

The U.S. state of Kansas is bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. The state is divided into 105 counties with 628 cities, with its largest county by area being Butler County.[1] Kansas is located equidistant from the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The geographic center of the 48 contiguous states is in Smith County near Lebanon. Until 1989, the Meades Ranch Triangulation Station in Osborne County was the geodetic center of North America: the central reference point for all maps of North America. The geographic center of Kansas is in Barton County.
Geology and Topography[edit]
Kansas is underlain by a sequence of horizontal to gently westward dipping sedimentary rocks. A sequence of Mississippian, Pennsylvanian and Permian rocks outcrop in the eastern and southern part of the state. The state's western half has exposures of Cretaceous through Tertiary sediments, the latter derived from the erosion of the uplifted Rocky Mountains to the west. These are underlain by older Paleozoic and Mesozoic sediments which correlate well with the outcrops to the east. The state's northeastern corner was subjected to glaciation in the Pleistocene and is covered by glacial drift and loess.
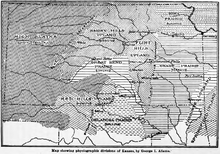
Kansas has been divided into eleven different physiographic regions.[3]
The western two-thirds of the state, lying in the great central plain of the United States, has a generally flat or undulating surface, while the eastern third has many hills and forests. The land gradually rises from east to west; its altitude ranges from 684 ft (208 m) along the Verdigris River at Coffeyville in Montgomery County, to 4,039 ft (1,231 m) at Mount Sunflower, 0.5 miles (0.80 kilometers) from the Colorado border, in Wallace County. It is a common misconception that Kansas is the flattest state in the nation—in 2003, a tongue-in-cheek study famously declared the state "flatter than a pancake".[4] In fact, Kansas has a maximum topographic relief of 3,360 ft (1,020 m),[5] making it the 23rd flattest U.S. state measured by maximum relief.[6]
Features[edit]
Rivers[edit]

Nearly 75 mi (121 km) of the state's northeastern boundary is defined by the Missouri River. The Kansas River (locally known as the Kaw), formed by the junction of the Smoky Hill and Republican rivers at appropriately-named Junction City, joins the Missouri River at Kansas City, after a course of 170 mi (270 km) across the northeastern part of the state.
The Arkansas River (pronunciation varies), rising in Colorado, flows with a bending course for nearly 500 mi (800 km) across the western and southern parts of the state. With its tributaries, (the Little Arkansas, Ninnescah, Walnut, Cow Creek, Cimarron, Verdigris, and the Neosho), it forms the southern drainage system of the state.
Kansas's other rivers are the Saline and Solomon Rivers, tributaries of the Smoky Hill River; the Big Blue, Delaware, and Wakarusa, which flow into the Kansas River; and the Marais des Cygnes, a tributary of the Missouri River. Spring River is located between Riverton and Baxter Springs.
National parks and historic sites[edit]
Areas under the protection of the National Park Service include:[7]
- Brown v. Board of Education National Historic Site in Topeka
- California National Historic Trail
- Fort Larned National Historic Site in Larned
- Fort Scott National Historic Site
- Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail
- Nicodemus National Historic Site at Nicodemus
- Oregon National Historic Trail
- Pony Express National Historic Trail
- Santa Fe National Historic Trail
- Tallgrass Prairie National Preserve near Strong City
Flora and fauna[edit]
In Kansas, there are currently 238 species of rare animals and 400 rare plants.[8] Among those include: Boechera laevigata, Virginia Rail, Cleft Ledge, Royal Fern, Turkey-tangle, Bobolink, Cave Salamander, Peregrine Falcon, and Black-footed ferret.[9][10] Common animal species and grasses include: Crows, Deer, Lesser Prairie Chicken, Mice, Moles, Opossum, Prairie Dogs, Raccoon, Tripsacum dactyloides, Prairie Dropseed, Indian Grass, Little Bluestem, Switch Grass, Northern Sea Oats, Tussock Sedge, Sideoats Grama, and Big Bluestem.[11][12]
Climate[edit]
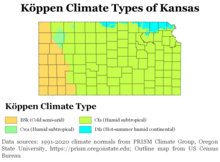


According to the Köppen climate classification, Kansas's climate can be characterized in terms of three types: it has humid continental, semi-arid steppe, and humid subtropical. The eastern two-thirds of the state (especially the northeastern portion) has a humid continental climate, with cool to cold winters and hot, often humid summers. Most of the precipitation falls during both the summer and the spring.
The western third of the state—from roughly the U.S. Route 83 corridor westward—has a semi-arid steppe climate. Summers are hot, often very hot, and generally less humid. Winters are highly changeable between warm and very cold. The western region receives an average of about 16 inches (410 millimeters) of precipitation per year. Chinook winds in the winter can warm western Kansas all the way into the 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27 degrees Celsius) range.
The south-central and southeastern portions of the state, including the Wichita area, have a humid subtropical climate with hot and humid summers, milder winters, and more precipitation than elsewhere in Kansas. Some features of all three climates can be found in most of the state, with droughts and changeable weather between dry and humid not uncommon, and both warm and cold spells in the winter.
Temperatures in areas between U.S. Routes 83 and 81, as well as the southwestern portion of the state along and south of U.S. 50, reach 90 °F (32 °C) or above on most days of June, July, and August. High humidity added to the high temperatures sends the heat index into life-threatening territory, especially in Wichita, Hutchinson, Salina, Russell, Hays, and Great Bend. Temperatures are often higher in Dodge City, Garden City, and Liberal, but the heat index in those three cities is usually lower than the actual air temperature.
Although temperatures of 100 °F (38 °C) or higher are not as common in areas east of U.S. 81, higher humidity and the urban heat island effect lead most summer days to heat indices between 107 °F (42 °C) and 114 °F (46 °C) in Topeka, Lawrence, and the Kansas City metropolitan area. Also, combined with humidity between 85 and 95 percent, dangerous heat indices can be experienced at every hour of the day.
Precipitation ranges from about 47 inches (1,200 mm) annually in the state's southeast corner to about 16 inches (410 mm) in the southwest. Snowfall ranges from around 5 inches (130 mm) in the fringes of the south, to 35 inches (890 mm) in the far northwest. Frost-free days range from more than 200 days in the south, to 130 days in the northwest. Thus, Kansas is the country's ninth or tenth sunniest state, depending on the source. Western Kansas is as sunny as parts of California and Arizona.
Kansas is prone to severe weather, especially in the spring and the early-summer. Despite the frequent sunshine throughout much of the state, due to its location at a climatic boundary prone to intrusions of multiple air masses, the state is vulnerable to strong and severe thunderstorms. Some of these storms become supercell thunderstorms; these can produce some tornadoes, occasionally those of EF3 strength or higher. Kansas averages more than 50 tornadoes annually.[13] Severe thunderstorms sometimes drop some very large hail over Kansas as well. Furthermore, these storms can even bring in flash flooding and damaging straight line winds.
According to NOAA, the all-time highest temperature recorded in Kansas is (121 °F or 49.4 °C) on July 24, 1936, near Alton in Osborne County, and the all-time low is −40 °F (−40 °C) on February 13, 1905, near Lebanon in Smith County. Alton and Lebanon are approximately 50 miles (80 km) apart.[14]
Kansas's record high of 121 °F (49.4 °C) ties with North Dakota for the fifth-highest record high in an American state, behind California (134 °F or 56.7 °C), Arizona (128 °F or 53.3 °C), Nevada (125 °F or 51.7 °C), and New Mexico (122 °F or 50 °C).[15][16]
Climate data[edit]
| City | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concordia | 36/17 | 43/22 | 54/31 | 64/41 | 74/52 | 85/62 | 91/67 | 88/66 | 80/56 | 68/44 | 51/30 | 40/21 |
| Dodge City | 41/19 | 48/24 | 57/31 | 67/41 | 76/52 | 87/62 | 93/67 | 91/66 | 82/56 | 70/44 | 55/30 | 44/22 |
| Goodland | 39/16 | 45/20 | 53/26 | 63/35 | 72/46 | 84/56 | 89/61 | 87/60 | 78/50 | 66/38 | 50/25 | 41/18 |
| Topeka | 37/17 | 44/23 | 55/33 | 66/43 | 75/53 | 84/63 | 89/68 | 88/65 | 80/56 | 69/44 | 53/32 | 41/22 |
| Wichita | 40/20 | 47/25 | 57/34 | 67/44 | 76/54 | 87/64 | 93/69 | 92/68 | 82/59 | 70/47 | 55/34 | 43/24 |
| Climate data for Topeka (Köppen Cfa/Dfa)[a] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 78 (26) |
84 (29) |
93 (34) |
97 (36) |
103 (39) |
109 (43) |
114 (46) |
113 (45) |
110 (43) |
97 (36) |
85 (29) |
77 (25) |
114 (46) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 63.0 (17.2) |
69.4 (20.8) |
78.7 (25.9) |
86.1 (30.1) |
90.2 (32.3) |
94.8 (34.9) |
99.7 (37.6) |
100.0 (37.8) |
93.7 (34.3) |
86.8 (30.4) |
74.5 (23.6) |
63.7 (17.6) |
101.8 (38.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 39.9 (4.4) |
45.0 (7.2) |
56.4 (13.6) |
66.7 (19.3) |
75.9 (24.4) |
84.7 (29.3) |
89.5 (31.9) |
88.6 (31.4) |
80.4 (26.9) |
68.4 (20.2) |
54.6 (12.6) |
41.7 (5.4) |
66.1 (18.9) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 29.7 (−1.3) |
34.4 (1.3) |
44.8 (7.1) |
55.1 (12.8) |
65.0 (18.3) |
74.2 (23.4) |
79.0 (26.1) |
77.4 (25.2) |
68.4 (20.2) |
56.6 (13.7) |
43.8 (6.6) |
32.0 (0.0) |
55.0 (12.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 19.6 (−6.9) |
23.8 (−4.6) |
33.3 (0.7) |
43.5 (6.4) |
54.2 (12.3) |
63.7 (17.6) |
68.4 (20.2) |
66.2 (19.0) |
56.3 (13.5) |
44.7 (7.1) |
33.0 (0.6) |
22.3 (−5.4) |
44.2 (6.8) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 0.2 (−17.7) |
3.2 (−16.0) |
15.7 (−9.1) |
27.1 (−2.7) |
38.8 (3.8) |
50.4 (10.2) |
56.6 (13.7) |
53.4 (11.9) |
38.8 (3.8) |
27.9 (−2.3) |
16.7 (−8.5) |
3.1 (−16.1) |
−6.3 (−21.3) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −23 (−31) |
−25 (−32) |
−7 (−22) |
10 (−12) |
26 (−3) |
36 (2) |
43 (6) |
40 (4) |
29 (−2) |
16 (−9) |
−5 (−21) |
−26 (−32) |
−26 (−32) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.86 (22) |
1.32 (34) |
2.49 (63) |
3.53 (90) |
4.91 (125) |
5.40 (137) |
3.82 (97) |
4.24 (108) |
3.66 (93) |
3.03 (77) |
1.85 (47) |
1.35 (34) |
36.46 (926) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 4.9 (12) |
4.5 (11) |
1.6 (4.1) |
0.3 (0.76) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.3 (0.76) |
1.0 (2.5) |
5.2 (13) |
17.8 (45) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 5.5 | 6.3 | 9.0 | 9.7 | 11.6 | 11.5 | 8.7 | 8.6 | 7.8 | 8.1 | 6.8 | 6.0 | 99.6 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 3.6 | 2.9 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.2 | 3.4 | 12.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 69.7 | 69.2 | 65.8 | 64.1 | 68.5 | 71.2 | 69.9 | 70.8 | 72.4 | 68.0 | 70.8 | 72.3 | 69.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 177.4 | 168.8 | 212.6 | 231.7 | 268.5 | 293.0 | 326.9 | 291.7 | 233.4 | 212.4 | 157.8 | 150.5 | 2,724.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 59 | 56 | 57 | 58 | 60 | 66 | 72 | 69 | 63 | 61 | 52 | 51 | 61 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990)[18][19][20] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Wichita (Köppen Cfa) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 75 (24) |
87 (31) |
92 (33) |
98 (37) |
102 (39) |
110 (43) |
113 (45) |
114 (46) |
108 (42) |
97 (36) |
86 (30) |
83 (28) |
114 (46) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 65.8 (18.8) |
71.6 (22.0) |
79.9 (26.6) |
85.3 (29.6) |
92.0 (33.3) |
98.4 (36.9) |
103.7 (39.8) |
102.2 (39.0) |
97.3 (36.3) |
89.0 (31.7) |
75.5 (24.2) |
65.3 (18.5) |
104.9 (40.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 43.9 (6.6) |
48.9 (9.4) |
59.1 (15.1) |
68.3 (20.2) |
77.5 (25.3) |
87.9 (31.1) |
92.6 (33.7) |
91.0 (32.8) |
83.3 (28.5) |
70.8 (21.6) |
57.0 (13.9) |
45.8 (7.7) |
68.8 (20.4) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 33.2 (0.7) |
37.6 (3.1) |
47.4 (8.6) |
56.5 (13.6) |
66.7 (19.3) |
76.9 (24.9) |
81.5 (27.5) |
79.9 (26.6) |
71.7 (22.1) |
59.0 (15.0) |
45.8 (7.7) |
35.6 (2.0) |
57.7 (14.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 22.5 (−5.3) |
26.3 (−3.2) |
35.7 (2.1) |
44.8 (7.1) |
55.9 (13.3) |
65.9 (18.8) |
70.4 (21.3) |
68.8 (20.4) |
60.1 (15.6) |
47.2 (8.4) |
34.7 (1.5) |
25.4 (−3.7) |
46.5 (8.1) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 5.1 (−14.9) |
8.4 (−13.1) |
17.1 (−8.3) |
28.2 (−2.1) |
40.5 (4.7) |
53.9 (12.2) |
61.4 (16.3) |
59.3 (15.2) |
44.6 (7.0) |
29.7 (−1.3) |
17.9 (−7.8) |
8.4 (−13.1) |
1.0 (−17.2) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −15 (−26) |
−22 (−30) |
−3 (−19) |
15 (−9) |
27 (−3) |
43 (6) |
51 (11) |
45 (7) |
31 (−1) |
14 (−10) |
1 (−17) |
−16 (−27) |
−22 (−30) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.85 (22) |
1.20 (30) |
2.30 (58) |
3.10 (79) |
5.17 (131) |
4.93 (125) |
3.98 (101) |
4.30 (109) |
3.05 (77) |
2.85 (72) |
1.36 (35) |
1.22 (31) |
34.31 (871) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 2.7 (6.9) |
3.6 (9.1) |
2.1 (5.3) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.8 (2.0) |
3.1 (7.9) |
12.7 (32) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 4.8 | 5.3 | 7.4 | 8.3 | 11.3 | 9.5 | 8.3 | 8.2 | 6.9 | 6.6 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 87.1 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 2.7 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 2.2 | 9.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 69.9 | 68.3 | 63.8 | 62.8 | 67.0 | 64.3 | 58.9 | 61.1 | 66.8 | 65.1 | 70.0 | 71.7 | 65.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 190.9 | 186.4 | 230.4 | 257.8 | 289.8 | 305.0 | 342.1 | 309.2 | 245.6 | 226.3 | 170.2 | 168.7 | 2,922.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 62 | 62 | 62 | 65 | 66 | 69 | 76 | 73 | 66 | 65 | 56 | 57 | 66 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| Source: National Weather Service (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990);[21][22][23] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Dodge City (Köppen BSk/Cfa)[b] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 80 (27) |
88 (31) |
98 (37) |
100 (38) |
106 (41) |
111 (44) |
109 (43) |
109 (43) |
107 (42) |
101 (38) |
91 (33) |
86 (30) |
111 (44) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 68.2 (20.1) |
73.9 (23.3) |
81.7 (27.6) |
88.6 (31.4) |
94.0 (34.4) |
99.7 (37.6) |
103.9 (39.9) |
102.1 (38.9) |
97.6 (36.4) |
89.8 (32.1) |
77.2 (25.1) |
66.9 (19.4) |
105.1 (40.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 44.2 (6.8) |
48.4 (9.1) |
57.8 (14.3) |
67.5 (19.7) |
76.9 (24.9) |
86.7 (30.4) |
92.8 (33.8) |
90.8 (32.7) |
82.4 (28.0) |
69.7 (20.9) |
55.9 (13.3) |
44.3 (6.8) |
68.2 (20.1) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 32.3 (0.2) |
36.0 (2.2) |
44.5 (6.9) |
54.0 (12.2) |
64.3 (17.9) |
74.0 (23.3) |
79.7 (26.5) |
78.2 (25.7) |
69.3 (20.7) |
56.6 (13.7) |
43.2 (6.2) |
32.9 (0.5) |
55.4 (13.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 20.1 (−6.6) |
23.4 (−4.8) |
31.0 (−0.6) |
40.2 (4.6) |
51.5 (10.8) |
61.0 (16.1) |
66.3 (19.1) |
65.3 (18.5) |
56.0 (13.3) |
43.4 (6.3) |
30.3 (−0.9) |
21.2 (−6.0) |
42.6 (5.9) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 2.9 (−16.2) |
4.7 (−15.2) |
12.9 (−10.6) |
24.7 (−4.1) |
36.3 (2.4) |
49.0 (9.4) |
56.3 (13.5) |
54.9 (12.7) |
39.1 (3.9) |
26.9 (−2.8) |
13.4 (−10.3) |
3.6 (−15.8) |
−4.3 (−20.2) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −20 (−29) |
−26 (−32) |
−15 (−26) |
9 (−13) |
19 (−7) |
36 (2) |
46 (8) |
43 (6) |
29 (−2) |
10 (−12) |
−13 (−25) |
−21 (−29) |
−26 (−32) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.58 (15) |
0.68 (17) |
1.59 (40) |
1.82 (46) |
2.85 (72) |
3.24 (82) |
3.08 (78) |
2.75 (70) |
1.67 (42) |
1.74 (44) |
0.76 (19) |
0.84 (21) |
21.60 (549) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 4.9 (12) |
3.9 (9.9) |
4.9 (12) |
1.1 (2.8) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.4 (1.0) |
1.8 (4.6) |
4.1 (10) |
21.1 (54) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 3.5 | 4.8 | 6.5 | 7.1 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 8.2 | 8.0 | 5.7 | 6.1 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 76.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 3.4 | 2.8 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 3.2 | 13.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 65.9 | 64.5 | 60.5 | 57.5 | 62.5 | 59.9 | 55.2 | 58.4 | 61.9 | 58.2 | 64.3 | 66.6 | 61.3 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 207.2 | 201.6 | 241.1 | 270.0 | 297.6 | 332.9 | 357.8 | 319.0 | 267.6 | 248.8 | 192.9 | 189.2 | 3,125.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 67 | 67 | 65 | 68 | 68 | 75 | 80 | 76 | 72 | 71 | 63 | 63 | 70 |
| Source: National Weather Service (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990)[24][25][26] | |||||||||||||
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "Kansas Land Area County Rank". www.usa.com.
- ^ Adams, George Irving. 1903. The physiographic divisions of Kansas. Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Science 18:109-123.
- ^ "Physiographic Regions". Kansas Geological Survey (KGS) at University of Kansas (KU). Archived from the original on October 6, 2021.
- ^ "Kansas Is Flatter Than a Pancake". Improbable.com. Archived from the original on July 30, 2010. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- ^ "Highest, Lowest, and Mean Elevations in the United States". infoplease.com. Retrieved May 20, 2018.
- ^ "Fracas over Kansas pancake flap". Geotimes.org. Archived from the original on January 24, 2004. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- ^ "Kansas". National Park Service. Archived from the original on December 17, 2006. Retrieved July 15, 2008.
- ^ "Kansas Natural Heritage Inventory: Rare plants and animals, and natural communities". Kansas Biological Survey. February 12, 2013. Retrieved March 16, 2021.
- ^ Kansas, Natural Heritage Inventory (January 9, 2014). "Rare Vertebrates Kansas" (PDF).
- ^ Kansas, Natural Heritage Inventory (January 9, 2014). "Rare Vertebrates of Kansas" (PDF).
- ^ K-State Research, and Extension. "Native Plants" (PDF). www.johnson.k-state.edu.
- ^ "Kansas Wildflowers and Grasses". www.kswildflower.org. Retrieved March 16, 2021.
- ^ "Annual Average Number of Tornadoes, 1953–2004". National Climatic Data Center. Archived from the original on October 16, 2011. Retrieved October 25, 2006.
- ^ "Records for the State of Kansas". National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office – Wichita, KS. NOAA. Retrieved January 31, 2012.
- ^ "Record Highest Temperatures by State (through 2003)" (PDF). NOAA.gov. NOAA. Retrieved January 31, 2012.
- ^ National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration; ‘Monthly State Maximum/Minimum Extremes’
- ^
- "Concordia Weather—Kansas—Average Temperatures and Rainfall". countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on November 3, 2016. Retrieved April 9, 2016.
- "Dodge City Weather—Kansas—Average Temperatures and Rainfall". countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved April 9, 2016.
- "Goodland Weather—Kansas—Average Temperatures and Rainfall". countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved April 9, 2016.
- "Topeka Weather—Kansas—Average Temperatures and Rainfall". countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved April 9, 2016.
- "Wichita Weather—Kansas—Average Temperatures and Rainfall". countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved April 9, 2016.
- ^ Team, National Weather Service Corporate Image Web. "National Weather Service Climate". www.nws.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2020-08-07.
- ^ "Station Name: KS TOPEKA MUNI AP". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2020-07-12.
- ^ "WMO Climate Normals for TOPEKA/MUNICIPAL ARPT KS 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- ^ "NOWData - NOAA Online Weather Data". National Weather Service Forecast Office - Wichita, KS. Retrieved 2021-10-13.
- ^ "Summary of Monthly Normals 1991-2020". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2021-10-13.
- ^ "WMO Climate Normals for WICHITA/MID-CONTINENT ARPT KS 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ "NOWData – NOAA Online Weather Data". Dodge City, Kansas: National Weather Service Forecast Office. Retrieved August 8, 2020.
- ^ "Station Name: KS DODGE CITY". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved March 26, 2014.
- ^ "WMO Climate Normals for DODGE CITY/MUNICIPAL, KS 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ 1981−2010 normals, extremes 1887−present. Official records for Topeka kept at the Weather Bureau Office from June 1887 to July 1946, and at Philip Billard Municipal Airport since August 1946. For more information, see Threadex
- ^ 1981–2010 normals. Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the expected highest and lowest temperature readings at any point during the year or given month) calculated based on data at said location from 1981 to 2010. Extremes 1874-present.