Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
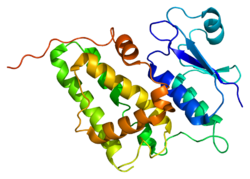
Chloride intracellular channel 4 , also known as CLIC4 ,p644H1 ,HuH1 , is a eukaryotic gene .[5]
Chloride channels are a diverse group of proteins that regulate fundamental cellular processes including stabilization of cell membrane potential, transepithelial transport, maintenance of intracellular pH , and regulation of cell volume. Chloride intracellular channel 4 (CLIC4) protein, encoded by the clic4 gene, is a member of the p64 family; the gene is expressed in many tissues. These channels are implicated in angiogenesis , pulmonary hypertension , cancer , and cardioprotection from ischemia-reperfusion injury . They exhibit an intracellular vesicular pattern in PANC-1 cells (pancreatic cancer cells).[5]
CLIC4 binds to dynamin I, α-tubulin , β-actin , creatine kinase and two 14-3-3 isoforms.[6]
Berryman M, Bretscher A (2000). "Identification of a Novel Member of the Chloride Intracellular Channel Gene Family (CLIC5) That Associates with the Actin Cytoskeleton of Placental Microvilli" . Mol. Biol. Cell . 11 (5): 1509–21. doi :10.1091/mbc.11.5.1509 . PMC 14863 PMID 10793131 . Ponnalagu D, Hamilton S, Sanghvi S, Antelo D, Schwieterman N, Hansra I, Xu X, Gao E, Edwards JC, Bansal SS, Wold LE, Terentyev, D, Janssen PM, Hund TJ, Khan M, Kohut AR, Koch WJ, Singh H (2022). "CLIC4 localizes to mitochondrial-associated membranes and mediates cardioprotection" . Science Advances . 8 (42): eabo1244. Bibcode :2022SciA....8O1244P . doi :10.1126/sciadv.abo1244 . PMC 9586484 PMID 36269835 . Berryman MA, Goldenring JR (2004). "CLIC4 is enriched at cell-cell junctions and colocalizes with AKAP350 at the centrosome and midbody of cultured mammalian cells". Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton . 56 (3): 159–72. doi :10.1002/cm.10141 . PMID 14569596 . Bohman S, Matsumoto T, Suh K, et al. (2006). "Proteomic analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelial cell differentiation reveals a role for chloride intracellular channel 4 (CLIC4) in tubular morphogenesis" . J. Biol. Chem . 280 (51): 42397–404. doi :10.1074/jbc.M506724200 PMID 16239224 . Chuang JZ, Milner TA, Zhu M, Sung CH (1999). "A 29 kDa intracellular chloride channel p64H1 is associated with large dense-core vesicles in rat hippocampal neurons" . J. Neurosci . 19 (8): 2919–28. doi :10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-08-02919.1999 PMC 6782274 PMID 10191309 . Duncan RR, Westwood PK, Boyd A, Ashley RH (1997). "Rat brain p64H1, expression of a new member of the p64 chloride channel protein family in endoplasmic reticulum" . J. Biol. Chem . 272 (38): 23880–6. doi :10.1074/jbc.272.38.23880 PMID 9295337 . Edwards JC (1999). "A novel p64-related Cl− channel: subcellular distribution and nephron segment-specific expression". Am. J. Physiol . 276 (3 Pt 2): F398–408. doi :10.1152/ajprenal.1999.276.3.F398 . PMID 10070163 . S2CID 19105320 . Qian Z, Okuhara D, Abe MK, Rosner MR (1999). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a mitogen-activated protein kinase-associated intracellular chloride channel" . J. Biol. Chem . 274 (3): 1621–7. doi :10.1074/jbc.274.3.1621 PMID 9880541 . Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)" . Genome Res . 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi :10.1101/gr.2596504 . PMC 528928 PMID 15489334 . Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA Cloning Using In Vitro Site-Specific Recombination" . Genome Res . 10 (11): 1788–95. doi :10.1101/gr.143000 . PMC 310948 PMID 11076863 . Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs" . Nat. Genet . 36 (1): 40–5. doi :10.1038/ng1285 PMID 14702039 . Rønnov-Jessen L, Villadsen R, Edwards JC, Petersen OW (2002). "Differential Expression of a Chloride Intracellular Channel Gene, CLIC4, in Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Mediated Conversion of Fibroblasts to Myofibroblasts" . Am. J. Pathol . 161 (2): 471–80. doi :10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64203-4 . PMC 1850723 PMID 12163372 . Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature . 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode :2005Natur.437.1173R . doi :10.1038/nature04209 . PMID 16189514 . S2CID 4427026 . Shiio Y, Suh KS, Lee H, et al. (2006). "Quantitative proteomic analysis of myc-induced apoptosis: a direct role for Myc induction of the mitochondrial chloride ion channel, mtCLIC/CLIC4" . J. Biol. Chem . 281 (5): 2750–6. doi :10.1074/jbc.M509349200 PMID 16316993 . Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, et al. (2001). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing" . EMBO Rep . 1 (3): 287–92. doi :10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058 . PMC 1083732 PMID 11256614 . Singh H, Ashley RH (2007). "CLIC4 (p64H1) and its putative transmembrane domain form poorly selective, redox-regulated ion channels". Mol. Membr. Biol . 24 (1): 41–52. doi :10.1080/09687860600927907 . PMID 17453412 . S2CID 9986497 . Singh H, Cousin MA, Ashley RH (2007). "Functional reconstitution of mammalian 'chloride intracellular channels' CLIC1, CLIC4 and CLIC5 reveals differential regulation by cytoskeletal actin". FEBS J . 274 (24): 6306–6316. doi :10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06145.x . PMID 18028448 . S2CID 22494250 . Singh H (2010). "Two decades with dimorphic Chloride Intracellular Channels (CLICs)" . FEBS Letters . 584 (10): 2112–21. Bibcode :2010FEBSL.584.2112S . doi :10.1016/j.febslet.2010.03.013 PMID 20226783 . Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences" . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A . 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode :2002PNAS...9916899M . doi :10.1073/pnas.242603899 PMC 139241 PMID 12477932 . Suginta W, Karoulias N, Aitken A, Ashley RH (2003). "Chloride intracellular channel protein CLIC4 (p64H1) binds directly to brain dynamin I in a complex containing actin, tubulin and 14-3-3 isoforms" . Biochem. J . 359 (Pt 1): 55–64. doi :10.1042/0264-6021:3590055 . PMC 1222121 PMID 11563969 . Valenzuela SM, Martin DK, Por SB, et al. (1997). "Molecular cloning and expression of a chloride ion channel of cell nuclei" . J. Biol. Chem . 272 (19): 12575–82. doi :10.1074/jbc.272.19.12575 PMID 9139710 . Wick M, Bürger C, Brüsselbach S, et al. (1994). "Identification of serum-inducible genes: different patterns of gene regulation during G0-->S and G1-->S progression". J. Cell Sci . 107 (1): 227–39. doi :10.1242/jcs.107.1.227 . PMID 8175911 . Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, et al. (2004). "From ORFeome to Biology: A Functional Genomics Pipeline" . Genome Res . 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi :10.1101/gr.2576704 . PMC 528930 PMID 15489336 . Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, et al. (2001). "Toward a Catalog of Human Genes and Proteins: Sequencing and Analysis of 500 Novel Complete Protein Coding Human cDNAs" . Genome Res . 11 (3): 422–35. doi :10.1101/gr.GR1547R . PMC 311072 PMID 11230166 .
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine , which is in the public domain .








Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction