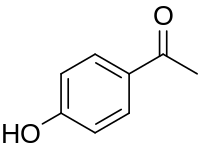
 Chemical structure of piceol
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethan-1-one | |
| Other names
1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanone
4-Hydroxyacetophenone 4'-Hydroxyacetophenone p-Hydroxyacetophenone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.548 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Piceol is a phenolic compound found in the needles and in mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces (Picea abies).[1][2] Picein is the glucoside of piceol.[3]
Uses[edit]
Piceol is used in the synthesis of several pharmaceutical drugs including octopamine, sotalol, bamethan, and dyclonine.[citation needed]
Piceol can be used to make acetaminophen by oxime formation with hydroxylamine and subsequent Beckmann rearrangement in acid.[4]
Anticonvulsants are also possible by Mannich reaction:[5]
Metabolism[edit]
Diprenylated derivatives of piceol can be isolated from Ophryosporus macrodon.[6]
4-Hydroxyacetophenone monooxygenase is an enzyme that transforms piceol into O-acetylhydroquinone. This enzyme is found in Pseudomonas fluorescens.
See also[edit]
- Paroxypropione, where the acetyl group is replaced by a propionyl group.
- Apocynin
References[edit]
- ^ Løkke, H. (1990). "Picein and piceol concentrations in Norway spruce". Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 19 (3): 301–9. doi:10.1016/0147-6513(90)90032-z. PMID 2364913.
- ^ Münzenberger, Babette; Heilemann, Jürgen; Strack, Dieter; Kottke, Ingrid; Oberwinkler, Franz (1990). "Phenolics of mycorrhizas and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruce". Planta. 182 (1): 142–8. doi:10.1007/BF00239996. PMID 24197010.
- ^ Løkke, Hans (1990). "Picein and piceol concentrations in Norway spruce". Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 19 (3): 301–309. doi:10.1016/0147-6513(90)90032-Z. PMID 2364913.
- ^ U.S. patent 4,524,217
- ^ Keshari, Amit K.; Tewari, Aseem; Verma, Shweta S.; Saraf, Shailendra K. (2017). "Novel Mannich-bases as Potential Anticonvulsants: Syntheses, Characterization and Biological Evaluation". Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry. 17 (3). doi:10.2174/1871524917666170717113524. ISSN 1871-5249.
- ^ Sigstad, Elizabeth; Catalán, César A.N.; Diaz, Jesús G.; Herz, Werner (1993). "Diprenylated derivatives of p-hydroxyacetophenone from Ophryosporus macrodon". Phytochemistry. 33: 165–169. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(93)85415-N.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction