
| |
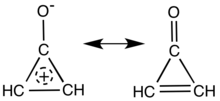 Main resonance structures of cyclopropenone.
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cycloprop-2-en-1-one | |
| Other names
Cyclopropenone, Cyclopropene-3-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H2O | |
| Molar mass | 54.048 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Melting point | −29 to −28 °C (−20 to −18 °F; 244 to 245 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cyclopropenone is an organic compound with molecular formula C3H2O consisting of a cyclopropene carbon framework with a ketone functional group. It is a colorless, volatile liquid that boils near room temperature.[1] Neat cyclopropenone polymerizes upon standing at room temperature,[2] and chemical vendors typically supply it as an acetal.[3] The chemical properties of the compound are dominated by the strong polarization of the carbonyl group, which gives a partial positive charge with aromatic stabilization on the ring and a partial negative charge on oxygen. It is an aromatic compound.[4][5]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ R. Breslow, J. Pecoraro, T. Sugimoto "Cyclpropenone" Org. Synth. 1977, vol. 57, pp. 41. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.057.0041
- ^ Breslow, Ronald; Oda, Masaji (1972-06-01). "Isolation and characterization of pure cyclopropenone". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 94 (13): 4787–4788. doi:10.1021/ja00768a089. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ^ Elliott, Gregory I.; Boger, Dale L. "Cyclopropene, 3,3‑Dimethoxy". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00486.
Dimethyl cyclopropenone ketal is less stable than the corresponding cyclic ketal derivatives....A direct route to cyclopropenone is the hydrolysis of 3,3‑dimethoxycyclopropene.
- ^ "Experiments show cyclopropenone is aromatic". Chem. Eng. News. 61 (38): 33. 1983. doi:10.1021/cen-v061n038.p033.
- ^ Peart, Patricia A.; Tovar, John D. (2010). "Poly(cyclopropenone)s: Formal Inclusion of the Smallest Hückel Aromatic into π-Conjugated Polymers". J. Org. Chem. 76 (15): 5689–5696. doi:10.1021/jo101108f. PMID 20704438.

Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction