 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
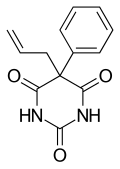
| Other names | 5-Phenyl-5-allylbarbituric acid |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.718 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H12N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 244.250 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Alphenal (Alphenal, Efrodal, Prophenal, Sanudorm), also known as 5-allyl-5-phenylbarbituric acid, is a barbiturate derivative developed in the 1920s.[1] It has primarily anticonvulsant properties, and was used occasionally for the treatment of epilepsy or convulsions, although not as commonly, as better known barbiturates such as phenobarbital.[2][3] [4][5]
LD50: Mouse (Oral): 280 mg/kg
References[edit]
- ^ DE 526854, "Verfahren zur Darstellung von C,C-disubstituierten Barbitursaeuren", issued 11 June 1931, assigned to Hoffmann La Roche
- ^ Carissimi M (1962). "Nuovi Barbiturici Alogenati Farmaco". Ediozione Scientifica. 17 (6): 390–413.
- ^ Martin JR, Godel T, Hunkeler W, Jenck F, Moreau JL, Sleight AJ, Widmer U (December 2000). "Psychopharmacological Agents". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.1619250313011820.a01. ISBN 0471238961.
- ^ Brandenberger H, Maes RA (1997). Analytical Toxicology: For Clinical, Forensic, and Pharmaceutical Chemists. Walter de Gruyter. p. 348. ISBN 978-3-11-010731-9. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ^ García PC, Cruz SV, Mirón CE (28 January 2005). Fundamentos de síntesis de fármacos. Edicions Universitat Barcelona. p. 161. ISBN 978-84-475-2876-9. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction