| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
iodite
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
dioxidoiodate(1−) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| IO− 2 | |
| Molar mass | 58.90 g/mol |
| Conjugate acid | Iodous acid |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Chlorite Bromite |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
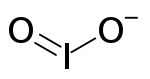
The iodite ion, or iodine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula IO−
2. Within the ion the Iodine exists in the oxidation state of +3.
Iodite anion
[edit]Iodites (including iodous acid) are highly unstable and have been observed[1] but never isolated.[citation needed] They will rapidly disproportionate to molecular Iodine and Iodates.[2] However, they have been detected as intermediates in the conversion between iodide and iodate.[3][4]
Iodous acid
[edit]
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
iodous acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| HIO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 159.91 g/mol | ||
| Conjugate base | Iodite | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Iodous acid is acid form of the iodite ion, with the formula HIO2.
Other oxyanions
[edit]Iodine can assume oxidation states of −1, +1, +3, +5, or +7. A number of neutral iodine oxides are also known.
| Iodine oxidation state | −1 | +1 | +3 | +5 | +7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Iodide | Hypoiodite | Iodite | Iodate | periodate |
| Formula | I− | IO− | IO− 2 |
IO− 3 |
IO− 4 or IO5− 6 |
References
[edit]- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Gupta, Yugul Kishore; Sharma, Devendra Nath (August 1971). "Kinetics and mechanism of the reduction of iodate to iodite by bromide in the presence of phenol". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 75 (16): 2516–2522. doi:10.1021/j100685a018.
- ^ Gilles, Mary K.; Polak, Mark L.; Lineberger, W. C. (1992). "Photoelectron spectroscopy of the halogen oxide anions FO−, ClO−, BrO−, IO−, OClO−, and OIO−". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 96 (11): 8012. Bibcode:1992JChPh..96.8012G. doi:10.1063/1.462352.


Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction