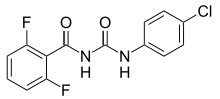
Benzoylureas are chemical derivatives of N-benzoyl-N′-phenylurea (benzoylurea). They are best known for their use as insecticides.[1] They act as insect growth regulators by inhibiting synthesis of chitin in the insect's body.
One of the more commonly used benzoylurea pesticides is diflubenzuron. Others include chlorfluazuron, flufenoxuron, hexaflumuron, and triflumuron. Lufenuron is the active compound in flea control medication for pet dogs and cats.
3-(Iodoacetamido)-benzoylurea (3-IAABU) is one of several benzoylurea compounds which have been investigated as potential anticancer agents. [2]
Environmental toxicity[edit]
When applied in a dispersed way, for example through fumigation or spraying, these chemicals have an effect against a wide range of insect species, some of which may be beneficial to human activities, including crop-pollinators such as bees. In addition, as with many insecticides, application may result in the killing of natural predators or controls along with the pest,[citation needed] risking the possibility of a 'rebound effect' or pest resurgence, where the original target for the treatment returns with equal or even greater voracity.
Flufenoxuron was banned in the European Union in 2011[3] due to its high potential for bioaccumulation in the food chain and high risk to aquatic organisms. Flufenoxuron is marketed as having 'high persistence' in the environment and the product data-sheet states that it does not biodegrade easily.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ Junquera, Pablo; Hosking, Barry; Gameiro, Marta; Macdonald, Alicia (2019). "Benzoylphenyl ureas as veterinary antiparasitics. An overview and outlook with emphasis on efficacy, usage and resistance". Parasite. 26: 26. doi:10.1051/parasite/2019026. ISSN 1776-1042. PMC 6492539. PMID 31041897.

- ^ Jiang, J. D.; Davis, A. S.; Middleton, K.; Ling, Y. H.; Perez-Soler, R.; Holland, J. F.; Bekesi, J. G. (1998-12-01). "3-(Iodoacetamido)-benzoylurea: a novel cancericidal tubulin ligand that inhibits microtubule polymerization, phosphorylates bcl-2, and induces apoptosis in tumor cells". Cancer Research. 58 (23): 5389–5395. PMID 9850070.
- ^ Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 942/2011 of 22 September 2011 concerning the non-approval of the active substance flufenoxuron
- ^ BASF Cascade Product Details
Further reading[edit]
- Lewis, W.H. and M.P.F. Elvin-Lewis. (2003). Medical Botany. Hoboken: Wiley. pg. 590
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction