 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2C19-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 4.8 to 7.7 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.120.697 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
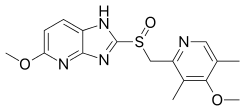
| Formula | C16H18N4O3S |
| Molar mass | 346.41 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Tenatoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor drug candidate that was undergoing clinical testing as a potential treatment for reflux oesophagitis and peptic ulcer as far back as 2003.[1] The compound was invented by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma and was licensed to Negma Laboratories (part of Wockhardt as of 2007[2]).[3]: 22
Mitsubishi reported that tenatoprazole was still in Phase I clinical trials in 2007[4]: 27 and again in 2012.[3]: 17
Tenatoprazole has an imidazopyridine ring in place of the benzimidazole moiety found in other proton pump inhibitors, and has a half-life about seven times longer than other PPIs.[5]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Gastrointestinal Disease Update". Digestive Disease Week. DataMonitor. March 2003.
- ^ "Investors unwilling to forgive Wockhardt, promoter for failings". Economic Times. 3 March 2011.
- ^ a b "State of New Product Development" (PDF). Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma. 8 May 2012.
- ^ "FY2007 Interim Financial Results". Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma.
- ^ Li H, Meng L, Liu F, Wei JF, Wang YQ (January 2013). "H+/K+-ATPase inhibitors: a patent review". Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents. 23 (1): 99–111. doi:10.1517/13543776.2013.741121. PMID 23205582. S2CID 44647770.
Well, that’s interesting to know that Psilotum nudum are known as whisk ferns. Psilotum nudum is the commoner species of the two. While the P. flaccidum is a rare species and is found in the tropical islands. Both the species are usually epiphytic in habit and grow upon tree ferns. These species may also be terrestrial and grow in humus or in the crevices of the rocks.
View the detailed Guide of Psilotum nudum: Detailed Study Of Psilotum Nudum (Whisk Fern), Classification, Anatomy, Reproduction