| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
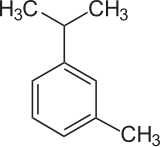
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Methyl-3-(propan-2-yl)benzene | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14 | |
| Molar mass | 134.22 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.86 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −63.8 °C (−82.8 °F; 209.3 K) |
| Boiling point | 175 °C (347 °F; 448 K) |
| 42.5 mg/L | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Flammable |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H226 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P280, P303+P361+P353, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |
| Flash point | 47.8 °C (118.0 °F; 320.9 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
m-Cymene is an organic compound classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Its structure consists of a benzene ring meta-substituted with a methyl group and an isopropyl group. It is a flammable colorless liquid which is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Isomers and production[edit]
In addition to m-cymene, there are two other geometric isomers called o-cymene, in which the alkyl groups are ortho-substituted, and p-cymene, in which they are para-substituted. p-Cymene is the most common and only natural isomer. The three isomers form the group of cymenes.
Cymenes can be produced by alkylation of toluene with propylene.[1][2]
References[edit]
- ^ Vora, Bipin V.; Kocal, Joseph A.; Barger, Paul T.; Schmidt, Robert J.; Johnson, James A. (2003). "Alkylation". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0112112508011313.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.
- ^ Griesbaum, Karl; Behr, Arno; Biedenkapp, Dieter; Voges, Heinz-Werner; Garbe, Dorothea; Paetz, Christian; Collin, Gerd; Mayer, Dieter; Höke (2002). "Hydrocarbons". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_227. ISBN 978-3527306732.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction