 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablet) |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H13N3 |
| Molar mass | 199.257 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Gapicomine (INN) is a coronary vasodilator. It has been withdrawn from the market in the countries it was used in.[1]
Also, gapicomine is a major component in the drug Bicordin.[2]
History[edit]
Gapicomine was discovered in 1970 by Polish chemist Stanisław Biniecki. It was first published about in an article of The Polish Journal of Medicine and Pharmacy describing the derivative drug Bicordin in 1974.[3]
Synthesis[edit]
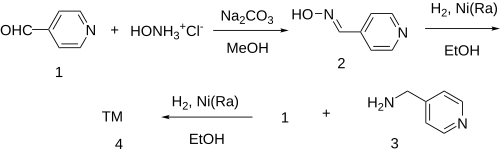
The oxime formation between isonicotinaldehyde [872-85-5] (1) and hydroxylamine gives 4-Pyridinealdoxime [696-54-8] (2). This is then reduced by catalytic hydrogenation over Raney-Nickel into 4-Picolylamine [3731-53-1] (3). Reductive amination of the last with a second equivalent of isonicotinaldehyde affords gapicomine (4).
References[edit]
- ^ "Gapicomine Monograph, The Index Nominum". Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ "Bicordin, PubChem". Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ Samochowiec L, Wójcicki J, Gregorczyk K, Szmatloch E (1974). "Bicordin--a new drug in the treatment of coronary heart disease". Mater Med Pol. 6 (4): 298–300. PMID 4453155.
- ^ Anon., GB 1058356 (1967 to Starogardzkie Zakl Farma).
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction