 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
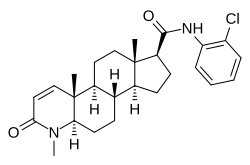
| Other names | N-(2-Chlorophenyl)-3-oxo-4-aza-4-methylandrost-1-en-17α-carboxamide |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H33ClN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 441.01 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cl-4AS-1 is a dual anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and 5α-reductase inhibitor.[1][2] It is a potent and selective full agonist of the androgen receptor (IC50 = 12 nM) and inhibitor of 5α-reductase types I and II (IC50 = 6 and 10 nM, respectively).[1][2] Structurally, Cl-4AS-1 is a 4-azasteroid.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Tolman RL, Sahoo SP, Bakshi RK, Gratale D, Patel G, Patel S, Toney J, Chang B, Harris GS (1997). "4-Methyl-3-oxo-4-aza-5alpha-androst-1-ene-17beta-N-aryl-carboxamides: an approach to combined androgen blockade [5alpha-reductase inhibition with androgen receptor binding in vitro]". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 60 (5–6): 303–9. doi:10.1016/s0960-0760(96)00199-9. PMID 9219921. S2CID 54405031.
- ^ a b Schmidt A, Harada S, Kimmel DB, Bai C, Chen F, Rutledge SJ, Vogel RL, Scafonas A, Gentile MA, Nantermet PV, McElwee-Witmer S, Pennypacker B, Masarachia P, Sahoo SP, Kim Y, Meissner RS, Hartman GD, Duggan ME, Rodan GA, Towler DA, Ray WJ (2009). "Identification of anabolic selective androgen receptor modulators with reduced activities in reproductive tissues and sebaceous glands". J. Biol. Chem. 284 (52): 36367–76. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.049734. PMC 2794752. PMID 19846549.
External links
[edit]
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction