Introduction


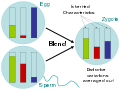
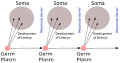
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments.
Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations. Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the scientific method to make observations, pose questions, generate hypotheses, perform experiments, and form conclusions about the world around them.
Life on Earth, which emerged more than 3.7 billion years ago, is immensely diverse. Biologists have sought to study and classify the various forms of life, from prokaryotic organisms such as archaea and bacteria to eukaryotic organisms such as protists, fungi, plants, and animals. These various organisms contribute to the biodiversity of an ecosystem, where they play specialized roles in the cycling of nutrients and energy through their biophysical environment. (Full article...)
Selected article -

An invasive species is an introduced species to an environment that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food web. Since the 20th century, invasive species have become a serious economic, social, and environmental threat worldwide.
Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range of invasion. For millennia, humans have served as both accidental and deliberate dispersal agents, beginning with their earliest migrations, accelerating in the Age of Discovery, and accelerating again with international trade. Invasive plant species include the kudzu vine, Japanese knotweed, and yellow starthistle. Invasive animals include European rabbits, domestic cats, and carp. (Full article...)Selected picture -

Major topics
Selected biography -
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and Maurice Wilkins were awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material".
Watson earned degrees at the University of Chicago (BS, 1947) and Indiana University (PhD, 1950). Following a post-doctoral year at the University of Copenhagen with Herman Kalckar and Ole Maaløe, Watson worked at the University of Cambridge's Cavendish Laboratory in England, where he first met his future collaborator Francis Crick. From 1956 to 1976, Watson was on the faculty of the Harvard University Biology Department, promoting research in molecular biology. (Full article...)General images -
Did you know -
- ... that one of the smallest fish, the Philippine goby, can only grow between 1 and 1.5 cm?
- ...that the largest flower, Rafflesia has a very foul odor?
- ... that mesoporous silica nanoparticles are prepared by the Stöber process and are used in preparing biosensors and delivering medications to within cellular structures?
Things you can do
Related portals
Biology portals
Categories

Anatomy - Anthropology - Astrobiology - Biochemistry - Bioengineering - Bioinformatics - Biotechnology - Botany - Cell biology - Conservation biology - Developmental biology - Ecology - Environmental science - Evolutionary biology - Genetics - Mathematical biology - Medicine - Microbiology - Immunology - Molecular biology - Mycology - Neuroscience - Paleontology - Palynology Parasitology - Pharmacology -
Phylogenetics - Physiology - Systems biology - Taxonomy - Toxicology - Virology - ZoologyMore topics
WikiProjects

WikiProjects connected with biology:
A complete list of scientific WikiProjects can be found here. See also Wikispecies, a Wikimedia project dedicated to classification of biological species.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-

-

-

-

-
Random portal
Shortcuts to this page: Biology portal • P:BIO Purge server cache