
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Borinine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H5B | |
| Molar mass | 75.91 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Borabenzene is a hypothetical organoboron compound with the formula C5H5B. Unlike the related but highly stable benzene molecule, borabenzene would be electron-deficient. Related derivatives are the boratabenzene anions, including the parent [C5H5BH]−.
Adducts[edit]
Adducts of borabenzene with Lewis bases are isolatable. Since borabenzene is unavailable, these adducts require indirect methods. 4-Silyl-1-methoxyboracyclohexadiene is used as a precursor to the borabenzene:
- C
5H
5N + MeOBC
5H
5SiMe
3 → C
5H
5N-BC
5H
5 + MeOSiMe3
The pyridine adduct C
5H
5N-BC
5H
5 is structurally related to biphenyl.[1] It is a yellow whereas biphenyl is colorless, indicating distinct electronic structures. The pyridine ligand is tightly bound: no exchange is observed with free pyridine, even at elevated temperatures.
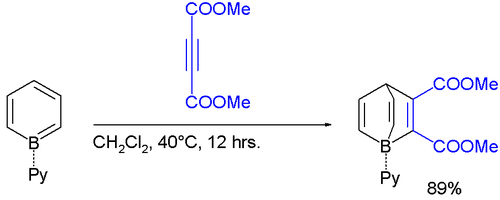
The borabenzene-pyridine adduct behaves like a diene, not an analog of biphenyl, and will undergo Diels-Alder reactions.[2]
See also[edit]
- 6-membered aromatic rings with one carbon replaced by another group: silabenzene, germabenzene, stannabenzene, pyridine, phosphorine, arsabenzene, stibabenzene, bismabenzene, pyrylium, thiopyrylium, selenopyrylium, telluropyrylium
- Borazine
References[edit]
- ^ Boese, Roland; Finke, Norbert; Henkelmann, Jochem; Maier, Günther; Paetzold, Peter; Reisenauer, Hans Peter; Schmid, Günter (1985). "Synthese und Strukturuntersuchung von Pyridin-Borabenzol und Pyridin-2-Boranaphthalin". Chemische Berichte. 118 (4): 1644–1654. doi:10.1002/cber.19851180431.
- ^ Wood, Thomas K.; Piers, Warren E.; Keay, Brian A.; Parvez, Masood (2006). "1-Borabarrelene Derivatives via Diels−Alder Additions to Borabenzenes". Organic Letters. 8 (13): 2875–2878. doi:10.1021/ol061201w. PMID 16774279.

Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction