undoing unexplained reversion of good faith edits. Please see talk page momentarily. |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Introduction== |
==Introduction== |
||
Physics attempts to describe the natural world by the application of [[logic]] and the [[scientific method]], through a process which includes both [[model (abstract)|modelling]] by [[theoretical physics|theoretician]]s and detailed observations and experiments. |
|||
Physics seeks to describe the natural world by developing [[theory|theories]] that explain the results of detailed observations and [[experiment]]s. Even in antiquity, [[natural philosophy|natural philosophers]] searched for laws to explain physical phenomena such as the motion of objects in the night sky and the tendency of objects to fall to the ground, but from the [[scientific revolution]] of the 16th and 17th centuries through the dawn of [[modern physics]] in the early 20th century, physics emerged as a field of modern [[science]] with a firm grounding in observation and [[experiment]], a rich set of explanatory [[theory|theories]], and an elegant [[mathematics|mathematical]] language, resulting in a multitude of contributions to [[philosophy]], [[science]], [[technology]], and all aspects of [[modernity|modern society]]. Physics continued to expand during the 20th century, with a growing body of [[research]] leading to discoveries such as the [[Standard Model]] of fundamental interactions and a detailed [[cosmology|history of the universe]], along with revolutionary new technologies like [[nuclear weapon]]s and [[semiconductor]]s. Research in physics today is progressing on a vast array of topics, including the understanding of high-temperature [[superconductivity]], the development of [[quantum computing]], the search for the [[Higgs boson]], the understanding of [[dark matter]] and [[dark energy]], and the [[String theory|attempt]] to develop a theory of [[quantum gravity]]. |
|||
"''Physics''" (often spelled ''physike'') formerly consisted of the study of its counterpart, [[natural philosophy]], from classical times until the separation of modern physics from philosophy as a [[positive science]] during the [[nineteenth century]]. |
|||
Discoveries in physics find connections throughout the other [[natural science]]s as they regard the basic constituents of the universe. Some of the phenomena studied in physics, such as the [[conservation of energy]], are common to ''all'' material systems. These often are referred to as [[law of physics|laws of physics]]. Other phenomena, such as [[superconductivity]], stem from these laws, but are not laws themselves because they only appear in some systems. Physics is often said to be the "fundamental science", because each of the other sciences ([[biology]], [[chemistry]], [[geology]], [[physiology]], [[archaeology]], [[anthropology]], etc.) deals with particular types of material systems that obey the laws of physics.<ref>''[[The Feynman Lectures on Physics]]'' Volume I, Chapter III. Feynman, Leighton and Sands. ISBN 0-201-02115-3 (For the philosophical issues of whether other sciences can be "reduced" to physics, see [[reductionism]] and [[special sciences]]).</ref> Discoveries in basic physics have important ramifications for all of science. For example, chemistry is the science of matter (such as [[atom]]s and [[molecule]]s) and the [[chemical substance]]s that they form in the bulk. The structure, reactivity, and properties of a [[chemical compound]] are determined by the properties of the underlying molecules, which can be described by areas of physics such as [[quantum mechanics]] (called in this case [[quantum chemistry]]), [[thermodynamics]], and [[electromagnetism]]. |
Discoveries in physics find connections throughout the other [[natural science]]s as they regard the basic constituents of the universe. Some of the phenomena studied in physics, such as the [[conservation of energy]], are common to ''all'' material systems. These often are referred to as [[law of physics|laws of physics]]. Other phenomena, such as [[superconductivity]], stem from these laws, but are not laws themselves because they only appear in some systems. Physics is often said to be the "fundamental science", because each of the other sciences ([[biology]], [[chemistry]], [[geology]], [[physiology]], [[archaeology]], [[anthropology]], etc.) deals with particular types of material systems that obey the laws of physics.<ref>''[[The Feynman Lectures on Physics]]'' Volume I, Chapter III. Feynman, Leighton and Sands. ISBN 0-201-02115-3 (For the philosophical issues of whether other sciences can be "reduced" to physics, see [[reductionism]] and [[special sciences]]).</ref> Discoveries in basic physics have important ramifications for all of science. For example, chemistry is the science of matter (such as [[atom]]s and [[molecule]]s) and the [[chemical substance]]s that they form in the bulk. The structure, reactivity, and properties of a [[chemical compound]] are determined by the properties of the underlying molecules, which can be described by areas of physics such as [[quantum mechanics]] (called in this case [[quantum chemistry]]), [[thermodynamics]], and [[electromagnetism]]. |
||
[[Image:Universe.jpg|thumb|250px|right|The deepest visible-light image of the [[universe]], the [[Hubble Ultra Deep Field]]]] |
[[Image:Universe.jpg|thumb|250px|right|The deepest visible-light image of the [[universe]], the [[Hubble Ultra Deep Field]]]] |
||
Physics is firmly rooted in and relies heavily upon [[mathematics]], which provides a language in which physical laws can be precisely formulated and their predictions quantified. Physical [[definitions]], [[model (abstract)|models]] and [[theory|theories]] are invariably expressed using mathematical relations. There is a large area of [[research]] intermediate between physics and mathematics, known as [[mathematical physics]]. |
Physics is firmly rooted in and relies heavily upon [[mathematics]], which provides a language in which physical laws can be precisely formulated and their predictions quantified. Physical [[definitions]], [[model (abstract)|models]] and [[theory|theories]] are invariably expressed using mathematical relations. There is a large area of [[research]] intermediate between physics and mathematics, known as [[mathematical physics]]. |
||
Many problems in physics lead to complex equations where [[analytic solution]]s are impossible, so [[numerical analysis]] and [[simulation#computer simulation|simulations]] are frequently utilized. [[Scientific computing|Scientific computation]] is an integral part of physics, and the field of [[computational physics]] is an active area of research. |
|||
Physics is closely related to [[engineering]] and [[technology]]. For example, [[electrical engineering]] is the study of the practical application of [[electromagnetism]]. [[Statics]], a subfield of [[mechanics]], is responsible for the building of [[bridge]]s. [[Physicist|Physicists]] involved in [[basic research|basic]] and [[applied research]] [[Invention|invent]] processes and [[tool|devices]], such as the [[transistor]]. [[Experiment|Experimental]] physicists design and perform experiments with [[particle accelerator]]s, [[nuclear reactor]]s, [[telescope]]s, [[barometer]]s, [[synchrotron]]s, [[cyclotron]]s, [[spectrometer]]s, [[laser]]s, and other equipment. |
Physics is closely related to [[engineering]] and [[technology]]. For example, [[electrical engineering]] is the study of the practical application of [[electromagnetism]]. [[Statics]], a subfield of [[mechanics]], is responsible for the building of [[bridge]]s. [[Physicist|Physicists]] involved in [[basic research|basic]] and [[applied research]] [[Invention|invent]] processes and [[tool|devices]], such as the [[transistor]]. [[Experiment|Experimental]] physicists design and perform experiments with [[particle accelerator]]s, [[nuclear reactor]]s, [[telescope]]s, [[barometer]]s, [[synchrotron]]s, [[cyclotron]]s, [[spectrometer]]s, [[laser]]s, and other equipment. |
||
| Line 118: | Line 122: | ||
{{main | History of physics}} |
{{main | History of physics}} |
||
{{further | [[Famous physicists]], [[Nobel Prize in physics]]}} |
|||
[[Image:Francesco Hayez 001.jpg|thumb|150px|left|[[Aristotle]]]] |
[[Image:Francesco Hayez 001.jpg|thumb|150px|left|[[Aristotle]]]] |
||
Revision as of 19:04, 8 April 2007
Physics (Greek: φύσις (phúsis), "nature" and φυσικῆ (phusiké), "knowledge of nature") is the science concerned with the fundamental laws of the universe. Physics deals with the elementary constituents of the universe, such as matter, energy, space, and time, and their interactions, as well as the analysis of systems best understood in terms of these fundamental principles.

Introduction
Physics attempts to describe the natural world by the application of logic and the scientific method, through a process which includes both modelling by theoreticians and detailed observations and experiments.
"Physics" (often spelled physike) formerly consisted of the study of its counterpart, natural philosophy, from classical times until the separation of modern physics from philosophy as a positive science during the nineteenth century.
Discoveries in physics find connections throughout the other natural sciences as they regard the basic constituents of the universe. Some of the phenomena studied in physics, such as the conservation of energy, are common to all material systems. These often are referred to as laws of physics. Other phenomena, such as superconductivity, stem from these laws, but are not laws themselves because they only appear in some systems. Physics is often said to be the "fundamental science", because each of the other sciences (biology, chemistry, geology, physiology, archaeology, anthropology, etc.) deals with particular types of material systems that obey the laws of physics.[1] Discoveries in basic physics have important ramifications for all of science. For example, chemistry is the science of matter (such as atoms and molecules) and the chemical substances that they form in the bulk. The structure, reactivity, and properties of a chemical compound are determined by the properties of the underlying molecules, which can be described by areas of physics such as quantum mechanics (called in this case quantum chemistry), thermodynamics, and electromagnetism.

Physics is firmly rooted in and relies heavily upon mathematics, which provides a language in which physical laws can be precisely formulated and their predictions quantified. Physical definitions, models and theories are invariably expressed using mathematical relations. There is a large area of research intermediate between physics and mathematics, known as mathematical physics.
Many problems in physics lead to complex equations where analytic solutions are impossible, so numerical analysis and simulations are frequently utilized. Scientific computation is an integral part of physics, and the field of computational physics is an active area of research.
Physics is closely related to engineering and technology. For example, electrical engineering is the study of the practical application of electromagnetism. Statics, a subfield of mechanics, is responsible for the building of bridges. Physicists involved in basic and applied research invent processes and devices, such as the transistor. Experimental physicists design and perform experiments with particle accelerators, nuclear reactors, telescopes, barometers, synchrotrons, cyclotrons, spectrometers, lasers, and other equipment.
The field of theoretical physics sometimes deals with speculative but precisely formulated ideas, such as multidimensional spaces and parallel universes.
Theories
Although physicists study a wide variety of phenomena, there are certain theories that are used by all physicists. Each of these theories has been tested in numerous experiments and proven to be a correct approximation of nature within its domain of validity. For example, the theory of classical mechanics accurately describes the motion of objects which are much larger than atoms and move at much less than the speed of light. While these theories have long been well-understood, they continue to be areas of active research—for example, a remarkable aspect of classical mechanics known as chaos was discovered in the 20th century, three centuries after its original formulation by Isaac Newton (1642–1727). The "central theories" are important tools for research into more specialized topics, and all physicists are expected to be literate in them.
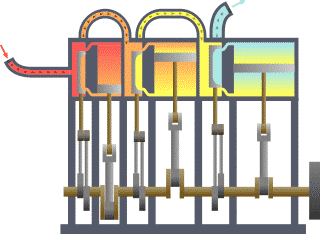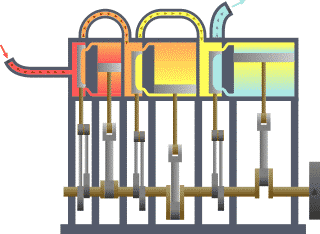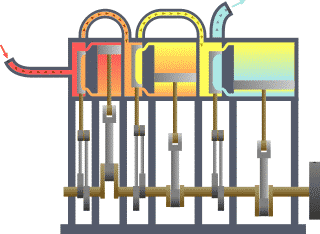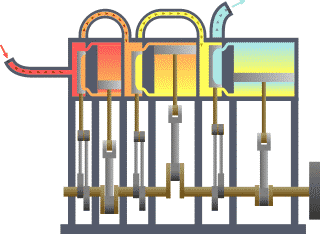
- Classical mechanics is a model of the physics of forces acting upon bodies. It is often referred to as "Newtonian mechanics" after Newton and his laws of motion. Classical mechanics is subdivided into statics, which models objects at rest, kinematics, which models objects in motion, and dynamics, which models objects subjected to forces. See also mechanics.
- Electromagnetism, or electromagnetic theory, is the physics of the electromagnetic field: a field, encompassing all of space, which exerts a force on those particles that possess the property of electric charge, and is in turn affected by the presence and motion of such particles. Electromagnetism encompasses various real-world electromagnetic phenomena.
- Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with the action of heat and the conversions from one to another of various forms of energy. Thermodynamics is particularly concerned with how these affect temperature, pressure, volume, mechanical action, and work. Statistical mechanics, a related theory, is the branch of physics that analyzes macroscopic systems by applying statistical principles to their microscopic constituents. It can be used to calculate the thermodynamic properties of bulk materials from the properties of individual molecules.
- Relativity is a generalization of classical mechanics that describes fast-moving or very massive systems. It includes special and general relativity:
- Special relativity, or the "special theory of relativity", is based on two postulates: (1) that the speed of light in a vacuum is constant and independent of the source or observer and (2) that the mathematical forms of the laws of physics are invariant in all inertial systems. It asserts an equivalence of mass and energy and a change in mass, dimension, and time with increased velocity.
- General relativity, or the "general theory of relativity", extends special relativity to include transformations between non-inertial frames. It is formulated using differential geometry and interprets gravity as a distortion of spacetime caused by the presence of mass or energy.
- Quantum mechanics generalizes classical mechanics to describe atomic and subatomic systems. It is based on the observation that all forms of energy are released in discrete units or bundles called quanta. Quantum theory typically predicts only the statistical behavior of systems, even if they involve only a single particle.
Classical and modern physics
"Modern physics" refers to physics based on relativity and quantum theory, the two ideas that revolutionized physics in the early 20th century. Most of modern physics involves applications and extensions of quantum mechanics, so descriptions of the fundamental interactions that have not been quantized are referred to as "classical." Thus general relativity, Newtonian gravity, and the unquantized version of electromagnetism are classical theories. Phenomena which display only some aspects of quantum mechanics are often described using semiclassical models.
Theories and concepts
The table below lists many physical theories and the concepts they employ.
Research
Contemporary research in physics is divided into several distinct fields.
- Condensed matter physics is concerned with how the properties of bulk matter, such as the ordinary solids and liquids we encounter in everyday life, arise from the properties and mutual interactions of the constituent atoms. A topic of current interest is high-temperature superconductivity.
- Atomic, molecular, and optical physics deals with small numbers of atoms and molecules, particularly with how they interact with light. A topic of current interest is the behavior of Bose-Einstein condensates.
- Particle physics, also known as "high-energy physics", is concerned with the properties of submicroscopic particles much smaller than atoms, including elementary particles such as electrons, photons, and quarks. A topic of current interest is the search for the Higgs boson.
- Astrophysics and cosmology apply the laws of physics to explain celestial phenomena, including stellar dynamics, black holes, galaxies, and the big bang. A topic of current interest is determining the nature of dark matter and dark energy.
Since the twentieth century, the individual fields of physics have become increasingly specialized, and today most physicists work in a single field for their entire careers. "Universalists" such as Albert Einstein (1879–1955) and Lev Landau (1908–1968), who worked in multiple fields of physics, are now very rare.
Theory and experiment
The culture of physics research differs from most sciences in the separation of theory and experiment. Since the twentieth century, most individual physicists have specialized in either theoretical physics or experimental physics. The great Italian physicist Enrico Fermi (1901–1954), who made fundamental contributions to both theory and experimentation in nuclear physics, was a notable exception. In contrast, almost all the successful theorists in biology and chemistry (e.g. American quantum chemist and biochemist Linus Pauling) have also been experimentalists, although this is changing as of late.
Roughly speaking, theorists seek to develop through abstractions and mathematical models theories that can both describe and interpret existing experimental results, and successfully predict future results, while experimentalists devise and perform experiments to explore new phenomena and test theoretical predictions. Although theory and experiment are developed separately, they are strongly dependent upon each other. Progress in physics frequently comes about when experimentalists make a discovery that existing theories cannot account for, necessitating the formulation of new theories. Likewise, ideas arising from theory often inspire new experiments. In the absence of experiment, theoretical research can go in the wrong direction; this is one of the criticisms that has been leveled against M-theory, a popular theory in high-energy physics for which no practical experimental test has ever been devised. Theorists working closely with experimentalists frequently employ phenomonology.
Applied physics is physics that is intended for a particular technological or practical use, as for example in engineering, as opposed to basic research. This approach is similar to that of applied mathematics. Applied physics is rooted in the fundamental truths and basic concepts of the physical sciences, but is concerned with the use of scientific principles in practical devices and systems, and in the application of physics in other areas of science. "Applied" is distinguished from "pure" by a subtle combination of factors such as the motivation and attitude of researchers and the nature of the relationship to the technology or science that may be affected by the work. [1]
Subfields
The table below lists many of the fields and subfields of physics along with the theories and concepts they employ.
History

Since antiquity, people have tried to understand the workings of Nature and the behavior of matter: why unsupported objects drop to the ground, why different materials have different properties, and so forth. The character of the universe was also a mystery, for instance the earth and the behavior of celestial objects such as the sun and the moon. Several theories were proposed, most of which were incorrect, such as the earth orbiting the moon. These first theories were largely couched in philosophical terms, and never verified by systematic experimental testing, as is popular today. The works of Ptolemy and Aristotle were not always found to match everyday observations. There were exceptions and there are anachronisms - for example, Indian philosophers and astronomers gave many correct descriptions in atomism and astronomy, and the Greek thinker Archimedes derived many correct quantitative descriptions of mechanics and hydrostatics.
The willingness to question previously held truths and search for new answers eventually resulted in a period of major scientific advancements, now known as the Scientific Revolution of the late seventeenth century. The precursors to the scientific revolution may be traced back to the important developments made in India and Persia, including the elliptical model of the planets based on the heliocentric solar system of gravitation developed by Indian mathematician-astronomer Aryabhata; the basic ideas of atomic theory developed by Hindu and Jaina philosophers; the theory of light being equivalent to energy particles developed by the Indian Buddhist scholars Dignāga and Dharmakirti; the optical theory of light developed by Muslim scientist Ibn al-Haitham (Alhazen); the Astrolabe invented by the Persian astronomer Muhammad al-Fazari; and the significant flaws in the Ptolemaic system pointed out by Persian scientist Nasir al-Din Tusi.
The Scientific Revolution
As the influence of the Arab Empire expanded to Europe, the works of Aristotle, preserved by the Arabs, and the works of the Indians and Persians, became known in medieval Europe by the twelfth and thirteenth centuries.

This eventually led to the scientific revolution, held by most historians (e.g., Howard Margolis) to have begun in 1543, when the first printed copy of Nicolaus Copernicus's De Revolutionibus was brought to the influential astronomer from Nuremberg (Nürnberg), where it had been printed by Johannes Petreius. Most of its contents had been written years prior, but the publication had been delayed. Copernicus died soon after receiving the copy.

Further significant advances were made over the following century by Galileo Galilei, Christiaan Huygens, Johannes Kepler, and Blaise Pascal. During the early seventeenth century, Galileo pioneered the use of experimentation to validate physical theories, which is the key idea in modern scientific method. Galileo formulated and successfully tested several results in dynamics, in particular the Law of Inertia.

The scientific revolution is considered to have culminated with the publication of the Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica in 1687 by the mathematician, physicist, alchemist and inventor Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727).In 1687, Newton published the Principia, detailing two comprehensive and successful physical theories: Newton's laws of motion, from which arise classical mechanics; and Newton's Law of Gravitation, which describes the fundamental force of gravity. Both theories agreed well with experiment. The Principia also included several theories in fluid dynamics.
From the late seventeenth century onward, thermodynamics was developed by physicist and chemist Boyle, Young, and many others. In 1733, Bernoulli used statistical arguments with classical mechanics to derive thermodynamic results, initiating the field of statistical mechanics. In 1798, Thompson demonstrated the conversion of mechanical work into heat, and in 1847 Joule stated the law of conservation of energy, in the form of heat as well as mechanical energy. Ludwig Boltzmann, in the nineteenth century, is responsible for the modern form of statistical mechanics.
Classical mechanics was re-formulated and extended by Leonhard Euler, French mathematician Joseph-Louis Comte de Lagrange, Irish mathematical physicist William Rowan Hamilton, and others, who produced new results in mathematical physics. The law of universal gravitation initiated the field of astrophysics, which describes astronomical phenomena using physical theories.
After Newton defined classical mechanics, the next great field of inquiry within physics was the nature of electricity. Observations in the seventeenth and eighteenth century by scientists such as Robert Boyle, Stephen Gray, and Benjamin Franklin created a foundation for later work. These observations also established our basic understanding of electrical charge and current.
The existence of the atom was proposed in 1808 by John Dalton.

In 1821, the English physicist and chemist Michael Faraday integrated the study of magnetism with the study of electricity. This was done by demonstrating that a moving magnet induced an electric current in a conductor. Faraday also formulated a physical conception of electromagnetic fields. James Clerk Maxwell built upon this conception, in 1864, with an interlinked set of twenty equations that explained the interactions between electric and magnetic fields. These twenty equations were later reduced, using vector calculus, to a set of four equations by Oliver Heaviside.
In addition to other electromagnetic phenomena, Maxwell's equations also can be used to describe light. Confirmation of this observation was made with the 1888 discovery of radio by Heinrich Hertz and in 1895 when Wilhelm Roentgen detected X-rays.
Modern physics

The ability to describe light in electromagnetic terms helped serve as a springboard for Albert Einstein's publication of the theory of special relativity in 1905. This theory combined classical mechanics with Maxwell's equations. The theory of special relativity unifies space and time into a single entity, spacetime. Relativity prescribes a different transformation between reference frames than classical mechanics; this necessitated the development of relativistic mechanics as a replacement for classical mechanics. In the regime of low (relative) velocities, the two theories agree. Einstein built further on the special theory by including gravity into his calculations, and published his theory of general relativity in 1915.
One part of the theory of general relativity is Einstein's field equation. This describes how the stress-energy tensor creates curvature of spacetime and forms the basis of general relativity. Further work on Einstein's field equation produced results which predicted the Big Bang, black holes, and the expanding universe. Einstein believed in a static universe. He tried, and failed, to fix his equation to allow for this. By 1929, however, Edwin Hubble's astronomical observations suggested that the universe is expanding at a possibly exponential rate.
In 1895, Röntgen discovered X-rays, which turned out to be high-frequency electromagnetic radiation.
Radioactivity was discovered in 1896 by Henri Becquerel, and further studied by Maria Sklodowska-Curie, Pierre Curie, and others. This initiated the field of nuclear physics.
In 1897, Joseph J. Thomson discovered the electron, the elementary particle which carries electrical current in circuits. In 1904, he proposed the first model of the atom, known as the plum pudding model. Its existence had been proposed in 1808 by John Dalton.
These discoveries revealed that the assumption of many physicists, that atoms were the basic unit of matter, was flawed, and prompted further study into the structure of atoms.
In 1911, Ernest Rutherford deduced from scattering experiments the existence of a compact atomic nucleus, with positively charged constituents dubbed protons. Neutrons, the neutral nuclear constituents, were discovered in 1932 by Chadwick. The equivalence of mass and energy (Einstein, 1905) was spectacularly demonstrated during World War II, as research was conducted by each side into nuclear physics, for the purpose of creating a nuclear bomb. The German effort, led by Heisenberg, did not succeed, but the Allied Manhattan Project reached its goal. In America, a team led by Fermi achieved the first man-made nuclear chain reaction in 1942, and in 1945 the world's first nuclear explosive was detonated at Trinity site, near Alamogordo, New Mexico.
In 1900, Max Planck published his explanation of blackbody radiation. This equation assumed that radiators are quantized, which proved to be the opening argument in the edifice that would become quantum mechanics. By introducing discrete energy levels, Planck, Einstein, Niels Bohr, and others developed quantum theories to explain various anomalous experimental results.
Quantum mechanics was formulated in 1925 by Heisenberg and in 1926 by Schrödinger and Paul Dirac, in two different ways, that both explained the preceding heuristic quantum theories. In quantum mechanics, the outcomes of physical measurements are inherently probabilistic; the theory describes the calculation of these probabilities. It successfully describes the behavior of matter at small distance scales. During the 1920s Schrödinger, Heisenberg, and Max Born were able to formulate a consistent picture of the chemical behavior of matter, a complete theory of the electronic structure of the atom, as a byproduct of the quantum theory.
Quantum field theory was formulated in order to extend quantum mechanics to be consistent with special relativity. It was devised in the late 1940s with work by Richard Feynman, Julian Schwinger, Sin-Itiro Tomonaga, and Freeman Dyson. They formulated the theory of quantum electrodynamics, which describes the electromagnetic interaction, and successfully explained the Lamb shift. Quantum field theory provided the framework for modern particle physics, which studies fundamental forces and elementary particles.
Chen Ning Yang and Tsung-Dao Lee, in the 1950s, discovered an unexpected asymmetry in the decay of a subatomic particle. In 1954, Yang and Robert Mills then developed a class of gauge theories which provided the framework for understanding the nuclear forces (Yang, Mills 1954). The theory for the strong nuclear force was first proposed by Murray Gell-Mann. The electroweak force, the unification of the weak nuclear force with electromagnetism, was proposed by Sheldon Lee Glashow, Abdus Salam, and Steven Weinberg and confirmed in 1964 by James Watson Cronin and Val Fitch. This led to the so-called Standard Model of particle physics in the 1970s, which successfully describes all the elementary particles observed to date.
Quantum mechanics also provided the theoretical tools for condensed matter physics, whose largest branch is solid state physics. It studies the physical behavior of solids and liquids, including phenomena such as crystal structures, semiconductivity, and superconductivity. The pioneers of condensed matter physics include Felix Bloch, who created a quantum mechanical description of the behavior of electrons in crystal structures in 1928. The transistor was developed by physicists John Bardeen, Walter Houser Brattain, and William Bradford Shockley in 1947 at Bell Laboratories.
The two themes of the twentieth century, general relativity and quantum mechanics, appear inconsistent with each other. General relativity describes the universe on the scale of planets and solar systems, while quantum mechanics operates on sub-atomic scales. This challenge is being attacked by string theory, which treats spacetime as composed, not of points, but of one-dimensional objects, strings. Strings have properties similar to a common string (e.g., tension and vibration). The theories yield promising, but not yet testable, results. The search for experimental verification of string theory is in progress.
The United Nations declared the year 2005, the centenary of Einstein's annus mirabilis, as the World Year of Physics.
Future directions
Research in physics is progressing constantly on a large number of fronts, and is likely to do so for the foreseeable future.
In condensed matter physics, the greatest unsolved theoretical problem is the explanation for high-temperature superconductivity. Strong efforts, largely experimental, are being put into making workable spintronics and quantum computers.
In particle physics, the first pieces of experimental evidence for physics beyond the Standard Model have begun to appear. Foremost amongst these are indications that neutrinos have non-zero mass. These experimental results appear to have solved the long-standing solar neutrino problem in solar physics. The physics of massive neutrinos is currently an area of active theoretical and experimental research. In the next several years, particle accelerators will begin probing energy scales in the TeV range, in which experimentalists are hoping to find evidence for the Higgs boson and supersymmetric particles.
Theoretical attempts to unify quantum mechanics and general relativity into a single theory of quantum gravity, a program ongoing for over half a century, have not yet borne fruit. Currently, the leading candidates are M-theory, superstring theory, and loop quantum gravity.
Many astronomical and cosmological phenomena have yet to be explained satisfactorily, including the existence of ultra-high energy cosmic rays, the baryon asymmetry, the acceleration of the universe, and the anomalous rotation rates of galaxies.
Although much progress has been made in high-energy, quantum, and astronomical physics, many everyday phenomena, involving complexity, chaos, or turbulence remain poorly understood. Complex problems that would appear to be soluble by a clever application of dynamics and mechanics, such as the formation of sand piles, nodes in trickling water, the shape of water droplets, mechanisms of surface tension catastrophes, or self-sorting in shaken heterogeneous collections are unsolved.
These complex phenomena have received growing attention since the 1970s for several reasons, not least of which has been the availability of modern mathematical methods and computers, which enabled complex systems to be modeled in new ways. The interdisciplinary relevance of complex physics also has increased, as exemplified by the study of turbulence in aerodynamics, or the observation of pattern formation in biological systems. In 1932, Horace Lamb correctly prophesied the success of the theory of quantum electrodynamics and the near-stagnant progress in the study of turbulence:
I am an old man now, and when I die and go to heaven there are two matters on which I hope for enlightenment. One is quantum electrodynamics, and the other is the turbulent motion of fluids. And about the former I am rather optimistic.
See also
Further reading
A large number of textbooks, popular books, and webpages about physics are available for further reading.
Organizations
- AIP.org is the website of the American Institute of Physics
- IOP.org is the website of the Institute of Physics
- APS.org is the website of the American Physical Society
- SPS National is the website of the Society of Physics Students
Notes
- ^ The Feynman Lectures on Physics Volume I, Chapter III. Feynman, Leighton and Sands. ISBN 0-201-02115-3 (For the philosophical issues of whether other sciences can be "reduced" to physics, see reductionism and special sciences).
- Yang, Mills 1954 Physical Review 95, 631; Yang, Mills 1954 Physical Review 96, 191.
External links
- Lecturefox Free University Lectures Physics