| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
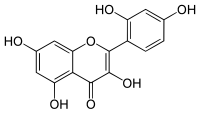
| IUPAC name
2′,3,4′,5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Aurantica
Al-Morin Morin hydrate Calico Yellow Toxylon pomiferum Bois d'arc Osage orange extract | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.858 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H10O7 | |
| Molar mass | 302.238 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.799 g/mL |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Morin is a yellow chemical compound that can be isolated from Maclura pomifera (Osage orange), Maclura tinctoria (old fustic), and from leaves of Psidium guajava (common guava).[1] In a preclinical in vitro study, morin was found to be a weak inhibitor of fatty acid synthase with an IC50 of 2.33 μM.[2] Morin was also found to inhibit amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide (or amylin) and disaggregate amyloid fibers.[3]
Morin can be used to test for the presence of aluminium or tin in a solution, since it forms characteristically fluorescent coordination complexes with them under UV light.
Glycosides
[edit]- Morin-3-O-arabinoside[1]
- Morin-3-O-lyxoside[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Rattanachaikunsopon, Pongsak; Phumkhachorn, Parichat (2007). "Bacteriostatic effect of flavonoids isolated from leaves of Psidium guajava on fish pathogens". Fitoterapia. 78 (6): 434–436. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2007.03.015. PMID 17553634.
- ^ Tian, Wei-Xi (2006). "Inhibition of Fatty Acid Synthase by Polyphenols". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 13 (8): 967–977. doi:10.2174/092986706776361012. PMID 16611078.
- ^ Noor, Harris; Cao, Ping; Raleigh, Daniel P. (2012). "Morin hydrate inhibits amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide and disaggregates amyloid fibers". Protein Science. 21 (3): 373–382. doi:10.1002/pro.2023. PMC 3375438. PMID 22238175.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction