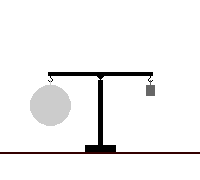
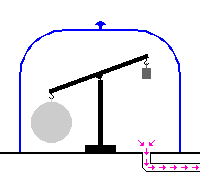
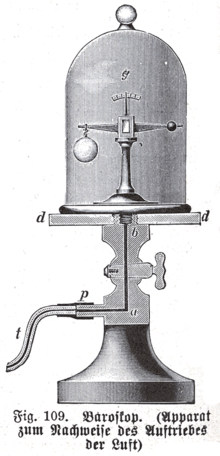
A dasymeter was meant initially as a device to demonstrate the buoyant effect of gases like air (as shown in the adjacent pictures). A dasymeter which allows weighing acts as a densimeter used to measure the density of gases.
Principle[edit]
The Principle of Archimedes permits to derive a formula which does not rely on any information of volume: a sample, the big sphere in the adjacent images, of known mass-density is weighed in vacuum and then immersed into the gas and weighed again.
(The above formula was taken from the article buoyancy and still has to be solved for the density of the gas.)
From the known mass density of the sample (sphere) and its two weight-values, the mass-density of the gas can be calculated as:
Construction and use[edit]
It consists of a thin sphere made of glass, ideally with an average density close to that of the gas to be investigated. This sphere is immersed in the gas and weighed.
History of the dasymeter[edit]
The dasymeter was invented in 1650 by Otto von Guericke. Archimedes used a pair of scales which he immersed into water to demonstrate the buoyant effect of water. A dasymeter can be seen as a variant of that pair of scales, only immersed into gas.
References[edit]
External links[edit]


Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction