A. (2001). Borderland jaguars: tigres de la frontera. Salt Lake City, UT: University of Utah Press.
- ^ Eizirik, E.; Yuhki, N.; Johnson, W. E.; Menotti-Raymond, M.; Hannah, S. S. & O'Brien, S. J. (2003). "Molecular Genetics and Evolution of Melanism in the Cat Family". Current Biology. 13 (5): 448–453. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00128-3. PMID 12620197. S2CID 19021807.
- ^ Dinets, V. & Polechla, P. J. (2005). "First documentation of melanism in the jaguar (Panthera onca) from northern Mexico". Cat News. 42: 18. Archived from the original on 26 September 2006.
- ^ Núñez, M.C. & Jiménez, E.C. (2009). "A new record of a black jaguar, Panthera onca (Carnivora: Felidae) in Costa Rica" (PDF). Brenesia. 71: 67–68.
- ^ Mooring, M. S.; Eppert, A. A. & Botts, R. T. (2020). "Natural Selection of Melanism in Costa Rican Jaguar and Oncilla: A Test of Gloger's Rule and the Temporal Segregation Hypothesis". Tropical Conservation Science. 13: 1–15. doi:10.1177/1940082920910364.
- ^ Merriam, C.H. (1919). "Is the Jaguar entitled to a place in the Californian fauna?". Journal of Mammalogy. 1 (1): 38–42. doi:10.1093/jmammal/1.1.38.
- ^ a b c Sanderson, E. W.; K. H., Redford; Chetkiewicz, C. B.; Medellin, R. A .; Rabinowitz, A. R.; Robinson, J. G. & Taber, A. B. (2002). "Planning to save a species: the jaguar as a model". Conservation Biology. 16 (1): 58–72. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.2002.00352.x. S2CID 3955250.
- ^ Brulliard, K. (2016). "Jaguar spotting: A new wild cat may be roaming the United States". The Washington Post. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ a b Pavlik, S. (2003). "Rohonas and Spotted Lions: The Historical and Cultural Occurrence of the Jaguar, Panthera onca, among the Native Tribes of the American Southwest". Wicazo Sa Review. 18 (1): 157–175. doi:10.1353/wic.2003.0006. JSTOR 1409436. S2CID 161236104.
- ^ Nijhawan, S. (2012). "Conservation units, priority areas and dispersal corridors for jaguars in Brazil" (PDF). Cat News (Special Issue): 43–47.
- ^ Petracca, L.S.; Ramírez-Bravo, O.E. & Hernández-Santín, L. (2014). "Occupancy estimation of jaguar Panthera onca to assess the value of east-central Mexico as a jaguar corridor" (PDF). Oryx. 48 (1): 133–140. doi:10.1017/S0030605313000069. S2CID 86460403.
- ^ "Structure and Character: Keystone Species". Mongabay. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 30 August 2006.
- ^ Wright, S. J.; Gompper, M. E.; DeLeon, B. (1994). "Are large predators keystone species in Neotropical forests? The evidence from Barro Colorado Island". Oikos. 71 (2): 279–294. doi:10.2307/3546277. JSTOR 3546277.
- ^ a b c Gutiérrez-González, C. E.; López-González, C. A. (2017). "Jaguar interactions with pumas and prey at the northern edge of jaguars' range". PeerJ. 5 (5): e2886. doi:10.7717/peerj.2886. PMC 5248577. PMID 28133569.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Iriarte, J. A.; Franklin, W.L.; Johnson, W.E. & Redford, K.H. (1990). "Biogeographic variation of food habits and body size of the America puma". Oecologia. 85 (2): 185–190. Bibcode:1990Oecol..85..185I. doi:10.1007/BF00319400. PMID 28312554. S2CID 10134066.
- ^ a b Miranda, E; Menezes, J; Rheingantz, M. L. (2016). "Reptiles as principal prey? Adaptations for durophagy and prey selection by jaguar (Panthera onca)". Journal of Natural History: 2021–2035. doi:10.1080/00222933.2016.1180717.
- ^ Amit, R.; Gordillo-Chávez, E.J. & Bone, R. (2013). "Jaguar and puma attacks on livestock in Costa Rica". Human-Wildlife Interactions. 7 (1): 77–84.
- ^ Zarco-González, M.M.; Monroy-Vilchis, O. & Alaníz, J. (2013). "Spatial model of livestock predation by jaguar and puma in Mexico: conservation planning". Biological Conservation. 159: 80–87. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2012.11.007.
- ^ a b c Emmons, L.H. (1987). "Comparative feeding ecology of fields in a neotropical rain forest". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 20 (4): 271–283. doi:10.1007/BF00292180. S2CID 24990860.
- ^ Rosa, C. L. de la; Nocke, C. C. (2000). "Jaguar (Panthera onca)". A guide to the carnivores of Central America: natural history, ecology, and conservation. University of Texas Press. pp. 39–?. ISBN 978-0-292-71604-9.
- ^ Schaller, G.B. & Vasconselos, J.M.C. (1978). "Jaguar predation on capybara" (PDF). Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde. 43: 296–301.
- ^ Harmsen, B.J.; Foster, R.J.; Silver, S. C.; Ostro, L.E.T. & Doncaster, C.P. (2011). "Jaguar and puma activity patterns in relation to their main prey". Mammalian Biology – Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde. 76 (3): 320–324. doi:10.1016/j.mambio.2010.08.007.
- ^ Astete, S.R.; Sollmann, R. & Silveira, L. (2008). "Comparative ecology of jaguars in Brazil". Cat News (Special Issue 4): 9–14. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.528.3603.
- ^ a b Baker, Natural History and Behavior, pp. 8–16.
- ^ "Determination That Designation of Critical Habitat Is Not Prudent for the Jaguar". Federal Register Environmental Documents. 12 July 2006. Retrieved 30 August 2006.
- ^ Baker, Nutrition, pp. 55–61.
- ^ Schaller, G. B. & Crawshaw, P. G. Jr. (1980). "Movement Patterns of Jaguar". Biotropica. 12 (3): 161–168. doi:10.2307/2387967. JSTOR 2387967.
- ^ Morato, R.G.; Stabach, J.A.; Fleming, C.H.; Calabrese, J.M.; De Paula, R.C.; Ferraz, K.M.; Kantek, D.L.; Miyazaki, S.S.; Pereira, T.D.; Araujo, G.R. & Paviolo, A. (2016). "Space use and movement of a neotropical top predator: the endangered Jaguar". PloS One. 11 (12): e0168176. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0168176.
- ^ a b Rabinowitz, A. R. & Nottingham, B.G. Jr. (1986). "Ecology and behaviour of the Jaguar (Panthera onca) in Belize, Central America". Journal of Zoology. 210 (1): 149–159. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1986.tb03627.x.
- ^ Harmsen, B. J.; Foster, R.J.; Gutierrez, S.M.; Marin, S.Y. & Doncaster, C.P. (2007). "Scrape-marking behavior of jaguars (Panthera onca) and pumas (Puma concolor)". Journal of Mammalogy. 91 (5): 1225–1234. doi:10.1644/09-mamm-a-416.1.
- ^ Hast, M. H. (1989). "The larynx of roaring and non-roaring cats". Journal of Anatomy. 163: 117–121. PMC 1256521. PMID 2606766.
- ^ Weissengruber, G. E.; Forstenpointner, G.; Peters, G.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Fitch, W. T. (2002). "Hyoid apparatus and pharynx in the lion (Panthera leo), jaguar (Panthera onca), tiger (Panthera tigris), cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus) and domestic cat (Felis silvestris f. catus)". Journal of Anatomy. 201 (3): 195–209. doi:10.1046/j.1469-7580.2002.00088.x. PMC 1570911. PMID 12363272.
- ^ Peters, G.; Tonin-Leyhausen, B. (1999). "Evolution of Acoustic Communication Signals of Mammals: Friendly Close-Range Vocalizations in Felidae (Carnivora)". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 6 (2): 129–159. doi:10.1023/A:1020620121416.
- ^ Leuchtenberger, C.; Crawshaw, P. G.; Mourão, G.; Lehn, C. R. (2009). "Courtship behavior by Jaguars in the Pantanal of Mato Grosso do Sul". Natureza & Conservaç~ao Revista Brasileira de Conservaç~ao Da Natureza. 7 (1): 218–222.
- ^ Wildt, D.E.; Platz, C.C.; Chakraborty, P.K. & Seager, S.W.J. (1979). "Oestrous and ovarian activity in a female jaguar (Panthera onca)". Reproduction. 56 (2): 555–558.
- ^ Barnes, S.A.; Teare, J.A.; Staaden, S.; Metrione, L. & Penfold, L.M. (2016). "Characterization and manipulation of reproductive cycles in the jaguar (Panthera onca)". General and Comparative Endocrinology. 225: 95–103. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2015.09.012.
- ^ Hemmer, H. (1976). "Gestation period and postnatal development in felids". In Eaton, R.L. (ed.). The world’s cats. Vol. 3. Contributions to Biology, Ecology, Behavior and Evolution. Seattle: Carnivore Research Institute, Univ. Washington. pp. 143–165.
- ^ Mondolfi, E.; Hoogesteijn, R. (1986). "Notes on the biology and status of the jaguar (Panthera onca) in Venezuela". In Miller, S.D.; Everett, D.D. (eds.). Cats of the world: biology, conservation and management. Washington, DC: National Wildlife Federation. pp. 85–123. ISBN 9780912186795.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Morato, R. G.; Guimaraes, M.A.B.; Ferriera, F.; Verreschi, I.T.d.N.; Barnabe, R.C. (1999). "Reproductive characteristics of captive male jaguars". Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Research and Animal Science. 36 (5). doi:10.1590/S1413-95961999000500008.
- ^ Pacifici, M.; Santini, L.; Di Marco, M.; Baisero, D.; Francucci, L.; Grottolo Marasini, G.; Visconti, P.; Rondinini, C. (2013). "Generation length for mammals". Nature Conservation. 5 (5): 87–94. doi:10.3897/natureconservation.5.5734.
- ^ Egerton, J. (2006). "Jaguars: Magnificence in the Southwest" (PDF). Wild Tracks. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 6 December 2009.
- ^ "Why did Audubon Zoo's escaped jaguar kill so many animals?".
- ^ Seidensticker, J.; Lumpkin, S. (2016). Cats in Question: The Smithsonian Answer Book. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution. ISBN 9781588345462.
- ^ V. Iserson, K.; Francis, Adama M. (2015). "Jaguar Attack on a Child: Case Report and Literature Review". Western Journal of Emergency Medicine. 16 (2): 303–309. doi:10.5811/westjem.2015.1.24043. PMC 4380383. PMID 25834674.
- ^ Porter, J. H. (1894). "The Jaguar". Wild beasts; a study of the characters and habits of the elephant, lion, leopard, panther, jaguar, tiger, puma, wolf, and grizzly bear. New York: C. Scribner's sons. pp. 174–195.
- ^ De La Torre, J.A.; González-Maya, J.F.; Zarza, H.; Ceballos, G. & Medellín, R.A. (2018). "The jaguar's spots are darker than they appear: assessing the global conservation status of the jaguar Panthera onca". Oryx. 52 (2): 300–315. doi:10.1017/S0030605316001046.
- ^ Ceballos, G.; Zarza, H.; Chávez, C. & González-Maya, J.F. (2016). "Ecology and Conservation of Jaguars in Mexico". In Aguirre, A. & Sukumar, R. (eds.). Tropical conservation: Perspectives on local and global priorities. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. pp. 273–289. ISBN 9780199766987.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Jędrzejewski, W.; Boede, E. O.; Abarca, M.; Sánchez-Mercado, A.; Ferrer-Paris, J. R.; Lampo, M.; Velásquez, G.; Carreño, R.; Viloria, Á. L.; Hoogesteijn, R.; Robinson, H. S.; Stachowicz, I.; Cerda, H.; Weisz, M. del Mar; Barros, T. R.; Rivas, Gilson A.; Borges, G.; Molinari, J.; Lew, D.; Takiff, H.; Schmidt, K. (2017). "Predicting carnivore distribution and extirpation rate based on human impacts and productivity factors; assessment of the state of jaguar (Panthera onca) in Venezuela". Biological Conservation. 206: 132–142. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2016.09.027.
- ^ Broad, S. (1987). The harvest of and trade in Latin American spotted cats (Felidae) and otters (Lutrinae). Cambridge, UK: IUCN Conservation Monitoring Centre.
- ^ Weber, W. & Rabinowitz, A. (1996). "A Global Perspective on Large Carnivore Conservation" (PDF). Conservation Biology. 10 (4): 1046–1054. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.1996.10041046.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 April 2012.
- ^ Knox, J.; Negrões, N.; Marchini, S.; Barboza, K.; Guanacoma, G.; Balhau, P.; Tobler, M.W. & Glikman, J.A. (2019). "Jaguar persecution without "cowflict": insights from protected territories in the Bolivian Amazon". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 7: 494. doi:10.3389/fevo.2019.00494.
- ^ Braczkowski, A.; Ruzo, A.; Sanchez, F.; Castagnino, R.; Brown, C.; Guynup, S.; Winter, S.; Gandy, D. & O'Bryan, C. (2019). "The ayahuasca tourism boom: An undervalued demand driver for jaguar body parts?". Conservation Science and Practice. 1 (12): e126. doi:10.1111/csp2.126.
- ^ Arias, M.; Hinsley, A. & Milner-Gulland, E.J. (2020). "Characteristics of, and uncertainties about, illegal jaguar trade in Belize and Guatemala". Biological Conservation. 250: 108765. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108765.
- ^ Zapata Ríos, G.; Araguillin, E.; Cevallos, J.; Moreno, F.; Ortega, A.; Rengel, J. & Valarezo, N. (2014). Plan de Acción para la Conservación del Jaguar en el Ecuador [Action Plan for the Conservation of the Jaguar in Ecuador] (PDF) (in Spanish). Quito: Ministerio del Ambiente y Wildlife Conservation Society Ecuador.
- ^ Kerman, I. (2010). Felix, M.-L. (ed.). Exploitation of the jaguar, Panthera onca and other large forest cats in Suriname. Paramaribo: WWF Guianas.
- ^ Brown, D.E. & González, C.A.L. (2000). "Notes on the occurrences of jaguars in Arizona and New Mexico". The Southwestern Naturalist. 45 (4): 537–542. doi:10.2307/3672607. JSTOR 3672607.
- ^ Lamberton-Moreno, J. (2015). "Student project results in new jaguar sighting". Sky Island Alliance. Retrieved 4 January 2015.
- ^ Handwerk, B. (2016). "Only known Jaguar in U.S. filmed in rare video". National Geographic News. Retrieved 4 February 2016.
- ^ Greenberg, S. H. (2012). "Kitty Corner: Jaguars Win Critical Habitat in U.S." Scientific American.
- ^ White, Mel (1 March 2009). "Path of the Jaguar". National Geographic. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Weckel, M., Giuliano, W. and Silver, S. (2006). "Cockscomb revisited: jaguar diet in the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary, Belize". Biotropica. 38 (5): 687–690. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7429.2006.00190.x. S2CID 85151201.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Soisalo, M. K. & Cavalcanti, S. M.C. (2006). "Estimating the density of a Jaguar population in the Brazilian Pantanal using camera-traps and capture-recapture sampling in combination with GPS radio-telemetry" (PDF). Biological Conservation. 129 (4): 487–496. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2005.11.023. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 September 2006. Retrieved 5 September 2006.
- ^ Gutierrez-Gonzalez, C.E.; Gomez-Ramirez, M.A.; Lopez-Gonzalez, C.A. & Doherty, P.F. (2015). "Are Private Reserves Effective for Jaguar Conservation?". PLOS ONE. 10 (9): e0137541. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1037541G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0137541. PMC 4580466. PMID 26398115.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Furtado, M. M.; Carrillo-Percastegui, S. E.; Jácomo, A. T. A.; Powell, G.; Silveira, L.; Vynne, C. & Sollmann, R. (2008). "Studying jaguars in the wild: past experiences and future perspectives" (PDF). Cat News (Special Issue 4).
- ^ a b "Jaguar Refuge in the Llanos Ecoregion". World Wildlife Fund. Archived from the original on 17 December 2014. Retrieved 1 September 2006.
- ^ "Glossary". Sonoran Desert Conservation Plan: Kids. Pima County Government. Archived from the original on 20 June 2006. Retrieved 1 September 2006.
- ^ Mossaz, A.; Buckley, R.C. & Castley, J.G. (2015). "Ecotourism Contributions to Conservation of African Big Cats". Journal for Nature Conservation. 28: 112–118. doi:10.1016/j.jnc.2015.09.009. hdl:10072/125191.
- ^ Museo Arqueologico Rafael Larco Herrera (1997). Berrin, K.; Benson, E. P. (eds.). The Spirit of Ancient Peru: Treasures from the Museo Arqueologico Rafael Larco Herrera. London, New York, Melbourne, Singapore, Hong Kong: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-01802-6.
- ^ Bulliet, R. W.; Crossley, P.; Headrick, D.; Hirsch, S.; Johnson, L., eds. (2000). The Earth and Its Peoples: A Global History. Vol. A 1: To 1200 (Fifth ed.). Houghton Mifflin. pp. 75–. ISBN 978-1-4390-8476-2.
- ^ Lockard, C. A. (2010). Societies, Networks, and Transitions. A Global History. Vol. To 1500 (Second ed.). Boston: Wadsworth Cengage Learning. pp. 215–. ISBN 978-1-4390-8535-6.
- ^ Ocampo López, J. (2007). Grandes culturas indígenas de América – Great indigenous cultures of the Americas (in Spanish). Bogotá, Colombia: Plaza & Janes Editores Colombia S.A. p. 231. ISBN 978-958-14-0368-4.
- ^ Kruschek, M. H. (2003). The evolution of the Bogotá chiefdom: A household view (PDF) (PhD). Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh.
- ^ "nymy" (in Spanish). Muysccubun Dictionary Online. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
- ^ "quyne" (in Spanish). Muysccubun Dictionary Online. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
- ^ Saunders, N.J. (1994). "Predators of culture: Jaguar symbolism and Mesoamerican elites". World Archaeology. 26 (1): 104–117. JSTOR 124867.
- ^ Christenson, A.J. (2007). Popol Vuh: The Sacred Book of the Maya. Oklahoma: University of Oklahoma Press. p. 196. ISBN 978-0-8061-3839-8. Retrieved 11 December 2011.
- ^ Dapcevich, Madison (20 March 2018). "Ancient Mayans Probably Kept Jaguars As Pets And Raised Dogs For Food". IFLScience. Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- ^ Daggett, P. M. & Henning, D. R. (1974). "The Jaguar in North America". American Antiquity. 39 (3): 465–469. doi:10.2307/279437. JSTOR 279437.
- ^ Khan, A. (2021). "National symbols: The Coat-Of-Arms". Guyana News and Information.
- ^ Gutterman, D. (2008). "Amazonas Department (Colombia)". Flag of the World. Retrieved 2 April 2010.
- ^ Davies, S. (2007). "Puma power: Argentinian rugby". BBC News. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
Bibliography
- Baker, W. K. Jr.; et al. Law, Christopher (ed.). Guidelines for Captive Management of Jaguars (PDF). Jaguar Species Survival Plan. American Zoo and Aquarium Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 January 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
External links
- "Jaguar Panthera onca". IUCN Cat Specialist Group.
- "Jaguar". BBC. 2014. Archived from the original on 22 September 2014.
- People and Jaguars a Guide for Coexistence
- Felidae Conservation Fund
- . Encyclopedia Americana. 1920.







