| Pennellidae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Lernaeenicus sprattae on host Sprattus sprattus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Copepoda |
| Order: | Siphonostomatoida |
| Family: | Pennellidae Burmeister, 1835 |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
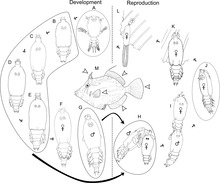
Pennellidae is a family of parasitic copepods.[1][3] When anchored on a host, they have a portion of the body on the outside of the host, whereas the remaining anterior part of the parasite is hidden inside tissues of the host.[3]
Genera
[edit]There are 24 genera:[1]
- Allotrifur Yamaguti, 1963
- Cardiodectes C. B. Wilson, 1917
- Creopelates Shiino, 1958
- Exopenna Boxshall, 1986
- Haemobaphes Steenstrup & Lutken, 1861
- Impexus Kabata, 1972
- Lernaeenicus C. B. Wilson, 1932
- Lernaeocera Blainville, 1822
- Lernaeolophus Heller, 1865
- Metapeniculus Castro-Romero & Baeza-Kurok, 1985
- Nagasawanus Uyeno, 2015
- Ophiolernaea Shiino, 1958
- Parinia Kazachenko & Avdeev, 1977
- Peniculisa C. B. Wilson, 1917
- Peniculus von Nordmann, 1832
- Pennella Oken, 1816
- Peroderma Heller, 1865
- Phrixocephalus C. B. Wilson, 1908
- Propeniculus Castro Romero, 2014
- Protosarcotretes Ohtsuka, Lindsay & Izawa, 2018 [4]
- Pseudopeniculus Castro Romero, 2014
- Sarcotretes Jungersen, 1911
- Serpentisaccus Blasiola, 1979
- Trifur C. B. Wilson, 1917
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Walter TC, Boxshall G, eds. (2021). "Pennellidae Burmeister, 1835". World of Copepods database. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ^ Ismail, Norshida; Ohtsuka, Susumu; Venmathi Maran, Balu Alagar; Tasumi, Satoshi; Zaleha, Kassim; Yamashita, Hirofumi (2013). "Complete life cycle of a pennellid Peniculus minuticaudae Shiino, 1956 (Copepoda: Siphonostomatoida) infecting cultured threadsail filefish, Stephanolepis cirrhifer". Parasite. 20: 42. doi:10.1051/parasite/2013041. PMC 3813946. PMID 24165196.
- ^ a b Hogans, W. E. (2017). "Cardiodectes medusaeus (Copepoda: Pennellidae) a synonym of Cardiodectes bellottii, a parasite of mid-water fishes in the North Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 130 (1): 250–255. doi:10.2988/17-00019. S2CID 89975409.
- ^ Ohtsuka, Susumu; Lindsay, Dhugal J.; Izawa, Kunihiko (2018). "A new genus and species of the family Pennellidae (Copepoda, Siphonostomatoida) infecting the Pacific viperfish Chauliodus macouni". Parasite. 25: 6. doi:10.1051/parasite/2018003. PMC 5806539. PMID 29424341.

Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction