m Reverted edits by 94.208.107.222 to last revision by Thingg (HG) |
65.71.6.130 (talk) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
The rainy season is the warmest part of the year. |
The rainy season is the warmest part of the year. |
||
The whole country is influenced by the [[Inter-tropical Convergence Zone]] during January. |
The whole country is influenced by the [[Inter-tropical Convergence Zone]] during January. |
||
IFANYONE CAN ACTUALLY SEE THIS..... HELP I'M TRAPPED IN SOME THIRTY YEAR OLD DUDE'S BASEMENT.... |
|||
== Terrain == |
== Terrain == |
||
Revision as of 15:22, 27 March 2009
Geographic coordinates: 20°00′S 30°00′E / 20.000°S 30.000°E
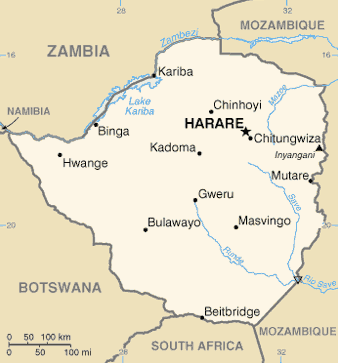


Zimbabwe is a landlocked country in southern Africa lying wholly within the tropics. It straddles an extensive high inland plateau that drops northwards to the Zambezi valley where the border with Zambia is and similarly drops southwards to the Limpopo valley and the border with South Africa. The country has borders with Botswana 813 km, Mozambique 1,231 km, South Africa 225 km, Zambia 797 km and meets Namibia at its westernmost point.
Area
It is the 59th largest country in the world (although below average size for Africa) just bigger than Japan but smaller than Paraguay, with a total area of 390,580 km², of which 3,910 km² comprises lakes and reservoirs.
Climate
The climate is tropical, although markedly moderated by altitude. There is a dry season, including a short cold season. The rainy season is the warmest part of the year. The whole country is influenced by the Inter-tropical Convergence Zone during January.
IFANYONE CAN ACTUALLY SEE THIS..... HELP I'M TRAPPED IN SOME THIRTY YEAR OLD DUDE'S BASEMENT....
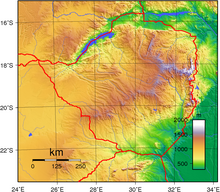
Terrain
Much of the country is high plateau with higher central plateau (high veld) forming a blockade between the Zambezi and Limpopo river systems. The Limpopo and the lower Zambezi valleys are broad and relatively flat plains. The eastern end of the watershed terminates in a north-south mountain spine, called the Eastern Highlands.
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: junction of the Runde and Save rivers 162 m
highest point: Mount Nyangani 2,592 m
Natural resources: coal, chromium ore, asbestos, gold, nickel, copper, iron ore, vanadium, lithium, tin, platinum group metals
Land use:
arable land: 8.4% (1998 est.), 7% (1993 est.)
permanent crops: 0.34% (1998 est.), 0% (1993 est.)
permanent pastures: 13% (1993 est.)
forests and woodland: 18% (2006 est.); deforestation occurring at the rate of 3,000 km² per annum[1]
other: 91.26% (1998 est.), 57% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 1,170 km² (1998 est.), 1,930 km² (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: recurring droughts; floods and severe storms are rare
Environment - current issues: deforestation; soil erosion; land degradation; air and water pollution; the black rhinoceros herd - once the largest concentration of the species in the world - has been significantly reduced by poaching; poor mining practices have led to toxic waste and heavy metal pollution
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Hydrology: Sediment transport has been studied for rivers in Zimbabwe using the HBV hydrology transport model.
Table 1.
Rainfall and land use suitability options in Zimbabwe's natural regions Natural region Rainfall Main land use type
1 Above 1050 mm/annum with some precipitation in all months of the year Afforestation, fruit, tea, coffee and intensive livestock production
2 750–1000 mm/annum seasonally confined with well-defined dry season Large scale intensive crop and livestock production
3 650–800 mm/annum with regular mid-season dry spells Livestock production with fodder crops. Marginal production of maize, tobacco and cotton
4 450-650 mm/annum with periodic seasonal drought and severe rainy season dry spells Livestock production and drought resistant crops
5 Too low and erratic for even drought resistant fodder and grain crops Extensive livestock and/or game ranching
Source: CSO (1997, 144).
See also
- Limpopo River
- Zimbabwe
- Soil Maps of Zimbabwe European Digital Archive on the Soil Maps of the world