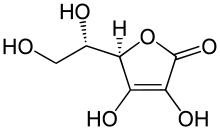
Mineral ascorbates are a group of salts of ascorbic acid (vitamin C).[1] They are composed of a mineral cation bonded to ascorbate (the anion of ascorbic acid).
Production[edit]
Mineral ascorbates are powders manufactured by reacting ascorbic acid with mineral carbonates in aqueous solutions, venting the carbon dioxide, drying the reaction product, and then milling the dried product to the desired particle size.
The choice of the mineral carbonates can be calcium carbonate, potassium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, magnesium carbonate, or many other mineral forms.
Uses[edit]
Mineral ascorbates are used as dietary supplements and food additives, and drugs. An example of a mineral ascorbate drug is sodium ascorbate injections (the acid form, ascorbic acid, of vitamin c is too acidic for injections).
Ascorbate salts may be better tolerated by the human body than the corresponding weakly acidic ascorbic acid.
Ascorbates are highly reactive antioxidants used as food preservatives.[2]
Examples of mineral ascorbates are:
- Sodium ascorbate (E301)
- Calcium ascorbate (E302)
- Potassium ascorbate (E303)
- Magnesium ascorbate
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "The Many Faces of Vitamin C by Thomas Levy". Archived from the original on 2015-01-09. Retrieved 2012-02-12.
- ^ UK Food Standards Agency: "Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers". Retrieved 2011-10-27.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction