| Danger space | |
|---|---|
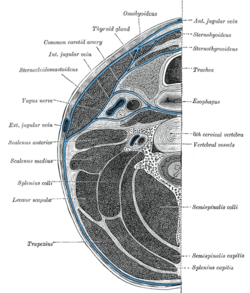 Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the fascia coli. | |
| Anatomical terminology |
The danger space or alar space, is a region of the neck.[1] The common name originates from the risk that an infection in this space can spread directly to the thorax, and, due to being a space continuous on the left and right, can furthermore allow infection to spread easily to either side.
Structure[edit]
It is bounded at the top by the skull base, at the front by the alar fascia and behind by the prevertebral fascia. It comes to an end at the level of the diaphragm.
The retropharyngeal space is found anterior to the danger space, between the alar fascia and buccopharyngeal fascia. There exists a midline raphe in this space so some infections of this space appear unilateral. The retropharyngeal space drains into the superior mediastinum, whereas the danger space drains into the posterior mediastinum.
Clinical significance[edit]
On CT or MRI it is only visible when distended by fluid or pus, below the level of T1-T6, as the retropharyngeal space ends at this level, allowing distinction between the two entities.[2] Superior spread of infection can affect the contents of the carotid sheath, including the internal jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, XI, and XII, while inferior spread of infection through the danger space can cause mediastinitis.
History[edit]
It was first characterized in 1938.[3][4]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Reynolds SC, Chow AW (2009). "Severe soft tissue infections of the head and neck: a primer for critical care physicians". Lung. 187 (5): 271–9. doi:10.1007/s00408-009-9153-7. PMID 19653038. S2CID 9009912.
- ^ Hoang, JK; Branstetter BF, 4th; Eastwood, JD; Glastonbury, CM (April 2011). "Multiplanar CT and MRI of collections in the retropharyngeal space: is it an abscess?". AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 196 (4): W426-32. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5116. PMID 21427307.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Adelson, Robert T. (2005). "Minimally invasive transoral catheter-assisted drainage of a danger-space infection". Ear, Nose & Throat Journal. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ Grodinsky M, Holyoke EA. The fasciae and fascial spaces of the head, neck and adjacent regions. Am J Anat 1938;63:367-408.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction