
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
rel-[(2R,3R)-Butane-2,3-diyl]bis(diphenylphosphane) | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.152.152 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C28H28P2 | |||
| Molar mass | 426.47 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | White powder | ||
| Melting point | 104 to 109 °C (219 to 228 °F; 377 to 382 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
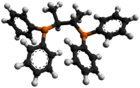
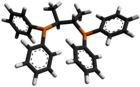
Chiraphos is a chiral diphosphine employed as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. This bidentate ligand chelates metals via the two phosphine groups. Its name is derived from its description — being both chiral and a phosphine. As a C2-symmetric ligand, chiraphos is available in two enantiomeric forms, S,S and R,R, each with C2 symmetry.
Preparation
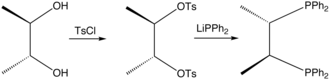
[edit]Chiraphos is prepared from S,S or R,R-2,3-butanediol, which are derived from commercially available S,S or R,R-tartaric acid; the technique of using cheaply available enantiopure starting materials is known as chiral pool synthesis. The diol is tosylated and then the ditosylate is treated with lithium diphenylphosphide.[1] The ligand was an important demonstration of how the conformation of the chelate ring can affect asymmetric induction by a metal catalyst. Prior to this work, in most chiral phosphines, e.g., DIPAMP, phosphorus was the stereogenic center.
References
[edit]- ^ Fryzuk, M. D.; Bosnich, B. (1977). "Asymmetric synthesis. Production of optically active amino acids by catalytic hydrogenation". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 99 (19): 6262–6267. doi:10.1021/ja00461a014. PMID 893889.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction