| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
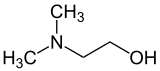
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(Dimethylamino)ethan-1-ol | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | DMAE, DMEA |
| 1209235 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.221 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Deanol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2051 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H11NO | |
| Molar mass | 89.138 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 890 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −59.00 °C; −74.20 °F; 214.15 K |
| Boiling point | 134.1 °C; 273.3 °F; 407.2 K |
| log P | −0.25 |
| Vapor pressure | 816 Pa (at 20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.23 (at 20 °C)[1] |
| Basicity (pKb) | 4.77 (at 20 °C) |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.4294 |
| Pharmacology | |
| N06BX04 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H302, H312, H314, H332 | |
| P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |
| Flash point | 39 °C (102 °F; 312 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.4–12.2% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
|
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanols
|
|
Related compounds
|
Diethylhydroxylamine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE or DMEA) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2OH. It is bifunctional, containing both a tertiary amine and primary alcohol functional groups. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is used in skin care products for improving skin tone and also taken orally as a nootropic. It is prepared by the ethoxylation of dimethylamine.[2]
Industrial uses[edit]
Dimethylaminoethanol is used as a curing agent for polyurethanes and epoxy resins. It is a precursor to other chemicals, such as the nitrogen mustard 2-dimethylaminoethyl chloride.[3] The acrylate ester, dimethylaminoethyl acrylate is used as a flocculating agent.[4]
Related compounds are used in gas purification, e.g. removal of hydrogen sulfide from sour gas streams.
Human uses[edit]
The bitartrate salt of DMAE, i.e. N,N-dimethylethanolamine bitartrate, is sold as a dietary supplement.[5] It is a white powder providing 37% DMAE.[6]
Animal tests show possible benefit for improving spatial memory[7] and working memory.[8]
See also[edit]
- Choline
- Diphenhydramine
- Doxylamine
- Ethanolamine
- Meclofenoxate (Centrophenoxine)
- Orphenadrine
References[edit]
- ^ Littel, RJ; Bos, M; Knoop, GJ (1990). "Dissociation constants of some alkanolamines at 293, 303, 318, and 333 K" (PDF). Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data. 35 (3): 276–77. doi:10.1021/je00061a014. INIST 19352048.
- ^ Matthias Frauenkron; Johann-Peter Melder; Günther Ruider; Roland Rossbacher; Hartmut Höke (2002). "Ethanolamines and Propanolamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_001. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- ^ Ashford, Robert D. (2011). Ashford's Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, 3rd edition. Wavelength. p. 3294. ISBN 9780952267430. OCLC 863579691. Retrieved 2023-10-04.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ "Dimethylaminoethyl Acrylate - Global Review 2020 to 2030". Fact.MR. Retrieved 2023-10-04.
- ^ Haneke, Karen E.; Masten, Scott (November 2002). Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE) [108-01-0] and Selected Salts and Esters: Review of Toxicological Literature (Update) | Report on National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Contract No. N01-ES-65402 (PDF). National Toxicology Program (Report). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-10-04. Retrieved 2015-04-30 – via Contractee Integrated Laboratory Systems, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, 27709.
- ^ "Sigma Aldrich: Safety Data Sheet: 2-Dimethylaminoethanol (+)-bitartrate". Archived from the original on 2023-10-04.
- ^ Blin, Olivier; Audebert, Christine; Pitel, Séverine; Kaladjian, Arthur; Casse-Perrot, Catherine; Zaim, Mohammed; Micallef, Joelle; Tisne-Versailles, Jacky; Sokoloff, Pierre; Chopin, Philippe; Marien, Marc (2009-12-01). "Effects of dimethylaminoethanol pyroglutamate (DMAE p-Glu) against memory deficits induced by scopolamine: evidence from preclinical and clinical studies". Psychopharmacology. 207 (2): 201–212. doi:10.1007/s00213-009-1648-7. ISSN 1432-2072. PMID 19756528. S2CID 8535134.
- ^ Levin, Edward D; Rose, Jed E; Abood, Leo (June 1995). "Effects of nicotinic dimethylaminoethyl esters on working memory performance of rats in the radial-arm maze". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 51 (2–3): 369–373. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(94)00406-9. PMID 7667355. S2CID 20685322.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction