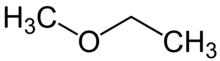
| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methoxyethane[1] | |
| Other names
ethyl methyl ether
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.128.000 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H8O | |
| Molar mass | 60.096 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless gas[2] |
| Density | 0.7251 g cm−3 (at 0 °C)[2] |
| Melting point | −113 °C (−171 °F; 160 K) |
| Boiling point | 7.4 °C (45.3 °F; 280.5 K) |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3420 (at 4 °C)[2] |
| Viscosity | 0.224 cP at 25 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Extremely Flammable (F+), Liquefied gas |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related Ethers
|
Dimethyl ether Diethyl ether Methoxypropane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Methoxyethane, also known as ethyl methyl ether, is a colorless gaseous ether with the formula CH3OCH2CH3. Unlike the related dimethyl ether and diethyl ether, which are widely used and studied, this mixed alkyl ether has no current applications. It is a structural isomer of isopropyl alcohol. Its utility as an anesthetic[3] and solvent[4] have been investigated.
References[edit]
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 703. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-00648. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c Haynes, William M. (2010). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (91 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press. p. 3-248. ISBN 978-1-43982077-3.
- ^ Bovill, J. G. (2008). "Inhalation Anaesthesia; From Diethyl Ether to Xenon". Modern Anesthetics. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Vol. 182. Springer. pp. 121–142. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-74806-9_6. ISBN 978-3-540-72813-9. PMID 18175089.
- ^ Campion, Christopher L.; Li, Wentao; Lucht, Brett L. (2005). "Thermal Decomposition of LiPF[sub 6]-Based Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries". Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 152 (12): A2327. doi:10.1149/1.2083267.

Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction