| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
(+)-gallocatechin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Gallocatechol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O7 | |
| Molar mass | 306.270 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
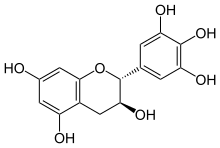
Gallocatechol or gallocatechin (GC) is a flavan-3-ol, a type of chemical compound including catechin, with the gallate residue being in an isomeric trans position.
This compound possesses two epimers. The most common, (+)-gallocatechin (GC), CAS number 970-73-0, is found notably in green tea. The other enantiomer is called (-)-gallocatechin or ent-gallocatechin. It was first isolated from green tea by Michiyo Tsujimura in 1934.[1]
Epigallocatechin is another type of catechin, with the gallate residue being in an isomeric cis position. It can be found in St John's wort.[2]
See also
References
- ^ "Michiyo Tsujimura (1888–1969)". Ochanomizu University. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- ^ Wei, Yun; Xie, Qianqian; Dong, Wanting; Ito, Yoichiro (2009). "Separation of epigallocatechin and flavonoids from Hypericum perforatum L. By high-speed counter-current chromatography and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography". Journal of Chromatography A. 1216 (19): 4313–4318. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.12.056. PMC 2777726. PMID 19150073.