Megabazus | |
|---|---|
 Megabazus was son of Megabates.[1] | |
| Native name | Bakabadus |
| Allegiance | Achaemenid Empire |
| Battles/wars | European Scythian campaign of Darius I Darius' Thracian campaign Unknown others |
| Children | Megabates[2] Oebares II Bubares Pherendates[3] |
| Relations | Megabates (father) |
Megabazus (Old Persian: Bagavazdā or Bagabāzu, Ancient Greek: Μεγαβάζος and Μεγάβυζος), son of Megabates, was a highly regarded Persian general under Darius, to whom he was a first-degree cousin. Most of the information about Megabazus comes from The Histories by Herodotus.
Scythian campaign (513 BC)[edit]
Megabazus led the army of the Persian King Darius I in 513 BC during his European Scythian campaign. After this had to be discontinued without result, Megabazos was left as commander-in-chief of an 80,000-man army in Europe, with the mission of subjugating the Greek cities on the Hellespont. The Persian troops first subjugated gold-rich Thrace after capturing Perinthos and the coastal Greek cities, and then defeated the powerful Paeonians, many of whom he deported to Phrygia.[6][7]
Subjugation of Macedon[edit]
Finally, Megabazus sent envoys to Amyntas I, king of Macedon, demanding acceptance of Persian domination, which the king accepted.[8][7] Megabazus received the present of "Earth and Water" from Amyntas, which symbolised submission to the Achaemenid Emperor.[9] Amyntas then acted as hyparch to Darius I.[10]
Disagreements arose when the members of the Persian delegation insulting the Macedonians by fraternising with their wives. The Macedonian prince Alexander I reacted to this by murdering several Persian diplomats and their followers. The conflict was later settled with the marriage of one of Megabazus' sons, Bubares, to the Macedonian princess Gygaia, a daughter of Amyntas.[9][1]
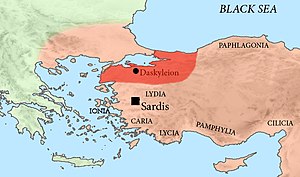
After his return to Asia Minor, Megabazus received the governorship of the province (satrapy) of Hellespontine Phrygia and was based in its capital Daskyleion.
Rivalry with Histiaeus[edit]
Megabazus was suspicious of Histiaeus, tyrant of Miletus, and advised Darius to bring him to the Persian capital of Susa to keep a closer eye on him. His suspicions turned out to be well founded as Histiaeus provoked a revolt in the town of which he was formally in charge and later sided with the Greeks against Persia. The successor to Megabazus' command was Otanes (son of Sisamnes).[11]
Family[edit]
According to Herodotus (Herodotus 6.33) Oebares was a son of Megabazus, and became satrap of Daskyleion (Hellespontine Phrygia) in 493 BC.[12][1]
Megabates was another son of Megabazus. He was a commander of the Achaemenid fleet that sailed against Naxos in 500/499 BC. He also was Satrap of Daskyleion in the early 470s.[1][13]
Sons[edit]
- Oebares: became satrap of Daskyleion c. 493 BC
- Bubares: managing engineer of the Athos Canal of Xerxes I
- Megabates: Achaemenid fleet commander and satrap of Daskyleion
- Pherendates: died c. 485 BC while satrap of Egypt.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d Foundation, Encyclopaedia Iranica. "Welcome to Encyclopaedia Iranica". iranicaonline.org.
- ^ "Megabazus - Livius". www.livius.org.
- ^ "Encyclopaedia of the Hellenic World, Asia Minor". asiaminor.ehw.gr.
- ^ "DNa - Livius". www.livius.org.
- ^ Olbrycht, Marck Jan (2010). "Macedonia and Persia". In Roisman, Joseph; Worthington, Ian (eds.). A Companion to Ancient Macedonia. Oxford, Chichester, & Malden: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 343–344. ISBN 978-1-4051-7936-2.
- ^ Roisman, Joseph; Worthington, Ian (7 July 2011). A Companion to Ancient Macedonia. ISBN 9781444351637. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ a b "Persian influence on Greece (2)". Archived from the original on 24 July 2020. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ Roisman, Joseph; Worthington, Ian (7 July 2011). A Companion to Ancient Macedonia. ISBN 9781444351637. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ a b Waters, Matt (2014). Ancient Persia: A Concise History of the Achaemenid Empire, 550–330 BCE. Cambridge University Press. p. 83. ISBN 9781107009608.
- ^ King, Carol J. (2017). Ancient Macedonia. Routledge. p. 27. ISBN 9781351710329.
- ^ "Perseus Under Philologic: Hdt. 5.25.1". Archived from the original on 2020-03-10. Retrieved 2019-01-13.
- ^ "LacusCurtius • Herodotus — Book VI: Chapters 1‑42". penelope.uchicago.edu.
- ^ Thucydides, 1.129; Herodotus, 5.32-35, 6.32


