| Eurotherium Temporal range: Early to Middle Eocene
| |
|---|---|
| |
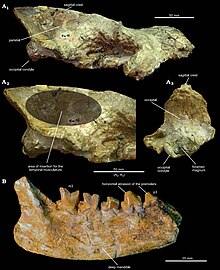
| skull and mandible of Eurotherium theriodis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | †Hyaenodonta |
| Superfamily: | †Hyaenodontoidea |
| Family: | †Hyaenodontidae |
| Genus: | †Eurotherium Polly and Lange-Badré, 1993[1] |
| Type species | |
| †Eurotherium theriodis Van Valen, 1965
| |
| Species | |
| Synonyms | |
|
synonyms of species:
| |
Eurotherium ("european beast") is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from extinct family Hyaenodontidae that lived from the early to middle Eocene in Europe.[1][6][7]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Polly, P. David; Lange-Badré, Brigitte (1993). "A new genus Eurotherium (Mammalia, Creodonta) in reference to taxonomic problems with some Eocene hyaenodontids from Eurasia". Comptes rendus de l'Académie des Sciences. 317: 9910996.
- ^ Solé, F.; Morlo, M.; Schaal, T.; Lehmann, T. (2021). "New hyaenodonts (Mammalia) from the late Ypresian locality of Prémontré (France) support a radiation of the hyaenodonts in Europe already at the end of the early Eocene". Geobios. 66–67: 119–141. Bibcode:2021Geobi..66..119S. doi:10.1016/j.geobios.2021.02.004. S2CID 234848856.
- ^ Langé-Badre, Brigitte; Haubold, Hartmut (1990). "Les Créodontes (Mammifères) du gisement du Geiseltal (Éocène Moyen, RDA)". Geobios. 5 (23): 607–637. Bibcode:1990Geobi..23..607L. doi:10.1016/0016-6995(90)80028-E.
- ^ Van Valen, Leigh (1965). "Some European Proviverrini (Mammalia, Deltatheridia)". Palaeontology. 8: 638–665.
- ^ Matthes H. W. (1967.) "Eine neue Creodontier-Art aus der eozänen Geiseltal fauna." Ber. deutsch Ges. Geol. Wiss., (A), 12, 6: 659-667.
- ^ Borths, Matthew R.; Holroyd, Patricia A.; Seiffert, Eric R. (2016). "Hyainailourinae and Teratodontinae cranial material from the late Eocene of Egypt and the application of parsimony and Bayesian methods to the phylogeny and biogeography of Hyaenodonta (Placentalia, Mammalia)". PeerJ. 4: e2639. doi:10.7717/peerj.2639. PMC 5111901. PMID 27867761.
- ^ Dubied, Morgane; Solé, Floréal; Mennecart, Bastien (2019). "The cranium of Proviverra typica (Mammalia, Hyaenodonta) and its impact on hyaenodont phylogeny and endocranial evolution". Palaeontology. 62 (6): 983–1001. Bibcode:2019Palgy..62..983D. doi:10.1111/pala.12437. S2CID 201310577.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction