 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
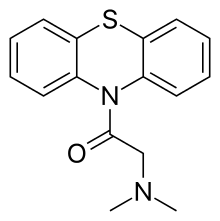
| Formula | C16H16N2OS |
| Molar mass | 284.38 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dacemazine (INN, also known as Ahistan and Histantine)[1] is a phenothiazine derivative which acts as a histamine antagonist at the H1 subtype. First described in 1951, it was never marketed as a drug on its own, although a combination of dacemazine and di-tert-butylnaphthalenesulfonate was sold as an antispasmodic and antitussive under the trade name Codopectyl.[1] It was also assessed as a possible anticancer drug.[2]
Synthesis
[edit]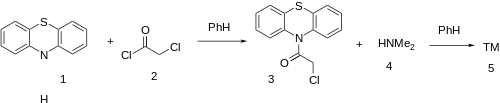
Amide formation between phenothiazine (1) and chloroacetyl chloride (2) gives 10-(Chloroacetyl)-phenothiazine [786-50-5] (3). The subsequent displacement of the remaining halogen with dimethylamine (4) completes the synthesis of dacemazine (5).
References
[edit]- ^ a b Triggle DJ, Ganellin CR, MacDonald F (1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. Vol. 1. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. p. 711. ISBN 0-412-46630-9. Retrieved on August 2, 2008 through Google Book Search.
- ^ Karolyhazy G, Havas I, Jansco G, Kapas L, Sellei C (August 1952). "[The anticarcinogenic effect of dimethylaminoacetyl-phentiazide (ahistan)]". Kiserletes Orvostudomany (in Romanian). 4 (4): 260–2. PMID 13023855.
- ^ Dahlbom, Richard; Ekstrand, Torsten; Rubin, Inger; Saluste, E.; Stjernholm, R.; Ehrensvärd, G. (1951). "10-Aminoacylphenothiazines. I. Aminoacetyl and Aminopropionyl Derivatives." Acta Chemica Scandinavica. 5: 102–114. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.05-0102.
- ^ Wassermann, N. et al, Rev. Chim., 1959, 10, 81 (synth) (only until 1991)
- ^ Kano; Makisumi Shionogi Kenkyusho Nenpo, 1957 , # 7 p. 511,514 Chem.Abstr., 1958 , p. 10094.
- ^ John W. Cusic, U.S. patent 2,694,705 (1954 to G. D. Searle & Co.).
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction