 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 6,7-Dihydrocanrenone; 7-Desthioacetylspironolactone; 20-Spirox-4-ene-3,20-dione |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Antimineralocorticoid; Progestogen; Steroidal antiandrogen |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.321 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H30O3 |
| Molar mass | 342.479 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
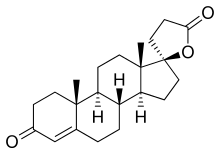
SC-5233, also known as 6,7-dihydrocanrenone or 20-spirox-4-ene-3,20-dione, is a synthetic, steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group which was developed by G. D. Searle & Company in the 1950s but was never marketed.[1][2] It was the first synthetic antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor to have been identified and tested in humans.[1][3] The drug was found to lack appreciable oral bioavailability and to be of low potency when administered parenterally,[4] but it nonetheless produced a mild diuretic effect in patients with congestive heart failure.[1] SC-8109, the 19-nor (19-demethyl) analogue, was developed and found to have improved oral bioavailability and potency, but still had low potency.[5] Spironolactone (SC-9420; Aldactone) followed and had both good oral bioavailability and potency, and was the first synthetic antimineralocorticoid to be marketed.[3] It has about 46-fold higher oral potency than SC-5233.[6]
SC-5233 is the propionic acid lactone of testosterone (androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one) and is also known 3-(3-oxo-17β-hydroxyandrost-4-en-17α-yl)propionic acid γ-lactone or as 17α-(2-carboxyethyl)testosterone γ-lactone.[7] It is the unsubstituted parent or prototype compound of the spirolactone family of steroidal antimineralocorticoids.[2][8]
Similarly to other spirolactones like canrenone and spironolactone, SC-5233 has some antiandrogenic activity and antagonizes the effects of testosterone in animals.[7] In addition, along with SC-8109, it has been found to possess potent progestogenic activity.[9]
Chemical structures of spirolactones
|
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Sherlock S (14 December 2013). "Diuretics in Liver Disease". In Buchborn E, Bock KD (eds.). Diuresis and Diuretics / Diurese und Diuretica: An International Symposium Herrenchiemsee, June 17th–20th, 1959 Sponsored by CIBA / Ein Internationales Symposium Herrenchiemsee, 17.–20. Juni 1959 Veranstaltet mit Unterstützung der CIBA. Springer-Verlag. pp. 224, 261. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-92756-0_11. ISBN 978-3-642-49716-2.
- ^ a b Szasz G, Budvari-Barany Z (19 December 1990). "Diuretics". Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Antihypertensive Agents. CRC Press. pp. 82–. ISBN 978-0-8493-4724-5.
- ^ a b Delcayre C, Fazal L, Ragot H, Prudhomme M, Azibani F, Samuel JL (6 November 2014). "The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Cardiovascular Disease". In Cokkinos DB (ed.). Introduction to Translational Cardiovascular Research. Springer. pp. 61–. ISBN 978-3-319-08798-6.
- ^ "Spironolactone". The British Encyclopaedia of Medical Practice: Medical progress. Butterworth & Company. 1961. p. 302.
Cena and Kagawa first synthesized 3-(3-oxo-17β-hydroxy-4-androsten-17α-yl)-propionic acid-gamma-lactone and later prepared its 19-nor analogue. These compounds were designated SC-5233 and SC-8109, respectively. Both have anti-aldosterone activity and most of the early work on aldosterone antagonism was done with their aid. SC-5233 is not appreciably absorbed when given by mouth and the parenteral dose is large. As in the case of certain other steroids the 19-nor derivative was an improvement on the parent compound (Klyne, 1959). SC-8109 is well absorbed from the alimentary tract, but the dose is about 2 g daily.
- ^ Brandon ML (1 January 1962). Corticosteroids in medical practice. Thomas. p. 310. ISBN 9780398002152.
- ^ Kolkhof P, Bärfacker L (July 2017). "30 YEARS OF THE MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: 60 years of research and development". The Journal of Endocrinology. 234 (1): T125–T140. doi:10.1530/JOE-16-0600. PMC 5488394. PMID 28634268.
- ^ a b Kagawa CM, Sturtevant FM, Van Arman CG (June 1959). "Pharmacology of a new steroid that blocks salt activity of aldosterone and desoxycorticosterone". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 126 (2): 123–130. PMID 13665517.
[SC-5233] (total dose of 5 mg/rat) partially blocked the effects of testosterone propionate on the seminal vesicles and prostate in similar animals.
- ^ Kalvoda J, de Gasparo M (24 August 2010). "Eplerenone: Selective Aldosterone Antagonist". In Fischer J, Ganellin CR (eds.). Analogue-based Drug Discovery II. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 361–. ISBN 978-3-527-63212-1.
- ^ Hertz R, Tullner WW (November 1958). "Progestational activity of certain steroid-17-spirolactones". Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 99 (2): 451–452. doi:10.3181/00379727-99-24380. PMID 13601900. S2CID 20150966.

Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction