| Structural formula | 
|

|

|
|
| Name | Fluoromethane Methyl fluoride |
Chloromethane Methyl chloride |
Bromomethane Methyl bromide |
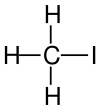
Iodomethane Methyl iodide |
| Melting point | −137,8 °C[1] | −97,4 °C[2] | −93,7 °C[3] | −66 °C[4] |
| Boiling point | −78,4 °C[1] | −23,8 °C[2] | 4,0 °C[3] | 42 °C[4] |
| Space-filling model | 
|

|

|

|
The monohalomethanes are organic compounds in which a hydrogen atom in methane is replaced by a halogen. They belong to the haloalkanes or to the subgroup of halomethanes.
The four common[a] members are fluoromethane, chloromethane, bromomethane and iodomethane.
Historical name for this group is methyl halides; it's still widely used. The compounds of this class are often described as CH3X or MeX (X - any halogen, Me - methyl group).
Related compounds
[edit]There are analogs with more than one hydrogen atom in methane is replaced by a halogen:
- Dihalomethane, CH2X2, two hydrogen atoms replaced
- Trihalomethane, CHX3, three hydrogen atoms replaced
- Tetrahalomethane, CX4, all four hydrogen atoms replaced
Analogs with carbon atom replaced with a heavier group 14 element are also known:
- Monohalosilane, SiH3X (with silicon, related to silane)
- Monohalogermane, GeH3X (with germanium, related to germane)
- Monohalostannane, SnH3X (with tin, related to stannane)
See also
[edit]- Methyl halide transferase, an enzyme producing some methyl halides
Notes
[edit]- ^ Highly radioactive CH3At (methyl astatide) has been detected.[5] The known isotopes of even heavier group 17 element, tennessine, are too short-lived to allow for chemical experimentation.
References
[edit]- ^ a b Record of Fluoromethane in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2020-02-29.
- ^ a b Record of Chloromethane in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2020-02-29.
- ^ a b Record of Bromomethane in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2020-02-29.
- ^ a b Record of Iodomethane in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2020-02-29.
- ^ "Chemical Fact Sheet: Astatine". European Virtual Institute for Speciation Analysis (EVISA).
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction