| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
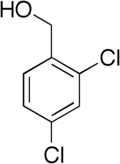
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)methanol | |
| Other names
Dybenal
Rapidosept Myacide SP | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.646 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6Cl2O | |
| Molar mass | 177.02 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 57 to 60 °C (135 to 140 °F; 330 to 333 K) |
| Boiling point | 150 °C (302 °F; 423 K) 25 mmHg |
| Pharmacology | |
| R02AA03 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol is a mild antiseptic, able to kill bacteria and viruses associated with mouth and throat infections. It is a common ingredient in throat lozenges such as Cofsils, Strepsils, Lorsept, and Gorpils. It is also an ingredient in the European product Neo Borocillina.[1] A low-pH throat lozenge containing dichlorobenzyl alcohol (1.2 mg) and amylmetacresol (0.6 mg) has been found to deactivate respiratory syncytial virus and SARS-Cov, but not adenovirus or rhinovirus.[2] A dentifrice containing 10% sodium benzoate and 0.3% dichlorobenzyl alcohol maintains antimicrobial activity for 5 to 10 minutes after brushing.[3]
References[edit]
- ^ "Neo Borocillina". drugs.com. Archived from the original on 2020-09-13. Retrieved 2018-01-23.
- ^ Oxford JS, Lambkin R, Gibb I, Balasingam S, Chan C, Catchpole A (2005). "A throat lozenge containing amyl meta cresol and dichlorobenzyl alcohol has a direct virucidal effect on respiratory syncytial virus, influenza A and SARS-CoV". Antiviral Chemistry & Chemotherapy. 16 (2): 129–34. doi:10.1177/095632020501600205. PMID 15889535.
- ^ Ostergaard E (1994). "Evaluation of the antimicrobial effects of sodium benzoate and dichlorobenzyl alcohol against dental plaque microorganisms. An in vitro study". Acta Odontol Scand. 52 (6): 335–45. doi:10.3109/00016359409029031. PMID 7887143.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction