| Arohanam | S R₁ G₂ M₂ P D₃ N₃ Ṡ |
|---|---|
| Avarohanam | Ṡ N₃ D₃ P M₂ G₂ R₁ S |
| Carnatic music |
|---|
 |
| Concepts |
| Compositions |
| Instruments |
|
Divyamani (pronounced Divyamaṇi,[1] meaning the divine gem) is a rāgam in the 72 melakarta rāgam system of Carnatic music. It is the 48th in the series. It is called Jeevantika[1] or Jeevantini[2][3] in Muthuswami Dikshitar school of Carnatic music.
Structure and Lakshana[edit]
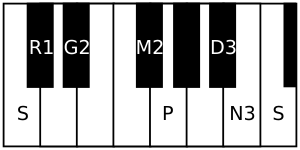
It is the 6th rāgam in the 8th chakra Vasu. The mnemonic name is Vasu-Sha. The mnemonic phrase is sa ra gi mi pa dhu nu.[2] Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows (see swaras in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms):
(the notes used in this scale are shuddha rishabham, sadharana gandharam, prati madhyamam, shatsruthi dhaivatham, kakali nishadham)
As it is a melakarta rāgam, by definition it is a sampoorna rāgam (has all seven notes in ascending and descending scale). It is the prati madhyamam equivalent of Roopavati, which is the 12th melakarta.
Janya rāgams[edit]
Divyamani has a few minor janya rāgams (derived scales) associated with it. See List of janya rāgams for all rāgams associated with Divyamani.
Compositions[edit]
A few compositions set to Divyamani are:
- Leela ganu joochi by Thyagaraja
- Appa muruga by Koteeswara Iyer
Related rāgams[edit]
This section covers the theoretical and scientific aspect of this rāgam.
Divyamani's notes when shifted using Graha bhedam, yields no other melakarta rāgam.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction