 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Minnebro |
| Other names | CS-3150; XL-550 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Antimineralocorticoid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
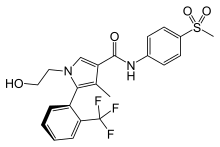
| Formula | C22H21F3N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 466.48 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Esaxerenone (INN) (brand name Minnebro; developmental code names CS-3150, XL-550) is a nonsteroidal antimineralocorticoid which was discovered by Exelixis and developed by Daiichi Sankyo Company and is approved in Japan for the treatment of hypertension.[1][2][3] It acts as a highly selective silent antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), the receptor for aldosterone, with greater than 1,000-fold selectivity for this receptor over other steroid hormone receptors, and 4-fold and 76-fold higher affinity for the MR relative to the existing antimineralocorticoids spironolactone and eplerenone.[1][2][3] As of January 2019, esaxerenone is in phase III clinical trials for diabetic nephropathies.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c "Esaxerenone - Daiichi Sankyo - AdisInsight".
- ^ a b Yang J, Young MJ (2016). "Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists-pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetic differences". Curr Opin Pharmacol. 27: 78–85. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2016.02.005. PMID 26939027.
- ^ a b Kolkhof P, Nowack C, Eitner F (2015). "Nonsteroidal antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor". Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 24 (5): 417–24. doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000147. PMID 26083526. S2CID 22113501.
External links
[edit]
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction