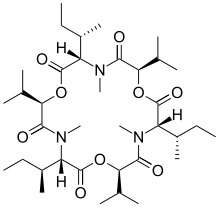
Enniatins are a class of organic chemical compounds found in Fusarium fungi. They appear in nature as mixtures of cyclic depsipeptides. The main variants are enniatin A, A1, B and B1 together with minor amounts of enniatin C, D, E and F.
The enniatins act as ionophores that bind ammonium,[1] and they have been proposed as replacements for nonactin in specific ammonium-based electrodes.
Enniatins have been also mentioned as potential anti-AIDS drugs.[citation needed]
See also
[edit]Biosynthesis
[edit]Chemical properties
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Ovchinnikov, Yu. A.; Ivanov, V. T.; Evstratov, A. V.; Mikhaleva, I. I.; Bystrov, V. F.; Portnova, S. L.; Balashova, T. A.; Meshcheryakova, E. N.; Tul'chinskii, V. M. (1974). "Enniatin ionophores. Conformation and ion binding properties". International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research. 6 (6): 465–498. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3011.1974.tb02407.x. PMID 4455641.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction