| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
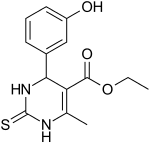
| IUPAC name
ethyl 4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2-sulfanylidene-3,4-dihydro-1H-pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
| |
| Other names
Monastrol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H16N2O3S | |
| Molar mass | 292.35344 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Monastrol is a cell-permeable small molecule inhibitor discovered by Thomas U. Mayer in the lab of Tim Mitchison. Monastrol was shown to inhibit the kinesin-5 (also known as KIF11, Kinesin Eg5), a motor protein important for spindle bipolarity.[1]
Mechanism of action[edit]
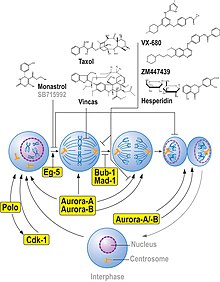
Monastrol binds to a long loop that is specific to the Eg5 (also known as KIF11 or kinesin-5) kinesin family, and allosterically inhibits ATPase activity of the kinesin [2]
References[edit]
- ^ Thomas U. Mayer; Tarun M. Kapoor; Stephen J. Haggarty; Randall W. King; Stuart L. Schreiber; Timothy J. Mitchison (1999). "Small Molecule Inhibitor of Mitotic Spindle Bipolarity Identified in a Phenotype-Based Screen". Science. 286 (5441): 971–974. doi:10.1126/science.286.5441.971. PMID 10542155. S2CID 15348455.
- ^ Maliga Z, Kapoor TM, Mitchison TJ (September 2002). "Evidence that monastrol is an allosteric inhibitor of the mitotic kinesin Eg5". Chem. Biol. 9 (9): 989–96. doi:10.1016/S1074-5521(02)00212-0. PMID 12323373.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction